Abstract
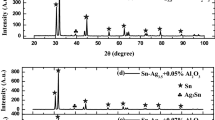
This study aims to investigate the impact of low-cost, highly hardened, and thermally stable Al2O3 nanoparticles (NPs) on the physical properties of the eutectic SAC355 solder alloy. Various concentrations ratios of (SAC355)100−x(Al2O3)x NPs where (x = 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, and 1 wt.%) were synthesized using the melt-spinning process. Phase identification and morphology features of the solder were systematically studied and investigated. Microstructure studies revealed that adding a trace amount of Al2O3 NPs to the eutectic (SAC355) system refine the crystallite size of both rhombohedral β-Sn, orthorhombic Cu6Sn5 and Ag3Sn IMCs. The elastic modulus (E) and Vickers microhardness (Hv) were improved. This can be attributed to the interstitial dispersion of Al2O3 NPs at grain boundaries, which make snail-like Ag3Sn particles more uniformly distributed within β-Sn matrix that could obstruct the dislocation slipping. The results showed that creep resistance (n) decreases from dislocation climb value at 0.1 wt.% to grain boundary sliding value at 1 wt.% Al2O3 NPs content. Electrical resistance (ρ), Fermi energy (Ef), and Fermi velocity (Vf) increased with Al2O3 NPs content, while electron concentration (N) decreased due to increased charge carrier scattering centers. However, increasing the doping content of Al2O3 NPs led to an increase in the melting temperature (Tm), compared with plain solder. All results showed that Al2O3 NPs addition has an effective method to enhance new lead-free solder joints.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.A. Alsorory, M.S.S. Gumaan, and R. Shalaby, Effect of TiO 2 Nanoparticles on the Microstructure, Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Rapid Quenching SAC355 Lead-Free Solder Alloy, Solder. Surf. Mt, Technol, 2022.
S. Tikale and K.N. Prabhu, Development of Low-Silver Content SAC0307 Solder Alloy with Al2O3 Nanoparticles, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Elsevier B V, 2020, 787, p 139439.
M.Z. Yahaya, N.A. Salleh, S. Kheawhom, B. Illes, M.F. Mohd Nazeri, and A.A. Mohamad, Selective Etching and Hardness Properties of Quenched SAC305 Solder Joints, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol., 2020, 32(4), p 225–233.
K. Kanlayasiri and N. Meesathien, Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Properties of SAC0307 Lead-Free Solder Paste, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng, Hindawi, 2018.
E. Anderson, Development of Sn-Ag-Cu and Sn-Ag-Cu-X Alloys for Pb-Free Electronic Solder Applications, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2007, 18(1–3), p 55–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10854-006-9011-9/FIGURES/21
A. Roshanghias, A.H. Kokabi, Y. Miyashita, Y. Mutoh, I. Ihara, R.G. Guan Fatt, and H.R. Madaah-Hosseini, Nanoindentation Creep Behavior of Nanocomposite Sn-Ag-Cu Solders, J. Electron. Mater., 2012, 41(8), p 2057–2064.
M.M. Jubair, M.S. Gumaan, and R.M. Shalaby, Reliable Sn-Ag-Cu Lead-Free Melt-Spun Material Required for High-Performance Applications, Zeitschrift für Kristallographie Cryst Mater., 2019, 234, p 757–767.
A. Olofinjana, R. Haque, M. Mathir, and N.Y. Voo, Studies of the Solidification Characteristics in Sn-Ag-Cu-Bi Solder Alloys, Procedia Manuf Elsevier B. V, 2019, 30, p 596–603.
J. Wu, S. Xue, J. Wang, and M. Wu, Coupling Effects of Rare-Earth Pr and Al2O3 Nanoparticles on the Microstructure and Properties of Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu Low-Ag Solder, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 784, p 471–487.
S. Tikale and K.N. Prabhu, Performance and Reliability of Al2O3 Nanoparticles Doped Multicomponent Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-Ni-Ge Solder Alloy, Microelectron. Reliab. Elsevier, 2020, 113, p 113933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2020.113933
Z.X. Li and M. Gupta, High Strength Lead-Free Composite Solder Materials Using Nano-Al 2O3 as Reinforcement, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2005, 7(11), p 1049–1054.
L.C. Tsao, R.W. Wu, T.H. Cheng, K.H. Fan, and R.S. Chen, Effects of Nano-Al2O3 Particles on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu Composite Solder Ball Grid Array Joints on Sn/Cu Pads, Mater. Des., 2013, 50, p 774–781.
L.C. Tsao, S.Y. Chang, C.I. Lee, W.H. Sun, and C.H. Huang, Effects of Nano-Al2O3 Additions on Microstructure Development and Hardness of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu Solder, Mater. Des. Elsevier Ltd, 2010, 31(10), p 4831–4835.
X. Bi, X. Hu and Q. Li, Effect of Co Addition into Ni Film on Shear Strength of Solder/Ni/Cu System: Experimental and Theoretical Investigations, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Elsevier, 2020, 788, p 139589.
