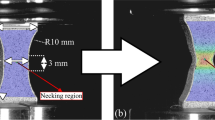
Abstract
The hot deformation behavior of 300M ultra-high strength steel is investigated through isothermal uniaxial compression tests under various thermo-mechanical processing conditions of 900-1250 °C and 0.01-50 s−1. Using the friction-corrected data of the experimental flow stress, the strain-compensated Arrhenius-type model, modified Johnson–Cook model and Khan–Huang–Liang model are developed. Based on the analysis of the reason of large deviation, the modified Johnson–Cook and Khan–Huang–Liang models are improved. The strain-compensated Arrhenius-type model exhibits the highest prediction accuracy. The determination coefficient and average absolute relative error of the strain-compensated Arrhenius-type model are 0.9971 and 3.57%, respectively. Meanwhile, the improved version of the modified Johnson–Cook model records the determination coefficient of 0.9964 and average absolute relative error of 3.59%, and the improved Khan–Huang–Liang model records 0.9949 and 5.08%. In view of the prediction accuracy and computation complexity, the improved versions of the modified Johnson–Cook and Khan–Huang–Liang models are preferred models. The improved phenomenological constitutive models enable us to predict the hot deformation behavior effectively for the optimization of the thermo-mechanical processing parameters of 300M ultra-high strength steel.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Liu, Y.G. Liu, H. Lin, and M.Q. Li, The Metadynamic Recrystallization in the Two-Stage Isothermal Compression of 300M Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 565, p 126.
R.C. Chen, S.Y. Zhang, M. Wang, X.L. Liu, and F. Feng, Unified Modelling of Flow Stress and Microstructural Evolution of 300M Steel under Isothermal Tension, Metals, 2021, 11, p 1086.
X.L. He, X.Q. Yang, G.D. Zhang, J.W. Li, and H.C. Hu, Quenching Microstructure and Properties of 300M Ultra-High Strength Steel Electron Beam Welded Joints, Mater. Des., 2012, 40, p 386.
R. Roumnia, J.D. Embury, O. Bouaziz, and H.S. Zurob, Mechanical Behavior of a Compositionally Graded 300M Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 578, p 140.
J. Luo, Y.G. Liu, and M.Q. Li, Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation and Experimental Analysis of Austenite Grain Growth Behavior in Hot Forging Processes of 300M Steel Large Components, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2016, 23, p 1012.
F.G. Liu, X. Lin, M.H. Song, K. Song, F.F. Wang, Q.G. Li, Y.F. Han, and W.D. Huang, Austenitizing Behavior of Laser Solid Formed Ultrahigh-Strength 300M Steel, Steel Res. Int., 2017, 88, p 1.
R. Zeng, L. Huang, H.L. Su, H.J. Ma, Y.F. Ma, and J.J. Li, Softening Characterization of 300M High-Strength Steel during Post-Dynamic Recrystallization, Metals, 2018, 340, p 1.
S. Hamtaei, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and A. Mohamadizadeh, Optimum Deformation Criteria and Flow Behavior Description of Boron-Alloyed Steel through Numerical Approach, Steel Res. Int., 2016, 87, p 1657.
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, and A.K. Bhaduri, A Comparative Study on Johnson Cook, modified Zerilli-Armstrong and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Models to Predict Elevated Temperature Flow Behaviour in Modified 9Cr-1Mo steel, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2009, 47, p 568.
H.Y. Li, Y.H. Li, X.F. Wang, J.J. Liu, and Y. Wu, A Comparative Study on Modified Johnson Cook, modified Zerilli-Armstrong and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Models to Predict The Hot Deformation Behavior in 28CrMnMoV Steel, Mater. Des., 2013, 49, p 493.
A. Hajari, M. Morakabati, S.M. Abbasi, and H. Badri, Constitutive Modeling for High-Temperature Flow Behavior of Ti-6242S Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 681, p 103.
Z.H. Liu, H. Zhao, J.P. Li, Z.T. Niu, and V. Ji, Modified Johnson–Cook Constitutive Model of 18CrNiMo7-6 Alloy Steel Under Ultrasonic Surface Burnishing Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07392-1
A.K. Gupta, H.N. Krishnamuthy, Y. Singh, K.M. Prasad, and S.K. Singh, Development of Constitutive Models for Dynamic Strain Aging Regime in Austenitic Stainless Steel 304, Mater. Des., 2013, 45, p 616.
A. He, G.L. Xie, H.L. Zhang, and X.T. Wang, A Comparative Study on Johnson–Cook, Modified Johnson–Cook and Arrhenius-Type Constitutive Models to Predict the High Temperature Flow Stress in 20CrMo Alloy Steel, Mater. Des., 2013, 62, p 677.
S.P. Liu, D.F. Li, J.Y. He, and S.L. Guo, Constitutive Analysis to Predict High-Temperature Flow Stress of 25vol.% B4Cp/2009Al Composite, Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2017, 46, p 2831.
P. Tao, J.W. Zhong, H.X. Li, Q.D. Hu, S.L. Gong, and Q.Y. Xu, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Constitutive Models for Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Metals, 2019, 447, p 1.
