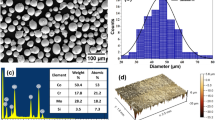
Abstract
By applying the TC4-Ti2AlC composite coatings to the Ti6Al4V substrate by laser, the wear resistance of the Ti6Al4V alloy was improved. Analysis was done on the composite coatings' microstructure, phase composition, microhardness, and tribological characteristics. According to the findings, coatings without defects can be created when Ti2AlC content ranges between 5 and 15 wt.%. Furthermore, the coating without Ti2AlC consisted of a α-Ti solid solution while coatings with Ti2AlC included a α-Ti solid solution, hard phases of TiC and Ti3Al, as well as a Ti2AlC ceramic phase. During laser cladding, Ti2AlC partially dissolved and turned into TiC and Ti3Al, resulting in an average hardness of 371.61 ± 3.95 HV0.5, 382.92 ± 3.61 HV0.5, 388.91 ± 3.29 HV0.5 for the coatings with Ti2AlC weight fractions of 5, 10, and 15%, respectively. These numbers were about 1.16 ~ 1.22 times the hardness of the titanium alloy matrix (320 ± 3.12 HV0.5). Besides, the Ti2AlC lubricant and hard phases act synergistically to bring composite coatings better performances in wear resistance and friction reduction compared to the pure TC4 coating. The lowest coefficient of friction (0.382) (COF) and the greatest wear resistance (8.87 × 10−5 mm3/N m) were obtained at the composition of TC4-10wt.%Ti2AlC; more particularly, the wear resistance at TC4-10wt.%Ti2AlC was 1.2–2.1 times that of pure TC4 coating. The principal causes of wear in a pure TC4 coating are adhesive wear and oxidation, however, these wear processes shift to minor abrasive wear and oxidation when assisted by oxide coatings, Ti2AlC lubricant, and TiC, Ti3Al hard phases.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.C. Fernandez, T. Tobie and J. Collazo, Increase wind Gearbox Power Density by Means of IGS (Improved Gear Surface), Int. J. Fatigue, 2022, 159, p 106789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.106789
T.M. Chen, C.C. Zhu, H.J. Liu, P.T. Wei, J.Z. Zhu and Y.Q. Xu, Simulation and Experiment of Carburized Gear Scuffing Under Oil Jet Lubrication, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106406
A. Suresh, K.V.V. Sai Kalyan, K.S. Sibin Kumar, K. Vinod Kumar, V. Tanishka Varma and B. Sravan Kumar, Design and Simulation of Gear Box for Stone Crushing Ball Mill, Mater. Today Proc., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.456
L. Shi, X.F. Cui, J. Li, G. Jin, J.N. Liu and H.L. Tian, Improving the Wear Resistance of Heavy-Duty Gear Steels by Cyclic Carburizing, Tribol. Int., 2022, 171, p 107576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107576
R.L. Dalcin, V.M.D. Menezes, L.F. Oliveira, C.H.D. Silva, J.C.K.D. Neves, C.A.T.S. Diehl and A.D.S. Rocha, Improvement on Pitting Wear Resistance of Gears by Controlled Forging and Plasma Nitriding, J. Market. Res., 2022, 18, p 4698–4713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.04.122
V. Kharka, N.K. Jain and K. Gupta, Sustainability and Performance Assessment of Gear Hobbing Under Different Lubrication Environments for Manufacturing of 20MnCr5 Spur Gears, Sustain. Mater. Technol., 2022, 31, e00388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00388
Z.Y. Zhou, X.B. Liu, S.G. Zhuang, X.H. Yang, M. Wang and C.F. Sun, Preparation and High Temperature Tribological Properties of Laser In-Situ Synthesized self-Lubricating Composite Coatings Containing Metal Sulfides on Ti6Al4V alloy, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 481, p 209–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.092
Y.Q. Zhao, Y. Han and Y. Xiao, An Asynchronous Dual-Frequency Induction Heating Process for Bevel Gears, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2020, 169, p 114981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.114981
J.W. Zhang, W. Li, H.Q. Wang, Q.P. Song, L.T. Lu, W.J. Wang and Z.W. Liu, A Comparison of the Effects of Traditional Shot Peening and Micro-Shot Peening on the Scuffing Resistance of Carburized and Quenched Gear Steel, Wear, 2016, 368–369, p 253–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.09.029
H.S. Gupta, M. Hussain, P.K. Singh, V. Kumar, S. Kumar and A.K. Das, Laser Surface Modification of SAE8620 HVD Material for Transmission Gear, Mater. Today Proc., 2019, 11, p 813–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.03.047
