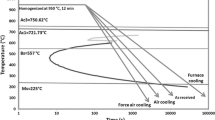
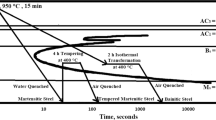
Abstract
The investigation discusses the influence of salinity, conductivity, total dissolved solids (TDS), and pH on the corrosion behavior of different morphologies of pearlitic steels with coarse, fine, and very fine microstructures obtained by furnace-annealed, air-cooled, and forced-air-cooled, respectively. Immersion test of the heat treated steels was carried out in freely aerated 3.5% NaCl solution for 28 days. The study also involves the effect of the water parameters on the composition, fraction, and morphology of corrosion products. Increase in cooling rate decreases the interlamellar spacings, and this refinement has resulted in higher corrosion resistance. The formation of large number of well-distributed microgalvanic cells between cementite and ferrite lamellae of the fine pearlitic air-cooled steel enhances the corrosion resistance. However, further refinement beyond a limit decreases the corrosion resistance due to the entanglement and breaking of cementite lamellae of the forced-air-cooled steel as compared to the air-cooled steel. Therefore, the air-cooled steel with fine pearlite shows better corrosion resistance than the furnace-annealed and forced-air-cooled steels. Generally, salinity and conductivity increase with a decrease in pH with time, whereas the increased TDS and protective index (α/γ*) as measured by the weight fraction of stable α-FeOOH over the other unstable γ-FeOOH and β-FeOOH have resulted in decreased corrosion susceptibility of the pearlitic steels irrespective of their interlamellar spacing between ferrite and cementite.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Panda, R. Balasubramaniam and G. Dwivedi, On the Corrosion Behavior of Novel High Carbon Rail Steels in Simulated Cyclic Wet-Dry Salt Fog Conditions, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50, p 1684–1692.
V. Rault, V. Vignal, H. Krawiec and O. Tadjoa, Corrosion Behavior of Heavily Deformed Pearlitic and Brass-Coated Pearlitic Steels in Sodium Chloride Solutions, Corros. Sci., 2014, 86, p 275–284.
S.I. Al-rubaiey, E.A. Anoon and M.M. Hanoon, The Influence of Microstructure on the Corrosion Rate of Carbon Steels, Eng. Tech. Journal., 2013, 31, p 1–12.
G.P. Singh, A.P. Moon, S. Sengupta, G. Deo, S. Sangal and K. Mondal, Corrosion Behavior of IF Steel in Various Media and its Comparison with Mild Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 1961–1974.
R. Balasubramaniam, B. Panda, G. Dwivedi, A.P. Moon, S. Mahapatra and A.K. Manuwal, Alloy Development of Corrosion-Resistant Rail Steel, Corros. Sci., 2011, 100, p 52–57.
I. Hlavaty, M. Sigmund, L. Krejci and P. Mohyla, The Bainitic Steels for Rail Applications, Mater. Eng., 2009, 16(4), p 44–50.
P.K. Katiyar, S. Misra and K. Mondal, Effect of Different Cooling Rates on the Corrosion Behavior of High-Carbon Pearlitic Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27(4), p 1753.
P.K. Katiyar, S. Misra and K. Mondal, Comparative Corrosion Behavior of Five Microstructures (Pearlite, Bainite, Spheroidized, Martensite, and Tempered Martensite) Made from a High Carbon Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2019, 50, p 1489–1501.
P.K. Katiyar, S. Misra and K. Mondal, Corrosion Behavior of Annealed Steels with Different Carbon Contents (0.002, 0.17, 0.43 And 0.7% C) in Freely Aerated 3.5% NaCl Solution, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28, p 4041–4052.
D.N. Staicopolus, The Role of Cementite in the Acidic Corrosion of Steel, J. Electro. Soc., 1963, 110, p 1121–1124.
S.A. Al-Fozan and A.U. Malik, Effect of Seawater Level on Corrosion Behavior of Different Alloys, Desalination, 2008, 228, p 61–67.
S. Atashin, M. Pakshir and A. Yazdani, Comparative Studying of Marine Parameters’ Effect, via Qualitative Method, T. App. Sci. Res., 2010, 5(2), p 120–128.
S.F.E. Boerlage, Measuring Salinity and TDS of Seawater and Brine for Process and Environmental Monitoring-Which One, When?, Desalin. Water Treat., 2012, 42(1–3), p 222–230.
R. Starosta, Influence of Seawater Salinity on Corrosion of Austenitic Steel, J. Kones Power. Trans., 2019, 26, p 3.
G. Priyotomo, L. Nuraini, S. Prifiharni and S. Sundjono, Corrosion Behavior of Mild Steel in Seawater from Karangsong & Eretan of West Java Region, Indonesia, J. Kelautan, 2018, 11, p 2.
W. Kirk and S. Pikul, Seawater Corrosivity Around The World: Results from Three Years of Testing, Corrosion in Natural Waters. C. Baloun Ed., West Conshohocken, ASTM International, 1990, p 2–36
K. Zakowski, M. Narozny, M. Szocinski and K. Darowicki, Influence of Water Salinity on Corrosion Risk—The Case of the Southern Baltic Sea Coast, Environ. Monit. Assess, 2014, 186, p 4871–4879.
F. Smith, F. Brownlie, T. Hodgkiess, A. Toumpis, A. Pearson and A.M. Galloway, Effect of Salinity on the Corrosive Wear Behaviour of Engineering Steels in Aqueous Solutions, Wear, 2020, 462–463, p 203515.
S. Choudhary, A. Garg and K. Mondal, Relation Between Open Circuit Potential and Polarization Resistance with Rust and Corrosion Monitoring of Mild Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 2969–2976.
