Abstract
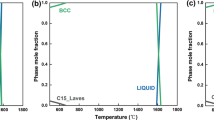
The microstructure, phase composition and elemental composition in the α- and β-phases of the two-phase wrought Ti-5.7Al-1.6V-3Mo titanium alloy at room temperature were studied by transmission electron microscopy and X-ray energy-dispersive spectroscopy. The temperature ranges of phase transformations in the alloy during heating from 298 to 1523 K were studied by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Two endothermic peaks were observed on the DSC curve at the temperatures of 1078 K and 1207 K, and one exothermic peak was observed at a temperature of 1123 K. The endothermic peak on the DSC curve at a temperature of 1078 K is due to the formation of α″-martensite, at a temperature of 1207 K is caused by α → β phase transformation. The exothermic peak at a temperature of 1123 K, presumably, corresponds to the polymorphic transformation of brookite → rutile in TiO2 oxide. High-temperature synchrotron studies were carried out from room temperature to 1373 K. It was found that the increase in lattice parameters during heating is nonlinear. Possible mechanisms of the nonlinear change in the lattice parameters at temperatures above 1200 K are discussed. At T > 1000 K α″-martensite was formed by β → α″ phase transformation. An increase in the volume fraction of α″-phase with increase in temperature was accompanied by a decrease in the volume fraction of β-phase. An increase in microstrain of the α-phase lattice and a decrease in microstrain of the β-phase lattice were observed upon heating.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.P. Akula, M. Ojha, K.L. Rao, and A.K. Gupta, A Review on Superplastic Forming of Ti-6Al-4V and Other Titanium Alloys, Mater. Today Commun., 2023, 34, p 105343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105343
A.O. Mosleh, A.D. Kotov, V. Vidal, A.G. Mochugovskiy, V. Velay, and A.V. Mikhaylovskaya, Initial Microstructure Influence on Ti-Al-Mo-V Alloys Superplastic Deformation Behavior and Deformation Mechanisms, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 802, p 140626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.146626
G.P. Grabovetskaya, I.P. Mishin, E.N. Stepanova, O.V. Zabudchenko, and I.V. Ratochka, Effect of the Structural and Phase State on the Deformation Behavior and Mechanical Properties of the Ultrafine-Grained Titanium Alloy (Ti-Al-V-Mo) at Temperatures in the Range of 293–973 K, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 800, p 140334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2020.140334
M. Qi, Y. Ma, J. Yang, Y. Jia, H. Weng, S. Huang, R. Zhang, J. Qiu, J. Lei, and R. Yang, Microtexture Evolution Effected by Mo Content in α+β Titanium Alloys, Mater. Charact., 2022, 188, p 111884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2022.111884
J.-W. Lu, Y.Q. Zhao, P. Ge, and H.-Z. Niu, Microstructure and Beta Grain Growth Behavior of Ti-Mo Alloys Solution Treated, Mater. Charact., 2013, 84, p 105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2013.07.014
H. Zhao, L. Xie, C. Xin, N. Li, B. Zhao, and L. Li, Effect of Molybdenum Content on Corrosion Resistance and Corrosion Behavior of Ti-Mo Titanium Alloy in Hydrochloric Acid, Mater. Today Commun., 2023, 34, p 105032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.105032
Phase diagrams of binary metallic systems, V.3. book 1, under the general editorship of N.P. Lyakishev (Moscow, Mashinostroenie, 2001)
R. Davis, H.M. Flower, and D.R.F. West, Martensitic Transformations in Ti-Mo Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 1979, 14, p 712–722.
X. Hu, L. Qi, C. Liu, H. Chen, X. Zhang, H. Yan, K. Zhou, and M. Song, Formation Mechanism of Stacking Faults Within α″ Martensite in Ti-7wt.%Mo Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2023, 934, p 168039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.168039
N. Chen, H. Kon, Z. Wu, F. Qiang, Ch. Wang, J. Li, and J.M. Molina-Aldareguia, Stress-Induced α″ Martensitic Phase Transformation and Martensitic Twinning in a Metastable β Titanium Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2021, 859, p 157809. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157809
H. Lu, P. Ji, B. Li, W. Ma, B. Chen, X. Zhang, M. Xinyu Zhang, and R. LiuMa, Mechanical Properties and Deformation Mechanism of a Novel Metastable β-Type Ti-4V-2Mo-2Fe Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2022, 848, p 143376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.143376
C. Ding, X. Li, H.Y. Zhu, F.-W. Chen, and F. Li, Microstructure Evolution and Phase Transformation Kinetics of Low Cost Ti-35421 Titanium Alloy During Continuous Heating, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, 14, p 620–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.071
C. Li, G. Li, Y. Yang, M. Varlioglu, and K. Yang, α″ Martensitic Twinning in Alpha+Beta Ti-35Al-45 Mo Titanium Alloy, J. Metal., 2011 https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/924032
O.B. Perevalova, A.V. Panin, M.S. Kazachenok, and E.A. Sinyakova, Effect of Ultrasonic Impact Treatment on Structural Phase Transformations in Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy, Phys. Mesomech., 2022, 25(3), p 248–258. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1029959922030055
P.B Hirsch, A. Howie, R. B. Nicholson, D. W. Pashley, and M. J. Whelan, Electron Microscopy of Thin Crystals (Krieger Pub Co., 1977)
S. S. Gorelik, L. N. Rastorguev, and Yu, A. Skakov, X-ray and Electron-Optical Analysis (Metallurgiya, Moscow, 1970)
L.K. Savitskaya, Methods of x-ray Diffraction Studies: Textbook, Tomsk State University, Tomsk, 2003.
