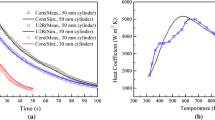
Abstract
High Co-Ni ultrahigh-strength steel parts are severely distorted after quenching. It is necessary to understand the relationship between phase transformation kinetics and stress evolution in the quenching process to reasonably control distortion. The evolution of stress and distortion in three different quenching processes, including water quenching, oil quenching, and vacuum gas quenching for U-shaped AF1410 steel samples, was investigated by experimental and numerical methods. A thermo-metallurgical–mechanical coupled model was developed to accurately predict the magnitude and distribution of the phase fraction, stress, and distortion. The results showed that the distortion of the U-shaped sample quenched by water, oil, and vacuum gas was decreased sequentially. The different distortion trends showed that it was necessary to comprehensively consider the influence of the cooling rate and solid-state phase transformation (SSPT) on stress and distortion. The influence of SSPT was more evident as the cooling rate increased. In addition, choosing a low quenching holding temperature could reduce the distortion magnitude of the U-shaped sample. The U-shaped sample and the corresponding finite element model could be an effective tool for evaluating the distortion behavior of aeronautical parts made of high Co-Ni ultrahigh-strength steel.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhang, D. Zhan, X. Qi and Z. Jiang, Effect of Solid-Solution Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of Ultra-High-Strength Ferrium S53® Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 730, p 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.05.099
X. Li, Z. Zhang, X. Cheng, G. Huo, Q. Song and Y. Xu, Direct Achievement of Ultra-High Strength and Good Ductility for High Co-Ni Secondary Hardening Steel by Combining Spark Plasma Sintering and Deformation, Mater. Lett., 2021, 290, 129465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129465
A. Mondiere, V. Déneux, N. Binot and D. Delagnes, Controlling the MC and M2C Carbide Precipitation in Ferrium® M54® Steel to Achieve Optimum Ultimate Tensile Strength/Fracture Toughness Balance, Mater. Charact., 2018, 140, p 103–112.
Z.B. Jiao, J.H. Luan, M.K. Miller, Y.W. Chung and C.T. Liu, Co-Precipitation of Nanoscale Particles in Steels with Ultra-High Strength for a New Era, Mater. Today, 2017, 20(3), p 142–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2016.07.002
F. Liu, W. Zhang, X. Lin, C. Huang, Z. Wang, F. Liu, W. Huang, P. Wang and X. Li, Achieving Superior Ductility for Laser Directed Energy Deposition 300 M Steel through Isothermal Bainitic Transformation, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 60, p 426–434.
J. Liu, J. Li, X. Cheng and H. Wang, Effect of Dilution and Macrosegregation on Corrosion Resistance of Laser Clad AerMet100 Steel Coating on 300M Steel Substrate, Surf. Coatings Technol., 2017, 325, p 352–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.04.035
Y. Li, X. Cheng, D. Liu and H. Wang, Influence of Last Stage Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Additive Manufactured AF1410 Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 713, p 75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.12.029
K. Li, J. Shan, C. Wang and Z. Tian, Effect of Post-Weld Heat Treatments on Strength and Toughness Behavior of T-250 Maraging Steel Welded by Laser Beam, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 663, p 157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.03.082
Z.X. Li, M. Zhan, X.G. Fan, X.X. Wang, F. Ma and R. Li, Multi-Mode Distortion Behavior of Aluminum Alloy Thin Sheets in Immersion Quenching, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2020, 279, p 116576.
D. Said Schicchi, A. Caggiano, S. Benito and F. Hoffmann, Mesoscale Fracture of a Bearing Steel: A Discrete Crack Approach on Static and Quenching Problems, Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech., 2017, 90, p 154–164.
Y. Bouissa, N. Bohlooli, D. Shahriari, H. Champliaud, J.B. Morin and M. Jahazi, FEM Modeling and Experimental Validation of Quench-Induced Distortions of Large Size Steel Forgings, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 58, p 592–605.
