Abstract
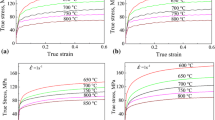
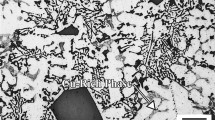
Cu-1.5 wt.% Zn alloy used in the present study was subjected to the hot impression creep tests at three stresses of 75, 110 and 150 MPa and three temperatures of 250, 300 and 350 °C for a constant dwell time of 2 h. The effect of stress and temperature on the impression depth with respect to time was studied. Irrespective of the test condition, the depth of impression increased with respect to the time. However, upon increasing the applied stress, the twins were observed. Stress exponent values and activation energies were determined for different test temperatures and stresses. Stress exponent values related to the plastic flow over the complete range of experimental conditions were found to lie between 4 and 5.5. Whereas the average activation energy value was determined to be 164 ± 10 kJ/mol. Calculated stress exponents and activation energy values reveal the dislocation climb phenomenon, controlled by dislocation pipe diffusion as the mechanism of the creep.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Copper Development Association Brass in Focus, 177, (2004), pp. 1–4, http://copperalliance.org.uk/docs/librariesprovider5/resources/pub-177-brass-in-focus-pdf.pdf?Status=Master&sfvrsn=0.
A. Waheed and N. Ridley, Microstructure and Wear of Some High-Tensile Brasses, J. Mater. Sci., 1994, 29, p 1692–1699.
M.R. Willis and J.P. Jones, Creep Mechanisms is Dual Phase Brass, Scripta Mater., 2001, 44, p 31–36.
S.V. Garimella, A.S. Fleischer, J.Y. Murthy, A. Keshavarzi, R. Prasher, and C. Patel, Thermal Challenges in Next-Generation Electronic Systems, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol., 2008, 31(4), p 801–815.
K. Puttaswamy and G.H. Loh, Thermal Analysis of a 3D Die-stacked High-Performance Microprocessor. Proceedings of the 16th ACM Great Lakes symposium on VLSI, 2006, Philadelphia. ACM, New York, 2006, p 19–24.
K. Zhang, J.R. Weertman, and J.A. Eastman, The Influence of Time, Temperature, and Grain Size on Indentation Creep in High-Purity Nanocrystalline and Ultrafine Grain Copper, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 85(22), p 5197–5199.
F. Sket, A. Isaac, K. Dzieciol, G. Sauthoff, A. Borbély, and A.R. Pyzalla, In situ Tomographic Investigation of Brass During High-Temperature Creep, Scripta Mater., 2008, 59(5), p 558–561.
J. A. La Manna Jr., Doctoral thesis on A Study of the Relationship between Indentation Creep and Uniaxial Creep. University of Tennessee, Knoxville.
W. Yan, S. Wen, J. Liu, and Z. Yue, Comparison Between Impression Creep and Uni-axial Tensile Creep Performed on Nickel-Based Single Crystal Superalloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 1850–1855.
H.Y. Yu, M.A. Imam, and B.B. Rath, Study of the Deformation Behaviour of Homogeneous Materials by Impression Tests, J. Mater. Sci., 1985, 20, p 636–642.
V.R. Rao, D.K. Pattanayak, and C. Vanitha, Hot Impression Creep Behavior of AlSi10Mg Alloy Fabricated through SLM Route, Trans. Indian Inst. Metals, 2022, 76(2), p 271–277.
P. Bharath Sreevatsava, E. Vara Prasad, A. Sai Deepak Kumar, M.F. Anwar, V.R. Rao, and V. Chilamban, Effects of Temperature and Load during Hot Impression Behavior of Cr-Ni Stainless Steel, Metall. Mater. Eng., 2021, 27(4), p 531–539.
K. Kuchařovă, F. Dobeš, A. Orlovă, K. Milička, and J. Čadek, High Temperature Creep in Precipitation Strengthened Cu-2Fe Alloy, Metal Sci., 1984, 18(3), p 137–142.
A. Akbari-Fakhrabadi, R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, and M. Jamshidijam, Impression Creep Behaviour of a Cu-6Ni-2Mn-2Sn-2Al Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 535, p 202–208.