R. Mostafa Shalaby, M. Kamal, E.A.M. Ali, and M.S. Gumaan, Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of Melt Spun Process Sn-3.5Ag and Sn-3.5Ag-XCu Lead-Free Solders for Low Cost Electronic Assembly, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Elsevier, 2017, 690, p 446–452.
K.H. Lee and S.W. Kim, Design and Preparation of High-Performance Bulk Thermoelectric Materials with Defect Structures, J. Korean Ceram. Soc., 2017, 54(2), p 75–85.
E. Schreiber, O.L. Anderson, and N. Soga, “Elastic Constants and Their Measurement,” (New York), 1974
D. Grabco and D. Leu, Deformation Mechanism as a Function of Applied Load under Metal Microindentation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Elsevier, 2010, 527(26), p 6987–6996.
R. Mostafa Shalaby, M. Kamal, E.A.M. Ali, and M.S. Gumaan, Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of Melt Spun Process Sn-3.5Ag and Sn-3.5Ag-XCu Lead-Free Solders for Low Cost Electronic Assembly, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Elsevier, 2017, 690(2016), p 446–452.
M. Changmai, J.P. Priyesh, and M.K. Purkait, Al2O3 Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Various Oxidizing Agents: Defluoridation Performance, J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices Elsevier Ltd, 2017, 2(4), p 483–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2017.09.001
V. Mote, Y. Purushotham, and B. Dole, Williamson-Hall Analysis in Estimation of Lattice Strain in Nanometer-Sized ZnO Particles, J. Theor. Appl. Phys., 2012, 6(1), p 2–9.
G.K. Williamson and W.H. Hall, x-ray Line Broadening from Filed Aluminium and Wolfram, Acta Metall. Pergamon, 1953, 1(1), p 22–31.
E.E.M. Noor and A. Singh, Review on the Effect of Alloying Element and Nanoparticle Additions on the Properties of Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Alloys, Solder, Surf. Mt. Technol. Emerald Group Publishing Ltd, 2014, 26(3), p 147–161.
J.C. Leong, L.C. Tsao, C.J. Fang, and C.P. Chu, Effect of Nano-TiO 2 Addition on the Microstructure and Bonding Strengths of Sn3.5Ag0.5Cu Composite Solder BGA Packages with Immersion Sn Surface Finish, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron., 2011, 22(9), p 1443–1449.
A. Gondal, T.A. Fasasi, A. Mekki, T.A. Saleh, A.M. Ilyas, T.F. Qahtan, and X. Chang, Phase Transformation and Structural Characterization Studies of Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Nanoparticles Synthesized Using an Elegant Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids Technique, Nanosci. Nanotechnol., Lett Am. Sci. Publ., 2016, 8, p 953–960.
R.M. Shalaby, Indium, Chromium and Nickel-Modified Eutectic Sn-0.7 Wt.% Cu Lead-Free Solder Rapidly Solidified from Molten State, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. Springer US, 2015, 26(9), p 6625–6632.
X. Gu, H. Bai, D. Chen, L. Zhao, J. Yi, X. Liu, and J. Yan, The Influences of Reactive Nanoparticles Alloying on Grain Boundary and Melting Properties about Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu Solder, Intermetallics, Elsevier Ltd, 2021, 138, p 107346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2021.107346
F. Stacey and R. Irvine, Theory of Melting: Thermodynamic Basis of Lindemann’s Law, Aust. J. Phys., 1977, 30(6), p 631.
C. Li, Y. Yan, T. Gao, and G. Xu, The Influence of Ag on the Microstructure, Thermal Properties and Mechanical Behavior of Sn-25Sb-XAg High Temperature Lead-Free Solder, Vacuum Elsevier Ltd, 2020, 2021(185), p 110015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2020.110015
Y.Y. Gafner, S.L. Gafner, I.S. Zamulin, L.V. Redel, and V.S. Baidyshev, Analysis of the Heat Capacity of Nanoclusters of FCC Metals on the Example of Al, Ni, Cu, Pd, and Au, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2015, 116(June), p 602–609.
S.L. Gafner, L.V. Redel, and Y.Y. Gafner, Molecular-Dynamics Simulation of the Heat Capacity for Nickel and Copper Clusters: Shape and Size Effects, J. Exp. Theor. Phys., 2012, 114(3), p 428–439.
R.M. Shalaby, Development of Holmium Doped Eutectic Sn-Ag Lead-Free Solder for Electronic Packaging, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol., 2022, (December 2021)
O.M. Yousri, M.H. Abdellatif, and G. Bassioni, Effect of Al 2O 3 Nanoparticles on the Mechanical and Physical Properties of Epoxy Composite, Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2018, 43(3), p 1511–1517.
S. Huang, W. Huang, J. Liu, J. Teng, N. Li, and Y. Wen, Internal Friction Mechanism of Fe-19Mn Alloy at Low and High Strain Amplitude, Mater. Sci. Eng. Elsevier, 2013, 560, p 837–840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2012.10.060
O.L. Anderson, A Simplified Method for Calculating the Debye Temperature from Elastic Constants, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 1963, 24, p 909–917.
