Abstract
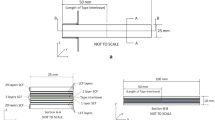
Using polylactic acid (PLA), polyamide (PA) and glass fiber–reinforced polyamide (GF/PA) as raw materials, samples with different printing temperature and speed were prepared. PLA samples were prepared by fused deposition modeling, and PA and PA/GF samples were prepared by selective laser sintering. The fracture toughness of 3D printed engineering plastics was characterized by three-point bending test. The results show that the process parameters have little effect on the fracture toughness of the specimen. With the change of printing temperature or speed, the fracture toughness of the specimen decreases by 4.9%. The raw materials have great influence on the fracture toughness of the specimens. The fracture toughness of PLA increases by 27.95% compared with PA and 58.71% with GF/PA. The results show that the fracture toughness of PLA is the highest among the three materials. Finally, the fracture surface of the specimen was scanned by scanning electron microscope, and the fracture microstructure was analyzed to reveal the influence of process parameters and raw materials on the fracture toughness of 3D printed engineering plastics.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.B. Rebelo, D. Lecompte, C. Cismasiu, A. Jonet, B. Belkassem and A. Maazoun, Experimental and Numerical Investigation on 3D Printed PLA Sacrificial Honeycomb Cladding, Int. J. Impact Eng., 2019, 131, p 162–173.
C. Lubombo and M.A. Huneault, Effect of Infill Patterns on the Mechanical Performance of Lightweight 3D-Printed Cellular PLA Parts, Mater. Today Commun., 2018, 17, p 214–228.
X. Tian, T. Liu, Q. Wang, A. Dilmurat, D. Li and G. Ziegmann, Recycling and Remanufacturing of 3D Printed Continuous Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA Composites, J. Clean. Prod., 2017, 142, p 1609–1618.
X. Tian, T. Liu, C. Yang, Q. Wang and D. Li, Interface and Performance of 3D Printed Continuous Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA Composites, Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2016, 88, p 198–205.
X.W. Chen, T.J. Zhang and S.H. Liu, Accelerated Ageing Behavior of PMMA under Hygrothermal Air and Water Conditions, Fail. Anal. Prev., 2009, 4, p 193–195.
R. Baptista and M. Guedes, Morphological and Mechanical Characterization of 3D Printed PLA Scaffolds with Controlled Porosity for Trabecular Bone Tissue Replacement, Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2021, 118, p 111528.
R.K. Upadhyay, A.K. Mishra and A. Kumar, Mechanical Degradation of 3D Printed PLA in Simulated Marine Environment, Surf. Interfaces, 2020, 21, p 100778.
R. Baptista, M. Guedes, M.F.C. Pereira, A. Maurício, H. Carrelo and T. Cidade, On the Effect of Design and Fabrication Parameters on Mechanical Performance of 3d printed PLA Scaffolds, Bioprinting, 2020, 20, p e96.
K.N. Gunasekaran, V. Aravinth, C.B. Muthu Kumaran, K. Madhankumar and S. Pradeep Kumar, Investigation of Mechanical Properties of PLA Printed Materials under Varying Infill Density, Mater. Today Proc., 2020, 45, p 1849–1856.
A. Lanzotti, M. Martorelli, S. Maietta, S. Gerbino, F. Penta and A. Gloria, A Comparison Between Mechanical Properties of Specimens 3D Printed with Virgin and Recycled PLA, Procedia CIRP, 2019, 79, p 143–146.
M.A. Salim, Z.H. Termiti and A.M. Saad, Mechanical Properties on ABS/PLA Materials for Geospatial Imaging Printed Product using 3D Printer Technology, Reference Module in Materials Science and Materials Engineering. J.G. Sereni Ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019
M. Heidari-Rarani, M. Rafiee-Afarani and A.M. Zahedi, Mechanical Characterization of FDM 3D Printing of Continuous Carbon Fiber Reinforced PLA Composites, Compos. Part B Eng., 2019, 175, p 107147.
