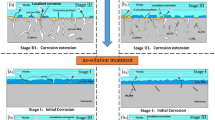
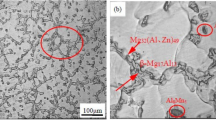
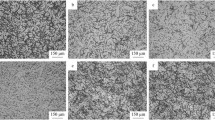
Abstract
In this work, AZ31 and AZ31-1 wt.% RE (RE = Nd, Dy, Nd+Dy) alloys were prepared by conventional casting. The effect of single and co-addition of rare earth (RE) on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of as-cast AZ31 magnesium alloys were investigated at ambient temperature, and after heat treatment at 400 °C for 1 h. The addition of 1 wt.% RE (RE = Nd, Dy, Nd+Dy) preferentially formed the Al2RE phase and completely suppressed the formation of the intermetallic β-Mg17Al12 phase. An excellent ultimate tensile strength (UTS)/ductility combination of 209 MPa/21% and 192 MPa/17% with an adequate yield strength (YS) of 90 MPa was observed for AZ31+Nd sample in as-cast and annealed states, respectively. The work-hardening rate of the AZ31 alloy containing Nd and Dy increased significantly after annealing compared to those of the as-cast state. Fracture analysis indicated that the additive RE did not obviously change the fracture mechanism of the Mg alloy. All specimens exhibit a hybrid fracture with cleavages and dimples. The weight loss test showed that the corrosion resistance of the AZ31 Mg alloy was improved with added RE as it interacts with Al to form Al-RE phase, which upgraded the corrosion resistance of the alloys. The co-addition of RE (RE = Nd+Dy) was proven to enhance corrosion resistance, and also stabilized the corrosion rate. In brief, the co-addition of Nd and Dy significantly improved the corrosion resistance of the AZ31 magnesium alloys than the counterpart of the mechanical properties.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Tie, F. Feyerabend, N. Hort, D. Hoeche, K.U. Kainer, R. Willumeit, and W.D. Mueller, In Vitro Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of Biodegradable Mg-Ag Alloys, Mater. Corros., 2014, 65, p 569-576.
Z.H. Wen, C.J. Wu, C.S. Dai, andF.X. Yang, Corrosion Behaviors of Mg and its Alloys with Different Al Contents in a Modified Simulated Body Fluid, J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 488, p 392-399.
J. Du, J. Yang, M. Kuwabara, W.F. Li, and J.H. Peng, Effects of Carbon and/or Alkaline Earth Elements on Grain Refinement and Tensile Strength of AZ31 Alloy, Mater. Trans., 2008, 49, p 2303-2309.
J. Zhang, S. Liu, R. Wu, L. Hou, and M. Zhang, Recent Developments in High-Strength Mg-RE-Based Alloys: Focusing on Mg-Gd and Mg-Y Systems, J. Magnes. Alloy., 2018, 6, p 277-291.
S. You, Y. Huang, K.U. Kainer, and N. Hort, Recent Research and Developments on Wrought Magnesium Alloys, J. Magnes. Alloy., 2017, 5, p 239-253.
D.K. Xu, L. Liu, Y.B. Xu, and E.H. Han, The Crack Initiation Mechanism of the Forged Mg-Zn-Y-Zr Alloy in the Super-Long Fatigue Life Regime, Scr. Mater., 2007, 56, p 1-4.
I.P. Moreno, T.K. Nandy, J.W. Jones, J.E. Allison, and T.M. Pollock, Microstructural Stability and Creep of Rare-Earth Containing Magnesium Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2003, 48, p 1029-1034.
M.S. Dargush, G.L. Dunlop, K. Pettersen, Transactions of 19th International Die Casting Congress; Higgins, W., Ed.; North American Die Casting Association: Rosemont, IL, USA, 1997; pp. 131-137.
J.Y. Bai, S. Sun, F. Xue, S. Xue, J. Qiang, and T.B. Zhu, Influence of Annealing on Microstructures, Mechanical and Creep Properties of Mg-4Al-2Sr Alloy, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, 22, p 1208-1212.
B. Jing, S. Yangshan, X. Feng, X. Shan, Q. Jing, and T. Weijian, Effect of Extrusion on Microstructures, and Mechanical and Creep Properties of Mg-Al-Sr and Mg-Al-Sr-Ca Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2006, 55, p 1163-1166.