M. Pyke, 2002 Elastic Properties and Pressure Effects, Struct. Chem. Glas. 401–427
S. Xiong, W. Qi, Y. Cheng, B. Huang, M. Wang, and Y. Li, Universal Relation for Size Dependent Thermodynamic Properties of Metallic Nanoparticles, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011, 13(22), p 10652–10660.
P. Mishra and B.K. Pandey, Variation of Debye Temperature with Size of Nanoparticles, 3Rd Int. Conf. Condens. Matter Appl. Phys., 2020, 2220(May), p 020061.
Y.D. Qu, X.L. Liang, X.Q. Kong, and W.J. Zhang, Size-Dependent Cohesive Energy, Melting Temperature, and Debye Temperature of Spherical Metallic Nanoparticles, Phys. Met. Metallogr., 2017, 118(6), p 528–534.
Y. Tang, G.Y. Li, and Y.C. Pan, Effects of TiO2 Nanoparticles Addition on Microstructure, Microhardness and Tensile Properties of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu-XTiO2 Composite Solder, Mater. Des., 2014, 55, p 574–582.
R.M. Shalaby, M. Kamal, E.A.M. Ali, and M.S. Gumaan, Design and Properties of New Lead-Free Solder Joints Using Sn-3.5Ag-Cu Solder, Silicon Silicon, 2018, 10(5), p 1861–1871.
A.E. Hammad and A.A. Ibrahiem, Enhancing the Microstructure and Tensile Creep Resistance of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Alloy by Reinforcing Nano-Sized ZnO Particles, Microelectron. Reliab., 2017, 75, p 187–194.
O. Şahin, O. Uzun, U. Kölemen, and N. Uçar, Stress Exponent Investigation of β-Sn Single Crystal by Depth-Sensing Indentation Tests, Phys. B Condens. Matter., 2007, 396(1–2), p 87–90.
M.S. Gumaan, R.M. Shalaby, E.A.M. Ali, and M. Kamal, Copper Effects in Mechanical, Thermal and Electrical Properties of Rapidly Solidified Eutectic Sn-Ag Alloy, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. Springer US, 2018, 29(11), p 8886–8894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8906-6
P. Ma, Y. Jia, P. konda Gokuldoss, Z.Y.S. Yang, J. Zhao, and C. Li, Effect of Al2O3 Nanoparticles as Reinforcement on the Tensile Behavior of Al-12Si Composites, Metals (Basel)., 2017, 7(9), p 1–11.
W. Zhu, Y. Ma, X. Li, W. Zhou, and P. Wu, Effects of Al2O3 Nanoparticles on the Microstructure and Properties of Sn58Bi Solder Alloys, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. Springer, 2018, 29(9), p 7575–7585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8749-1
A.M. Sadoun, M.M. Mohammed, E.M. Elsayed, A.F. Meselhy, and O.A. El-Kady, Effect of Nano Al2O3 Coated Ag Addition on the Corrosion Resistance and Electrochemical Behavior of Cu-Al2O3 Nanocomposites, J. Mater Res. Technol. Korea Inst. Orient. Med., 2020, 3, p 4485–4493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.02.076
F. Ternero, E.S. Caballero, R. Astacio, J. Cintas, and J.M. Montes, Nickel Porous Compacts Obtained by Medium-Frequency Electrical Resistance Sintering, Mater. Basel, 2020, 13(9), p 1–15.
S.M.L. Nai, J. Wei, and M. Gupta, Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on the Shear Strength and Electrical Resistivity of a Lead-Free Solder, J. Electron. Mater., 2008, 37(4), p 515–522.
H.S. Tekce, D. Kumlutas, I.H. Tavman, H. Serkan Tekce, D. Kumlutas, I.H. Tavman, H.S. Tekce, D. Kumlutas, and I.H. Tavman, Effect of Particle Shape on Thermal Conductivity of Copper Reinforced Polymer Composites, J. Reinf. Plast. Compos., 2016, 26(1), p 113–121. https://doi.org/10.1177/0731684407072522
P.F. Lang, Fermi Energy, Metals and the Drift Velocity of Electrons, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2021, 770, p 138447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138447
E.E.M. Noor, A. Singh, Y.T. Chuan, and A. Review, Influence of Nano Particles Reinforced on Solder Alloy, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol., 2013, 25(4), p 229–241.
N.-C. Lee, “Reflow Soldering Processes and Troubleshooting: SMT, BGA, CSP and Flip Chip Technologies,” Newnes, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-sorory, H., Gumaan, M.S. & Shalaby, R.M. Effect of Al2O3 Nanoparticle Addition on the Microstructure, Mechanical, Thermal, and Electrical Properties of Melt-Spun SAC355 Lead-Free Solder for Electronic Packaging. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 8600–8611 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07752-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07752-x