R. Mahmudi, A. Karsaz, A. Akbari-Fakhrabadi, and A.R. Geranmayeh, Impression Creep Study of a Cu-0.3Cr-0.1Ag Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 2702–2708.
R. Mahmudi, A. Akbari-Fakhrabadi, A. Karsaz, and A.R. Geranmayeh, Creep Behavior of Copper and Cu-0.3Cr-0.1Ag Alloy, J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 2010, 132, p 044501–044511.
S.D. Kumar, M.F. Anwar, E. Vara Prasad, P. Bharath Sreevatsava, and C. Vanitha, Effect of Temperature and Load during Hot Impression Creep of Cu-Zn-Al Alloy, Mater. Today Proc., 2021, 39, p 1296–1302.
Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Creep and Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures, Pineridge Press Ltd., Swansea, (1984) pp. 235.
S.I. Shakil, A. Hadadzadeh, H. Pirgazi, M. Mohammadi, and M. Haghshenas, Indentation-derived Creep Response of Cast and Laser Powder Bed Fused AlSi10Mg Alloy: Air Temperature, Micron, 2021, 150, p 103145.
S.N. Chu and J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep; A New Creep Test, J. Mater. Sci., 1977, 12, p 2200–2208.
S.V. Raj and T.G. Langdon, Creep Behaviour of Copper at Intermediate Temperatures-I. Mechanical Characteristics, Acta Metall., 1989, 37, p 843–852.
F. Yang and J.C.M. Li, Impression and Diffusional Creep of Anisotropic Media, J. Appl. Phys., 1995, 77(1), p 110–117.
D.H. Sastry, Impression Creep Technique-An Overview, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 409(1–2), p 67–75.
S. Li, D. Purdy, S.J. Brett, D. Deng, A. Shibli, and W. Sun, Effect of Indentation Depth in Impression Creep Test: Conversion Relationships and Correction Functions, Mater. High Temp., 2021, 38(5), p 358–367.
T.G. Langdon, Identifiying Creep Mechanisms at Low Stresses, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, 283, p 266–273.
W. H. Bowyer, Creep of the Copper Canister-A Critical Review of the Literature. SKI report 2003:23, Meadow End Farm, Tilford, Farnham, Surrey, GU10 2DB, England, April 2003.
M.D. Mathew, H. Yang, S. Movva, and K.L. Murty, Creep Deformation Characteristics of Tin and Tin-Based Electronic Solder Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36, p 99–105.
S.S. Vagarali and T.G. Langdon, Deformation Mechanisms in hcp Metals at Elevated Temperatures—I. Creep Behaviour of Magnesium, Acta Metall., 1981, 29(12), p 1969–1982.
B. Sivaiah and S.P. Gupta, Diffusion Induced Grain Boundary Migration in the Cu-Zn System, Mater. Charact., 2008, 59(9), p 1141–1151.
H.J. Frost and M.F. Ashby, Deformation-Mechanism Maps, the Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics, Pergamon, Oxford, UK, 1982, p 21
J.P. Poirier, Creep of Crystals, High Temperature Deformation Processes in Metals, Ceramics, and Minerals, Cambridge University Press, New York, 1985.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the administration of NIT Warangal for providing research facilities to carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is an invited submission to the Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance selected from presentations at the 4th International Conference on Processing & Characterization of Materials (ICPCM 2022) held December 9–11, 2022, at the National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, Odisha, India. It has been expanded from the original presentation. The issue was organized by Prof. Joao Pedro Oliveira, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, Portugal; Prof. B. Venkata Manoj Kumar, Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India; Dr. D. Arvindha Babu, DMRL, DRDO, Hyderabad, India; Prof. Kumud Kant Mehta and Prof. Anshuman Patra, National Institute of Technology Rourkela, Odisha, India; and Prof. Manab Mallik, National Institute of Technology Durgapur, India.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vanitha, C., Kaushik, B. & Sashank, C. Effect of Temperature and Stress on Hot Impression Creep Behavior of Cu-1.5 Zn Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08567-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08567-0