M. Fan, R.L. Sun and H. Wang, Quality Analysis of Ni60/Ni/MoS2 Self-Lubricating Composite Coating on TC4 Surface by Laser Cladding, Hot Work. Technol., 2016, 45(12), p 123–126. https://doi.org/10.14158/j.cnki.1001-3814.2016.12.037
P. Wang and Y.S. Ye, Solid Self-Lubricating Coatings on TC4 Titanium Alloy by Laser Cladding with h-BN, Surf. Technol., 2015, 44(08), p 44–48. https://doi.org/10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2015.08.008
J. Xu, W.J. Liu and M.L. Zhong, Microstructure and Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of MoS2/TiC/Ni Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 200, p 4227–4232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.01.036
M.S. Yang, X.B. Liu, J.W. Fan, X.M. He, S.H. Shi, G.Y. Fu, M.D. Wang and S.F. Chen, Microstructure and Wear Behaviors of Laser Clad NiCr/Cr3C2–WS2 High Temperature Self-Lubricating Wear-Resistant Composite Coating, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, 258(37), p 57–3762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.12.021
B. Podgornik, T. Kosec, A. Kocijan and Č Donik, Tribological Behavior and Lubrication Performance Of Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) as a Replacement for Graphite in Aluminium Forming, Tribol. Int., 2015, 81, p 267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.09.011
H. Torres, S. Slawik, C. Gachot, B. Prakash and M. Rodríguez Ripoll, Microstructural Design of Self-Lubricating Laser Claddings for Use in High Temperature Sliding Applications, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2018, 337, p 24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.12.060
A.K. Das, Effect of Solid Lubricant Addition in Coating Produced by Laser Cladding Process: A Review, Mater. Today Proc., 2022, 56, p 1274–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.11.217
H. Torres, T. Vuchkov, S. Slawik, C. Gachot, B. Prakash and M. Rodríguez Ripoll, Self-Lubricating Laser Claddings for Reducing Friction and Wear from Room Temperature to 600 °C, Wear, 2018, 408, p 22–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2018.05.001
M.M. Quazi, M.A. Fazal, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, F. Yusof, H.H. Masjuki and A. Arslan, A Review to the Laser Cladding of Self-Lubricating Composite Coatings, Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process., 2016, 3, p 67–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40516-016-0025-8
G.M. Song, Y.T. Pei, W.G. Sloof, S.B. Li, J.T.M. Hosson and S. van der Zwaag, Oxidation-Induced Crack Healing in Ti3AlC2 Ceramics, Scr. Mater., 2008, 58, p 13–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.09.006
A.S. Farle, C. Kwakernaak, S. van der Zwaag and W.G. Sloof, A Conceptual Study into the Potential of Mn+1AXn-Phase Ceramics for Self-Healing of Crack Damage, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2015, 35, p 37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.08.046
S. Li, G. Song, K. Kwakernaak, S. van der Zwaag and W.G. Sloof, Multiple Crack Healing of a Ti2AlC Ceramic, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2012, 32, p 1813–1820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2012.01.017
H.J. Yang, Y.T. Pei and J.T.M. Hosson, Oxide-Scale Growth on Cr2AlC Ceramic and its Consequence for Self-Healing, Scr. Mater., 2013, 69, p 203–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.04.013
Z. Feng, P. Ke, Q. Huang and A. Wang, The Scaling Behavior and Mechanism of Ti2AlC MAX Phase Coatings in Air and Pure Water Vapor, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2015, 272, p 380–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.03.037
J. Cao, Z.W. Yin, H.L. Li, G.Y. Gao and X.L. Zhang, Tribological and Mechanical Properties of Ti2AlC Coating at Room Temperature and 800°C, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44, p 1046–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.10.045
M.W. Barsoum, The MN+1AXN Phases: A New Class of Solids: Thermodynamically Stable Nanolaminates, Prog. Solid State Chem., 2000, 28, p 201–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6786(00)00006-6