T. Misawa, K. Asami, K. Hashimoto and S. Shimodaira, The Mechanism of Atmospheric Rusting and The Protective Amorphous Rust on Low Alloy Steel, Corros. Sci., 1974, 14, p 279–289.
T. Kamimura, S. Hara, H. Miyuki, M. Yamashita and H. Uchida, Composition and Protective Ability of Rust Layer Formed on Weathering Steel Exposed to Various Environments, Corros. Sci., 2006, 48, p 2799–2812.
P.K. Behera, P.K. Katiyar, S. Misra and K. Mondal, Effect of Pre-induced Plastic Strains on the Corrosion Behavior of Reinforcing Bar in 3.5 pct NaCl Solution, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2021, 52A, p 605.
H. Bhadeshia, Materials Algorithm Project Program Library, Phase Transformation Group, Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy. (University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK), https://www.phasetrans.msm.cam.ac.uk/map/steel/programs/mucg46-b.html
W.C. Leslie, The physical metallurgy of steels, Hempisphere Pub. Corp., (1981)
P.K. Behera, A.P.K. Moon, K. Mondal and S. Misra, Estimating Critical Corrosion for Initiation of Longitudinal Cracks in RC Structures Considering Phases and Composition of Corrosion Products, J. Mater. Civ. Eng., 2016, 28(12), p 04016158.
A.P. Moon, S. Sangal, S. Layek, S. Giribaskar and K. Mondal, Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength Bainitic Rail Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 46A, p 1500–1518.
H. Wu, H. Lei, Y.F. Chen and J. Qiao, Comparison on Corrosion Behaviour and Mechanical Properties of Structural Steel Exposed Between Urban Industrial Atmosphere and Laboratory Simulated Environment, Constr. Build. Mater., 2019, 211, p 228–243.
B.Y.R. Surnam, C.W. Chui, H. Xiao and H. Liang, Investigating atmospheric corrosion behavior of carbon steel in coastal regions of Mauritius using Raman Spectroscopy, Rev. Mater., 2016, 21, p 151–168.
A. Raman, S. Nasrazadani and L. Sharma, Morphology of Rust Phases Formed on Weathering Steels in Various Laboratory Corrosion Tests, Metallography, 1989, 22, p 79–96.
R.A. Antunes, I. Costa and D.L.A. de Faria, Characterization of Corrosion Products Formed on Steels in The First Months of Atmospheric Exposure, Mater. Res., 2003, 6, p 403.
Ph. Dillmann, F. Mazaudier and S. Hoerle, Advances in Understanding Atmospheric Corrosion of Iron: I. Rust Characterisation of Ancient Ferrous Artefacts Exposed to Indoor Atmospheric Corrosion, Corros. Sci., 2004, 46(6), p 1401.
S. Fonna, I.B.M. Ibrahim, S. Gunawarman, M. Huzni and S. Thalib. Ikhsan, Investigation of Corrosion Products Formed on the Surface of Carbon Steel Exposed in Banda Aceh’s Atmosphere, Heliyon, 2021, 7, p e06608.
T.D. Marcotte and C.M. Hansson, Corrosion Products that Form on Steel within Cement Paste, Mater. Struct., 2007, 40(3), p 325–340.
R. Balasubramaniam, A.V. Ramesh Kumar and P. Dillmann, Characterization of Rust on Ancient Indian Iron, Curr. Sci., 2003, 85, p 1546.
R. Balasubramaniam and A.V. Ramesh Kumar, Characterization of Delhi Iron Pillar Rust by X-Ray Diffraction, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Mossbauer Spectroscopy, Corros. Sci., 2000, 42, p 2085–2101.
M. Morcillo, B. Chico, J. Alcantara, I. Diaz, R. Wolthuis and D. de la Fuente, SEM/Micro-Raman Characterisation of the Morphologies of Marine Atmospheric Corrosion Products Formed on Mild Steel, J. Electro. Soc., 2016, 163, p 426–439.
Y. Waseda and S. Suzuki Eds., Characterization of Corrosion Products on Steel Surfaces, Springer, Berlin, 2006
C.Y. Da-Allada, G. Alory, Y. du Penhoat, E. Kestenare, F. Durand and N.M. Hounkonnou, Seasonal Mixed-Layer Salinity Balance in the Tropical Atlantic Ocean: Mean State and Seasonal Cycle, J. Geo. Res. Oceans, 2013, 118, p 332–345.
A. Toloei, S. Atashin and M. Pakshir, Corrosion Rate of Carbon Steel Under Synergistic Effect of Seawater Parameters including pH, Temperature, and Salinity in Turbulent Condition, Corros. Rev., 2013, 31(3–6), p 135–144.
G. Sundjono, L. Priyaotomo and S. Nuraini, Prifiharni, Corrosion Behaviour of Mild Steel in Seawater from Northern Coast of Java and Southern Coast of Bali, Indonesia, J. Eng. Technol. Sci., 2017, 49(6), p 770–784.
M. Stratmann, K. Bohnenkamp and H.J. Engell, An Electrochemical Study of Phase-Transitions in Rust Layers, Corros. Sci., 1983, 23, p 969–985.
M. Yamashita, H. Nagano, T. Misawa and H.E. Townsend, Structure of Protective Rust Layers Formed on Weathering Steels by Long-Term Exposure in the Industrial Atmospheres of Japan and North America, ISIJ Int., 1998, 38, p 285–290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Godbole, K., Mondal, K. Influence of Salinity, Total Dissolved Solids, Conductivity, and pH on Corrosion Behavior of Different Morphologies of Pearlitic Steels. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 875–885 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07137-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07137-0