J. Wang, G.Q. Zhao, L. Chen, and J.L. Li, A Comparative Study of Several Constitutive Models for Powder Metallurgy Tungsten at Elevated Temperature, Mater. Des., 2016, 90, p 91.
X. Hu, L.J. Xie, F.N. Gao, and J.F. Xiang, On the Development of Material Constitutive Model for 45CrNiMoVA Ultra-High-Strength Steel, Metals, 2019, 374, p 1.
Y.H. Zhao, J. Sun, J.F. Li, Y.Q. Yan, and P. Wang, A Comparative Study on Johnson–Cook and Modified Johnson–Cook Constitutive Material Model to Predict the Dynamic Behavior Laser Additive Manufacturing FeCr Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 723, p 179.
Y.C. Lin, X.M. Chen, and G. Liu, A Modified Johnson–Cook Model for Tensile Behaviors of Typical High-Strength Alloy Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 6980.
Y.C. Lin and X.M. Chen, A Combined Johnson–Cook and Zerilli–Armstrong Model For Hot Compressed Typical High-Strength Alloy Steel, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2010, 49, p 628.
H.Y. Li, X.F. Wang, J.Y. Duan, and J.J. Liu, A Modified Johnson Cook Model for Elevated Temperature Flow Behavior of T24 Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 577, p 138.
A.S. Khan, H.Y. Zhang, and L. Takacs, Mechanical Response and Modelling of Fully Compacted Nanocrystalline Iron and Copper, Int. J. Plast., 2000, 16, p 1459.
J.X. Du, H.B. Li, Y.S. Zhang, and A.J. Mo, Investigation on Constitutive Relationship of 300M High Strength Steel during Hot Deformation, Forg. Stamp. Tech., 2014, 39, p 109.
Y.G. Liu, J. Luo, and M.Q. Li, The Fuzzy Neural Network Model of Flow Stress in the Isothermal Compression of 300M Steel, Mater. Des., 2012, 41, p 83.
S.S. Zhang, M.Q. Li, Y.G. Liu, J. Luo, and T.Q. Liu, The Growth Behavior of Austenite Grain in the Heating Process of 300M Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 4967.
A. Mohamadizadeh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and H.R. Abedi, Modified Constitutive Analysis and Activation Energy Evolution of a Low-Density Steel Considering the Effects of Deformation Parameters, Mech. Mater., 2016, 95, p 60.
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, A.K. Bhaduri, and P.V. Sivaprasad, An Overview on Constitutive Modelling to Predict Elevated Temperature Flow Behaviour of Fast Reactor Structural Materials, Trans. Ind. Inst. Met., 2010, 63, p 823.
R. Ebrahimi and A. Najafizadeh, A New Method for Evaluation of Friction in Bulk Metal Forming, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2002, 152, p 136.
P. Wanjara, M. Jahazi, H. Monajati, and S. Yue, Immarigeon, Hot Working Behavior of Near-α Alloy IMI834, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 396, p 50.
Y.P. Li, E. Onodera, H. Matsumoto, and A. Chiba, Correcting the Stress-Strain Curve in Hot Compression Process to High Strain Level, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, 40, p 982.
D. Trimble, H. Shipley, L. Lea, A. Jardine, and G.E. O’Donnell, Constitutive Analysis of Biomedical Grade Co-27Cr-5Mo Alloy at High Strain Rates, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 682, p 466.
E. Farabi, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, and H.R. Abedi, High Temperature Formability Prediction of Dual Phase Brass Using Phenomenological and Physical Constitutive Models, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 209.
C. Zener and J.H. Hollomon, Effect of Strain Rate Upon Plastic Flow of Steel, J. Appl. Phys., 1944, 15, p 22.
K.H. Sim, Y.C. Li, C.H. Li, M.O. Kim, and H.C. Kim, Constitutive Modeling of a Fine-Grained Ti2AlNb-Based Alloy Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying and Subsequent Spark Plasma Sintering, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2021, 23, p 1.
L. Luo, Z.Y. Liu, S. Bai, J.G. Zhao, D.P. Zeng, J. Wang, J. Cao, and Y.C. Hu, Hot Deformation Behavior Considering Strain Effects, and Recrystallization Mechanism of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy, Materials, 2020, 1743, p 1.
X.K. Yang, K.S. Wang, Z.J. Zhang, M. Guo, J. Cai, and Q.X. Yang, Flow Stress Prediction for As-Cast TC17 Titanium Alloy, Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2020, 49, p 1131.
A.S. Khan and R. Liang, Behaviors of Three BCC Metal Over a Wide Range of Strain Rates and Temperatures: Experiments and Modeling, Int. J. Plast., 1999, 15, p 1089.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Central Research Fund of Kim Chaek University of Technology (MIRAE 2022595).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sim, K.H., Kim, L.S., Han, M.J. et al. Development and Improvement of Phenomenological Constitutive Models for Thermo-Mechanical Processing of 300M Ultra-High Strength Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 33, 1021–1033 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08030-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08030-0