M. Magnuson and M. Mattesini, Chemical Bonding and Electronic-Structure in MAX Phases as Viewed by X-ray Spectroscopy and Density Functional Theory, Thin Solid Films, 2017, 621, p 108–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.11.005
P. Eklund, M. Beckers, U. Jansson, H. Hogberg and L. Hultman, The Mn+1AXn Phases: Materials Science and Thin-Film Processing, Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518, p 1851–1878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2009.07.184
M.W. Qureshi, X.X. Ma, X.H. Zhang, G.Z. Tang, R. Paudel and D. Paudyal, Ab-Initio Predictions of Phase Stability, Electronic Structure, and Optical Properties of (0001)-MAXsurfaces in M2AC (M = Cr, Zr, Hf; A = Al, Ga), J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2022, 160, p 110338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110338
N. Goossens, B. Tunca, T. Lapauw, K. Lambrinou, J. Vleugels, in MAX Phases, Structure, Processing, and Properties, ed. by M. Pomeroy. Encyclopedia of Materials: Technical Ceramics and Glasses, (Elsevier, 2021), pp. 182–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818542-1.00015-1
J.L. Smialek, Environmental resistance of a Ti2AlC-type MAX Phase in a High Pressure Burner Rig, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 37, p 23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2016.07.038
Y. Xiao, H.Q. Xiao, J.Y. Feng, B. Lin and Y. Wang, Core-shell ZrC/Ti2AlC Reinforced Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding on Zr-Alloy Substrates, Ceram. Int., 2022, 48(6), p 8136–8142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.12.016
Q.Y. Tan, W.M. Zhuang, M. Attia, R. Djugum and M.X. Zhang, Recent Progress in Additive Manufacturing of Bulk MAX Phase Components: A Review, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2022, 131, p 30–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2022.05.026
X.J. Li, S.H. Wang, G.X. Wu, D.P. Zhou, J.B. Pu, M. Yu, Q. Wang and Q.S. Sun, Oxidation and Hot Corrosion Behaviors of MAX-Phase Ti3SiC2, Ti2AlC, Cr2AlC, Ceram. Int., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.05.356
Y. Zhu, X.B. Liu, Y.F. Liu, G. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Meng and J. Liang, Development and Characterization of Co-Cu/Ti3SiC2 Self-Lubricating Wear Resistant Composite Coatings onTi6Al4V Alloy by Laser Cladding, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 424, p 127664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127664
P. Richardson, D. Cuskelly, M. Brandt and E. Kisi, Microstructural Analysis of In-Situ Reacted Ti2AlC MAX Phase Composite Coating by Laser Cladding, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2020, 385, p 125360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125360
M. Das, S. Bysakh, D. Basu, T.S.S. Kumar, V.K. Balla, S. Bose and A. Bandyopadhyay, Microstructure, Mechanical and Wear Properties of Laser Processed SIC Particle Reinforced Coatings on Titanium, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2011, 205, p 4366–4373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.03.027
X. Lei and N. Lin, Structure and Synthesis of MAX Phase Materials: A Brief Review, Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2021 https://doi.org/10.1080/10408436.2021.1966384
T.T. Ai, Q.F. Niu, Z.F. Deng, W.H. Li, H.F. Dong, R. Jing and X.Y. Zou, Nature-Inspired Nacre-Like Ti6Al4V-(Ti2AlC/TiAl) Laminate Composites Combining Appropriate Strengthand Toughness with Synergy Effects, Intermetallics, 2020, 121, p 106774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intermet.2020.106774
H. Zhang, C.H. Zhang, Q. Wang, C.L. Wu, S. Zhang, J. Chen and A.O. Abdullah, Effect of Ni Content on Stainless Steel Fabricated by Laser Melting Deposition, Opt. Laser Technol., 2018, 101, p 363–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.11.032
G.R. Xu, X.S. Guan, Y.L. Qiao and Y. Gao, Analysis and Innovation for Penetrant Testing for Airplane Parts, Proc. Eng., 2015, 99, p 1438–1442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.681
J.H. Ye and D.L. Hu, Utility Inorganic Materials Thermodynamics Data Handbook, 2nd ed. Metallurgy Industry Press, Beijing, 2002.