F.P. Quinelato, W.J.L. Garção, K.G. Paradela, R.C. Sales, L.A. de Souza Baptista, and A.F. Ferreira, An Experimental Investigation of Continuous Casting Process: Effect of Pouring Temperatures on the Macrosegregation and Macrostructure in Steel Slab, Mater. Res., 2020, 23(4).
C.R. Xavier, H.G. Delgado Junior, J.A. de Castro, and A.F. Ferreira, Numerical Predictions for the Thermal History, Microstructure and Hardness Distributions at the HAZ during Welding of Low Alloy Steels, Mater. Res., 2016, 19(3), pp. 520–533, Doi:https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2015-0068.
S.J. Lee and Y.K. Lee, Finite Element Simulation of Quench Distortion in a Low-Alloy Steel Incorporating Transformation Kinetics, Acta Mater., 2008, 56(7), p 1482–1490.
M. Jung, M. Kang and Y.K. Lee, Finite-Element Simulation of Quenching Incorporating Improved Transformation Kinetics in a Plain Medium-Carbon Steel, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(2), p 525–536.
Y. Tian, Z. Tan, H. Li, B. Gao, J. Zhu, Y. Liu, and M. Zhang, A New Finite Element Model for Mn-Si-Cr Bainitic/Martensitic Product Quenching Process: Simulation and Experimental Validation, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2021, 294.
D. Tong, J. Gu and F. Yang, Numerical Simulation on Induction Heat Treatment Process of a Shaft Part: Involving Induction Hardening and Tempering, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2018, 262, p 277–289.
D.W. Kim, H.H. Cho, W.B. Lee, K.T. Cho, Y.G. Cho, S.J. Kim and H.N. Han, A Finite Element Simulation for Carburizing Heat Treatment of Automotive Gear Ring Incorporating Transformation Plasticity, Mater. Des., 2016, 99, p 243–253.
L. Taleb, N. Cavallo and F. Waeckel, Experimental Analysis of Transformation Plasticity, Int. J. Plast., 2001, 17(1), p 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-6419(99)00090-X
Y. Liu, S. Qin, Q. Hao, N. Chen, X. Zuo and Y. Rong, Finite Element Simulation and Experimental Verification of Internal Stress of Quenched AISI 4140 Cylinders, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 2017, 48(3), p 1402–1413.
S. Neubert, A. Pittner, and M. Rethmeier, Experimental Determination of TRIP-Parameter K for Mild- and High-Strength Low-Alloy Steels and a Super Martensitic Filler Material, SpringerPlus, 2016, 5(1).
R.K. Dutta, M. Amirthalingam, M.J.M. Hermans and I.M. Richardson, Kinetics of Bainitic Transformation and Transformation Plasticity in a High Strength Quenched and Tempered Structural Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559, p 86–95.
E. Troell, H. Kristoffersen, J. Bodin, and S. Segerberg, Controlling the Cooling Process—Measurement, Analysis, and Quality Assurance, Comprehensive Materials Processing, 2014, pp. 99–121.
J. Li, X. Cai, Y. Wang, and X. Wu, Multiscale Analysis of the Microstructure and Stress Evolution in Cold Work Die Steel during Deep Cryogenic Treatment, Materials (Basel)., 2018, 11(11).
H. Farivar, M.J. Deepu, M. Hans, G. Phanikumar, W. Bleck and U. Prahl, Influence of Post-Carburizing Heat Treatment on the Core Microstructural Evolution and the Resulting Mechanical Properties in Case-Hardened Steel Components, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 744, p 778–789.
A.D. Da Silva, T.A. Pedrosa, J.L. Gonzalez-Mendez, X. Jiang, P.R. Cetlin and T. Altan, Distortion in Quenching an AISI 4140 C-Ring—Predictions and Experiments, Mater. Des., 2012, 42, p 55–61.
X. Chen, S. Zhang, B. Rolfe and D. Li, The FEM Simulation and Experiment of Quenching Distortion of a U-Shape Sample and the Sensitivity Analysis of Material Properties, Mater Res Express, 2019, 6(11), p 116539. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab46ee
D.A. Tanner and J.S. Robinson, Time Transient Validation of Residual Stress Prediction Models for Aluminium Alloy Quenching, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2016, 32(14), p 1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1080/02670836.2016.1195122
M. Jung, S.J. Lee, W.B. Lee and K. Il Moon, Finite Element Simulation and Optimization of Gas-Quenching Process for Tool Steels, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27(8), p 4355–4363.