T. Rzychoń, A. Kiełbus, J. Cwajna, and J. Mizera, Microstructure Stability and Creep Properties of Die-Casting Mg-4Al-4RE Alloy, Mater. Charact., 2009, 60, p 1107-1113.
B.R. Powell, V. Rezhets, M.P. Balogh, and R.A. Waldo, Microstructure and Creep Behavior in AE42 Magnesium Die-Casting Alloy, JOM., 2002, 54, p 34-38.
Y.-X. Wang, J.-W. Fu, and Y.-S. Yang, Effect of Nd Addition on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of AZ80 Magnesium Alloys, Trans. Nonferrous. Met. Soc. China., 2012, 22, p 1322-1328.
J. Zhang, J. Wang, X. Qiu, D. Zhang, Z. Tian, X.D. Niu, D.X. Tang, and M. Jian, Effect of Nd on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Die-Cast Mg-4Al-Based Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2008, 464, p 556-564.
Y. Lu, Q. Wang, X. Zeng, W. Ding, C. Zhai, and Y. Zhu, Effect of Rare Earths on the Microstructure, Properties and Fracture Behavior of Mg-Al Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2000, 278, p 66-76.
Y. Guangyin, L. Manping, D. Wenjiang, and A. Inoue, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Mg-Al-Zn-Si-base Alloy, Mater. Trans., 2003, 44, p 458-462.
C.C. Jain and C.H. Koo, Creep and Corrosion Properties of the Extruded Magnesium Alloy Containing Rare Earth, Mater. Trans., 2007, 48, p 265-272.
F. Guo, D.F. Zhang, X.S. Yang, L.Y. Jiang, and F.S. Pan, Strain-Induced Dynamic Precipitation of Mg17Al12 Phases in Mg-8Al Alloys Sheets Rolled at 748 K, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2015, 636, p 516-521.
X.-P. Xu and A. Needleman, Void Nucleation by Inclusion Debonding in a Crystal Matrix, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 1993, 1, p 111-132.
D.K. Xu, L. Liu, Y.B. Xu, and E.H. Han, Effect of Microstructure and Texture on the Mechanical Properties of the as-Extruded Mg-Zn-Y-Zr Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2007, 443, p 248-256.
X.H. Shao, Z.Q. Yang, and X.L. Ma, Strengthening and Toughening Mechanisms in Mg-Zn-Y Alloy with a Long Period Stacking Ordered Structure, Acta Mater., 2010, 58, p 4760-4771.
L.Y. Wei and G.L. Dunlop, The Solidification Behavior of Mg-Al-Rare Earth Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 1996, 232, p 264-268.
Z.F. Li, J. Dong, X.Q. Zeng, C. Lu, and W.J. Ding, Influence of Mg17Al12 Intermetallic Compounds on the Hot Extruded Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Mg-9Al-1Zn Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2007, 466, p 134-139.
G. Song, A. Atrens, and D. St John, An Hydrogen Evolution Method for the Estimation of the Corrosion Rate of Magnesium Alloys, Magnesium Technology. Springer, Cham, 2001, p 255-262
M. Dixit, R.S. Mishra, and K.K. Sankaran, Structure-Property Correlations in Al 7050 and Al 7055 High-Strength Aluminum Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2008, 478, p 163-172.
U.M. Chaudry, A. Farooq, K.-B. Tayyab, A. Malik, M. Kamran, J.-G. Kim, C. Li, K. Hamad, and T.-S. Junis, Corrosion behavior of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy with Calcium Addition, Corrosion Sci., 2022, 199, p 110205.
J. Xie, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Q. Yang, K. Guan, Y. He, R. Wang, H. Zhang, X. Qiu, and R. Wu, New Insights on the Different Corrosion Mechanisms of Mg Alloys with Solute-Enriched Stacking Faults or Long Period Stacking Ordered Phase, Corrosion Sci., 2022, 198, p 110163.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from a project to develop environment friendly pyrometallurgy processes for high purity HREE and materialization (Project No.: 20000970) by the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT) in the Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lwin, M.L., Shin, Dw., Nam, S.W. et al. Effect of Single and Co-addition of Rare Earth on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Corrosion Behavior of AZ31 Magnesium Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08674-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08674-y