Y. Song, Y. Li, W. Song, K. Yee, K.Y. Lee and V.L. Tagarielli, Measurements of the Mechanical Response of Unidirectional 3D-Printed PLA, Mater. Des., 2017, 123, p 154–164.
X.W. Chen, G.L. Pei and Y.S. Jin, Study on Accelerated Ageing of Aeronautical Perspex(PMMA) in Ultraviolet, J. Aeronaut. Mater., 2009, 29, p 107–112.
S. Bhagia, R.R. Lowden, D. Erdman, M. Rodriguez, B.A. Haga, I.R.M. Solano, N.C. Gallego, Y. Pu, W. Muchero, V. Kunc and A.J. Ragauskas, Tensile Properties of 3D-Printed Wood-Filled PLA Materials Using Poplar Trees, Appl. Mater. Today, 2020, 21, p 100832.
M.R. Ayatollahi, A. Nabavi-Kivi, B. Bahrami, M. Yazid Yahya and M.R. Khosravani, The Influence of In-Plane Raster Angle on Tensile and Fracture Strengths of 3D-Printed PLA Specimens, Eng. Fract. Mech., 2020, 237, p 107225.
T. Yao, J. Ye, Z. Deng, K. Zhang, Y. Ma and H. Ouyang, Tensile Failure Strength and Separation Angle of FDM 3D Printing PLA Material: Experimental and Theoretical Analyses, Compos. Part B Eng., 2020, 188, p 107894.
T. Yao, Z. Deng, K. Zhang and S. Li, A Method to Predict the Ultimate Tensile Strength of 3D Printing Polylactic Acid (PLA) Materials with Different Printing Orientations, Compos. Part B Eng., 2019, 163, p 393–402.
S.K. Dhinesh, P.S. Arun, K.K.L. Senthil and A. Megalingam, Study on Flexural and Tensile Behavior of PLA, ABS and PLA-ABS Materials, Mater. Today Proc., 2020, 45, p 1175–1180.
O.H. Ezeh and L. Susmel, On the Notch Fatigue Strength of Additively Manufactured Polylactide (PLA), Int. J. Fatigue, 2020, 136, p 105.
O.H. Ezeh and L. Susmel, Fatigue Strength of Additively Manufactured Polylactide (PLA): Effect of Raster Angle and Non-zero Mean Stresses, Int. J. Fatigue, 2019, 126, p 319–326.
O.H. Ezeh and L. Susmel, On the Fatigue Strength of 3D-Printed Polylactide (PLA), Procedia Struct. Integr., 2018, 9, p 29–36.
F.S. Senatov, K.V. Niaza, A.A. Stepashkin and S.D. Kaloshkin, Low-cycle Fatigue Behavior of 3d-Printed PLA-Based Porous Scaffolds, Compos. Part B Eng., 2016, 97, p 193–200.
J.V. Ecker, I. Burzic, A. Haider, S. Hild and H. Rennhofer, Improving the Impact Strength of PLA and Its Blends with PHA in Fused Layer Modelling, Polym. Test, 2019, 78, p 105929.
P. Kakanuru and K. Pochiraju, Moisture Ingress and Degradation of Additively Manufactured PLA, ABS and PLA/SiC Composite Parts, Addit. Manuf., 2020, 36, p 101529.
J. Kiendl and C. Gao, Controlling Toughness and Strength of FDM 3D-Printed PLA Components Through the Raster Layup, Compos. Part B Eng., 2020, 180, p 107562.
L. Fixtures, ASTM Standard Test Method for Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness of Metallic Materials, 1997.
M. Janssen, J. Zuidema and R. Wanhill, Fracture Mechanics, 2nd ed. Spon Press, London, 2004.
Acknowledgment
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by the Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (Grant No. 2019-KTHY-059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Liu, Y., Hao, W. et al. Study on the Fracture Toughness of 3D Printed Engineering Plastics. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 2889–2895 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06439-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06439-z