K. Zhang, W. Dong and S. Lu, Transformation Plasticity of AF1410 Steel and Its Influences on the Welding Residual Stress and Distortion: Experimental and Numerical Study, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 821, 141628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141628
J.B. Leblond and J. Devaux, A New Kinetic Model for Anisothermal Metallurgical Transformations in Steels Including Effect of Austenite Grain Size, Acta Metall., 1984, 32(1), p 137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(84)90211-6
D.P. Koistinen and R.E. Marburger, A General Equation Prescribing the Extent of the Austenite-Martensite Transformation in Pure Iron-Carbon Alloys and Plain Carbon Steels, Acta Metall., 1959, 7(1), p 59–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(59)90170-1
J.B. Lévesque, J. Lanteigne, H. Champliaud and D. Paquet, Modeling Solid-State Phase Transformations of 13Cr-4Ni Steels in Welding Heat-Affected Zone, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2020, 51(3), p 1208–1220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05587-1
M. Yaakoubi, M. Kchaou and F. Dammak, Simulation of the Thermomechanical and Metallurgical Behavior of Steels by Using ABAQUS Software, Comput. Mater. Sci., 2013, 68, p 297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.10.001
J.B. Leblond, J. Devaux and J.C. Devaux, Mathematical Modelling of Transformation Plasticity in Steels I: Case of Ideal-Plastic Phases, Int. J. Plast., 1989, 5(6), p 551–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/0749-6419(89)90001-6
J.B. Leblond, Mathematical Modelling of Transformation Plasticity in Steels II: Coupling with Strain Hardening Phenomena, Int. J. Plast., 1989, 5(6), p 573–591.
S. Denis, E. Gautier, S. Sjöström and A. Simon, Influence of Stresses on the Kinetics of Pearlitic Transformation during Continuous Cooling, Acta Metall., 1987, 35(7), p 1621–1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/0001-6160(87)90109-X
A. Shan and L. Fu, Heat Treating of Air-Hardening High-Strength Structural Steels, Heat Treat. Irons Steels, 2014, pp. 169–178, Doi:https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v04d.a0005953.
Y. Liu, S. Qin, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Rong, X. Zuo and N. Chen, Influence of Transformation Plasticity on the Distribution of Internal Stress in Three Water-Quenched Cylinders, Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci., 2017, 48(10), p 4943–4956. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4230-7
K. Zhang, W. Dong and S. Lu, Finite Element and Experiment Analysis of Welding Residual Stress in S355J2 Steel Considering the Bainite Transformation, J. Manuf. Process., 2021, 62, p 80–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.12.029
H. Zhang, Y. Wang, T. Han, L. Bao, Q. Wu and S. Gu, Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Formation Mechanism and the Distribution of the Welding Residual Stress Induced by the Hybrid Laser Arc Welding of AH36 Steel in a Butt Joint Configuration, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 51, p 95–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.008
H.P. Li, R. Jiang, L.F. He, H. Yang, C. Wang and C.Z. Zhang, Influence of Deformation Degree and Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Phase Transformation Temperature of B1500HS Steel, Acta Metall. Sin. (English Lett.), 2018, 31(1), p 33–47.
J.P. Galler, J.N. DuPont and J.A. Siefert, Influence of Alloy Type, Peak Temperature and Constraint on Residual Stress Evolution in Satoh Test, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2016, 21(2), p 106–113. https://doi.org/10.1179/1362171815Y.0000000071
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NSFC funded program of Liaoning Province [Grant No. 2019-MS-338], the major R&D project of Liaoning Province [Grant No. 2019JH3/30100039], and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences [Grant No. XDC04030601].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Dong, W. & Lu, S. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Stress and Distortion in AF1410 Steel Under Varying Quenching Conditions. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 6858–6869 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06688-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06688-6