S.K. Sangal and P.K. Sharma, Mean Square Displacements of Atoms in Cubic Metals at Melting Point, Czech. J. Phys, 1968, B18, p 1413–1415.
C. Marinescu, A. Sofronia, C. Rusti, R. Piticescu, V. Badilita, E. Vasile, R. Baies, and S. Tanasescu, DSC Investigation of Nanocrystalline TiO2 Powder, J. Therm Anal Calorim., 2011, 103, p 49–57. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10973-010-1072-6
L.I. Mirkin, Handbook on x-ray Analysis of Polycrystals, Fizmatlit, Moscow, 1961.
O.B. Perevalova and M.S. Syrtanov, In Situ Study of Phase Transformations in Electron Beam Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy by High Temperature Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction and TEM, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 917, p 165463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165463
A.I. Kahveci and G.E. Welsch, Effect of Oxygen on the Hardness and Alpha/Beta Phase Ratio of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Scripta Metall., 1986, 20(9), p 1287–1290. https://doi.org/10.1016/0036-9748(86)90050-5
H.C. Kaushik, M.H. Korayem, and A. Hadadzadeh, Determination of α to β Phase Transformation Kinetics in Laser-Powder Bed Fused Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo-0.08Si and Ti-6Al-4V Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2022, 860, p 144294.
J.W. Elmer, T.A. Palmer, S.S. Babu, and E.D. Specht, In Situ Observations of Lattice Expansion and Transformation Rates of α and β Phases in Ti-6Al-4V, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 391, p 104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.08.084
F. Bruneseaux, E. Aeby-Gautier, G. Geandier, J. Da Costa Teixeira, B. Applaire, P. Weisbecker, and A. Mauro, In Situ Characterization of Phase Transformations Kinetics in the Ti17 Titanium Alloy by Electrical Resistivity and High Temperature Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 476, p 60–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.04.072
W. Sha and S. Malinov, Titanium Alloys: Modeling of Microstructure, Properties and Applications, Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press LLC, UK, 2009.
O.B. Perevalova, E.V. Konovalova, N.A. Koneva, and E.V. Kozlov, Effect of Atomic Ordering on Grain Boundary Ensembles of FCC Solid Solutions (NTL, Tomsk, 2014)
A.A. Bondar, T.Ya. Velikanova, V.M. Danilenko, V.M. Dementiev, E.V. Kozlov, G.M. Lukashenko, V.P. Sidorko, and D.M. Shtern, Phase Stability and Phase Equilibria in TRANSITION Metal Alloys (Kiev, Naukova Dumka, 1991)
T. Wang, L.-Q. Chen, and Z.-K. Liu, Lattice parameters and local lattice distortions in fcc-Ni solutions, Metall. and Mater. Trans. A., 2007, 38, p 562–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9091-z
T.V. Pryadko, Features of Hydrogenation of Ti-V Alloys, Metallofiz. Nov. Tekhnol., 2015, 37(2), p 243–255. https://doi.org/10.15407/mfint.37.02.0243
C. Catanio Bortolan, L. Contri Campanelli, P. Mengucci, G. Barucca, N. Giguere, N. Brodusch, C. Paternoster, and C. Bolfarini, Development of Ti-Mo-Fe Alloys Combining Different Plastic Deformation Mechanisms for Improved Strength-Ductility Trade-off and High Work Hardening Rate, J. Alloys Compd., 2022, 925, p 166757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166757
Y. Duan, W. Zhang, W. Wang, and L. Shi, Studies on Mutual Diffusion Between Mo and α-Ti During Thermal Evaporation, Vacuum, 2021, 187, p 110115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110115
M. Fellah, N. Hezil, M. Abdul Samad, R. Djellabi, A. Montagne, A. Mejias, S. Kossman, A. Iost, A. Purnama, A. Obrosov, and S. Weiss, Effect of Molybdenum Content on Structural, Mechanical, and Tribological Properties of Hot Isostatically Pressed β-type Titanium Alloys for Orthopedic Applications, J. Mater. Eng. Perf., 2019, 28(10), p 5988–5999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04348-w
Q. MiaoHu and R. Yang, Unconventional Non-uniform Local Lattice Distortion in Dulute Ti-Mo Solid Solution, Acta Mater., 2020, 197, p 91–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.033
