Abstract
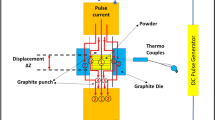
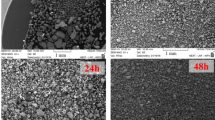
Cu+Mo+C powders were mechanically alloyed and hot-pressed to obtain in-situ micro/nanoscale Mo2C reinforced Cu-matrix composites. Both powders and sintered compacts were characterized and assessed for the hardness and electrical conductivity to study the alloying time effect on materials microstructure evolution and properties. During milling, Mo reacted with C forming a little MoC. As the milling time increased from 60 to 120 h, flaky powder particles were replaced by finer granular particles composed of Cu and Mo nanocrystals. For 84 h- and 120 h-milled powders, Mo combined with C besides MoC+Mo forming P63/mmc hexagonal-structured Mo2C without residual Mo during sintering, instead of primitive hexagonal Mo2C in the case of un-milled powders. Both types of Mo2C occurred in the sintered sample of 60 h-milled powders. In-situ formed Mo2C especially with nanoscale sizes in the 120 h-milled powders’ sintered composites with good electrical property was responsible for the hardness improvement by 63.6% than the un-milled case.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z.F. Jia, T.D. Chen, J. Wang and J.J. Ni, Synthesis, Characterization and Tribological Properties of Cu/Reduced Grapheme Oxide Composites, Tribol. Int., 2015, 88, p 17–24.
C. Ziejewska, J. Marczyk, A. Szewczyk-Nykiel, M. Nykiel and M. Hebda, Influence of Size and Volume Share of WC Particles on the Properties of Sintered Metal Matrix Composites, Adv. Powder Technol., 2019, 30, p 835–842.
Z.F. Jia, P. Zhao, J. Ni, X. Shao, L. Zhao and B. Huang, The Electrical Conductivities and Tribological Properties of Vacuum Hot-Pressed Cu/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26, p 4434–4441.
G.H.A. Bagheri, The Effect of Reinforcement Percentages on Properties of Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced with TiC Particles, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 676, p 120–126.
H.M. Yehia, F. Nouh and O. El-Kady, Effect of Graphene Nano-Sheets Content and Sintering Time on the Microstructure, Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, and Mechanical Propterties of (Cu/WC-TiC-Co) Nanocomposites, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 764, p 36–43.
H. Zuhailawati, H.M. Salihin and Y. Mahani, Microstructure and Properties of Copper Composite Containing in In Situ NbC Reinforcement: Effects of Milling Speed, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 489, p 369–374.
M.I. Abd El Aal and H.S. Kim, Effect of the Fabrication Method on the Wear Properties of Copper Silicon Carbide Composites, Tribol. Int., 2018, 128, p 140–154.
M.A. Eryomina, S.F. Lomayeva, S.N. Paranin, S.L. Demakov and E.P. Yelsukov, Effect of the Method for Producing Cu-Cr3C2 Bulk Composites on the Structure and Properties, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2017, 40, p 1021–1028.
S.H. Chang, C.Y. Chuang and K.T. Huang, Mechanical Properties and Microstructures of Mo2C Strengthened Vanadis 4 Extra Alloy Steel by Powder Metallurgy and Heat Treatments, ISIJ Int., 2019, 59, p 1354–1361.
C. Liu, N. Lin and Y.H. He, Influence of Mo2C and TaC Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Ti(C, N)-Based Cermets, Ceram. Int., 2016, 42, p 3569–3574.
Z.Y. Zhao, P.F. Hui, T. Wang, Y.H. Xu, L.S. Zhong, M.X. Zhao, D.X. Yang and R. Wei, Fabrication of Mo2C Coating on Molybdenum by Contact Solid Carburization, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 462, p 48–54.
Q. Kang, X. He, S.B. Ren, L. Zhang, M. Wu, T. Liu, Q. Liu, C. Guo and X.H. Qu, Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Copper-Diamond Composites using Molybdenum Carbide-Coated Diamond Particles, J. Mater. Sci., 2013, 48, p 6133–6140.
Q. Liu, X.B. He, S.B. Ren, T. Liu, Q. Kang and X.H. Qu, Fabrication and Thermal Conductivity of Copper Matrix Composites Reinforced with Mo2C or TiC Coated Graphite Fibers, Mater. Res. Bull., 2013, 48(11), p 4811–4817.
J. Song, Q.G. Guo, X. Gao, Z. Tao, J. Shi and L. Liu, Mo2C Intermediate Layers for the Wetting and Infiltration of Graphite Foams by Liquid Copper, Carbon, 2011, 49, p 3165–3170.
R.X. Liu, G.Q. Luo, Y. Li, J. Zhang, Q. Shen and L.M. Zhang, Microstructure and Thermal Properties of Diamond/Copper Composites with Mo2C In-Situ Nano-Coating, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2019, 360, p 376–381.
S. Guo, X. Zhang, C. Shi, E. Liu, C. He, F. He and N. Zhao, Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity of Graphene Nanoplatelets/Cu Composites by In Situ Formation of Mo2C Nanoparticles, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2019, 766, p 138365.
K. Zuo, S. Xi and J. Zhou, Phase Transformation of Cu-Mo-C during Mechanical Alloying and Annealing Process, Adv. Mater. Res., 2011, 233–235, p 1678–1683.
E. Liu, Y. Gao, J. Jia, Y. Bai and W. Wang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of In Situ NiAl–Mo2C Nanocomposites Prepared by Hot-Pressing Sintering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 592, p 201–206.
C. Suryanarayana, Mechanical Alloying and Milling, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2001, 46, p 1–184.
N.L. Cheng, Thermochemical data of pure substances, Science Press, 2015, p 1788–1789
D. Nunes, V. Livramento and R. Mateus, Mechanical Synthesis of Copper-Carbon Nanocomposites: Structural Changes, Strengthening and Thermal Stabilization, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 8610–8620.
Y. Bian, J. Ni, C. Wang, J. Zhen, H. Hao, X. Kong, H. Chen, J. Li, X. Li, Z. Jia, W. Luo and Z. Chen, Microstructure and Wear Characteristics of In-Situ Micro/Nanoscale Niobium Carbide Reinforced Copper Composites Fabricated Through Powder Metallurgy, Mater. Charact., 2021, 172, p 110847.
S.C. Liao, W.E. Mayo and K.D. Pae, Theory of High Pressure/Low Temperature Sintering of Bulk Nanocrystalline TiO2, Acta Mater., 1997, 45, p 4027–4040.
J.L. Cabezas-Villa, L. Olmos, H.J. Vergara-Hernández, O. Jiménez, P. Garnica, D. Bouvard and M. Flores, Constrained Sintering and Wear Properties of Cu-WC Composite Coatings, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2017, 27, p 2214–2224.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China under Grant Number ZR2017MEM001 and National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Number 52174346.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, Y., Ni, J. Microstructure Evolution and Properties of In Situ Micro/Nanoscale Mo2C Reinforced Copper Composite Synthesized by Hot-Pressing Consolidation of Mechanical Alloying Powders. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 4604–4610 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06572-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06572-9