J. Li, Z.S. Yu and H.P. Wang, Wear behaviors of an (TiB+TiC)/Ti Composite Coating Fabricated on Ti6Al4V by Laser Cladding, Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(15), p 4804–4808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2011.01.034
B. He, L.J. Zhang, Q.H. Zhu, J. Wang, X. Yun, J.S. Luo and Z.K. Chen, Effect of Solution Treated 316L Layer Fabricated by Laser Cladding on Wear and Corrosive Wear Resistance, Opt. Laser Technol., 2020, 121, p 105788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105788
B.X. Song, T.B. Yu, X.G. Jiang, W.C. Xi and X.L. Lin, The Relationship Between Convection Mechanism and Solidification Structure of the Iron-Based Molten Pool in Metal Laser Direct Deposition, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2020, 165, p 105207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105207
A. Khorram, A.D. Jamaloei, A. Jafari, M. Paidar and X.J. Cao, Microstructural Evolution of Laser-Clad 75Cr3C2+25(80Ni20Cr) Powder on Inconel 718 Superalloy, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020, 284, p 116735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116735
R. Benitez, W.H. Kan, H. Gao, M. O’Neal, G. Proust, A. Srivastava and M. Radovic, Mechanical Properties and Microstructure Evolution of Ti2AlC Under Compression in 25–1100 °C Temperature Range, Acta Mater., 2020, 189, p 154–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.02.057
Y. Wang, X.B. Liu, Y.F. Liu, Y.S. Luo and Y. Meng, Microstructure and Tribological Performance of Ni60-Based Composite Coatings on Ti6Al4V Alloy with Different Ti3SiC2 Ceramic Additions by Laser Cladding, Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(18), p 28996–29010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.071
Z.Y. Wang, G.S. Ma, Z.C. Li, H.T. Ruan, J.G. Yuan, L. Wang, P.L. Ke and A.Y. Wang, Corrosion Mechanism of Ti2AlC MAX Phase Coatings Under the Synergistic Effects of Water Vapor and Solid NaCl at 600 °C, Corros. Sci., 2021, 192, p 109788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109788
H.X. Liu, X.W. Zhang, Y.H. Jiang and R. Zhou, Microstructure and High Temperature Oxidation Resistance of In-Situ Synthesized TiN/Ti3Al Intermetallic Composite Coatings on Ti6Al4V Alloy by Laser Cladding Process, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 670, p 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.168
S. Saroj, C.K. Sahoo, D. Tijo, K. Kumar and M. Masanta, Sliding Abrasive Wear Characteristic of TIG Cladded TiC Reinforced Inconel825 Composite Coating, Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater., 2017 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2017.08.005
X. Zhao, L.Y. Duan and Y.G. Wang, Improved Shear Strength of SiC-coated 3DC/SiC Composite Joints with a Tailored Ti-Si-C Interlayer, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2019, 39(4), p 788–797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.11.016
A. Bansal, D.K. Goyal, P. Singh, A.K. Singla, M.K. Gupta, N. Bala, J. Kolte and G. Setia, Erosive Wear Behavior of HVOF-Sprayed Ni-20Cr2O3 Coating on Pipeline Materials, Int. J. Refract Metal Hard Mater., 2020, 92, p 105332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2020.105332
X. Li, C.H. Zhang, S. Zhang, C.L. Wu, Y. Liu, J.B. Zhang and M. Babar Shahzad, Manufacturing of Ti3SiC2 Lubricated Co-Based Alloy Coatings Using Laser Cladding Technology, Opt. Laser Technol., 2019, 114, p 209–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.02.001
Acknowledgments
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52075559) and the Open Project of the State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication (No. LSL-2102) provided financial support for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SH: investigation, Data curation, Writing original draft. MP: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis. JC: Supervision, Writing-review and editing. JZ: Investigation. F-QJ: Investigation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors affirm that they have no known financial or interpersonal conflicts that would have seemed to impact the research presented in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, SW., Pang, M., Chen, J. et al. Microstructure and Tribological Performance of Laser Cladding Ti2AlC Particle Reinforced Coatings on Ti6Al4V. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 8452–8466 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07714-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07714-3