A. Idhil Ismail, M. Dehmas, and E. Aeby-Gautier, In Situ Monitoring of Phase Transformation Kinetics under Rapid Heating of Ti-6Al-4V Titanium Alloy, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2022, 17, p 2518–2527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.02.006
M. Li, X. Min, K. Yao, and F. Ye, Novel Insight into the Formation of α″-Martensite and ω-Phase with Cluster Structure in Metastable Ti-Mo Alloys, Acta Mater., 2019, 164, p 322–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2018.10.048
A. Panin, A. Dmitriev, A. Nikonov, O. Perevalova, L. Kazantseva, A. Bakulin, and S. Kulkova, Transformations of the Microstructure and Phase Compositions of Titanium Alloys During Ultrasonic Impact Treatment Part II Ti-6Al-4V, Metals, 2022, 12, p 732–748. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12050732
S.O. Kasparyan, A.V. Bakulin, and S.E. Kulkova, Effect of V Nb and Mo impurities on the stability of Titanium phases, Russian Phys. J., 2022, 65(8), p 1283–1289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-023-02763-0
L. Zeng and T.R. Bieler, Effects of Working, Heat Treatment, and Aging on Microstructural Evolution and Crystallographic Texture of α, α′, α″ and β Phases in Ti-6Al-4V Wire, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, 392, p 403–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.09.072
A.R. Kilmametov, Yu. Ivanisenko, B.B. Straumal, A.S. Gornakova, A.A. Mazilkin, and H. Hahn, The α→ω Transformation in Titanium-Cobalt Alloys under High-Pressure Torsion, Metals, 2018, 8, p 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8010001
A. Kilmametov, Yu. Ivanisenko, B. Straumal, A.A. Mazilkin, A.S. Gornakova, M.J. Kriegel, O.B. Fabrichnaya, D. Rafaja, and H. Hahn, Transformations of α′ Martensite in Ti-Fe Alloys under High Pressure Torsion, Scripta Mater., 2017, 136, p 46–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.04010
A. Panin, A. Dmitriev, A. Nikonov, M. Kazachenok, O. Perevalova, and E. Sklyarova, Transformations of the Microstructure and Phase Compositions of Titanium Alloys During Ultrasonic Impact Treatment Part I Commercially Pure Titanium, Metals, 2021, 11, p 562–574. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11040562
A.N. Didenko, Yu. P. Sharkeev, E.V. Kozlov, and A.I. Ryabchikov, Long-Range Effects in Ion-Implantable Metallic Materials (NTL, Tomsk, 2004)
L.L. Meisner, A.I. Lotkov, M.G. Ostapenko, and EYu. Gudimova, X-ray Diffraction Study of Residual Elastic Stress and Microstructure of Near-Surface Layers in Nickel-Titanium Alloy Irradiated with Low-Energy High-Current Electrons Beams, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 280, p 398–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.04.168
M.G. Ostapenko, V.O. Semin, F.A.D. yachenko, A.A. Neiman, and L.L. Meisner, Structure and Residual Stress Distribution in TiNi Substrate After Fabrication of Surface Alloy using Electron-Beam Treatments, Acta Mater., 2022, 231, p 117893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2022.117893
O.B. Perevalova, A.V. Panin, and M.S. Kazachenok, Concenration Dependent Transformation Plasticity Effect during Hydrogenation of Technically Pure Titanium Irradiated with an Electron Beam, Russian Physics J., 2019, 61(11), p 1992–2000. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-019-01629-8
Acknowledgments
The work has been performed under the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation (Grant No.21-19-00795). The investigations was carried out using the equipments of Share Use Centre “Nanotech” of the ISPMS SB RAS, the CSU NMNT TPU and the shared research center SSTRC on the basis of the VEPP-4-VEPP-2000 complex at BINP SB RAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
OBP contributed to formal analysis, investigation, and writing—original. AVP contributed to conceptualization. MSS contributed to resources and investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Perevalova, O.B., Panin, A.V. & Syrtanov, M.S. In Situ Synchrotron Study of the Phase Transformations in Ti-5.7Al-1.6V-3Mo Titanium Alloy at High Temperature. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08675-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08675-x