Abstract
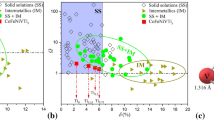
In this work, the alloying effects of Ta element on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of CoCu0.5FeNiTax (x = 0-0.6 at.%) high-entropy alloys were studied. The microstructure changed from single solid solution to hypoeutectic, then to eutectic, and finally to hypereutectic with the increase in Ta content, which is because Ta element facilitates the Laves phase to form. The volume fraction of hard and brittle Laves phase increases with the Ta content, which increases the yield strength, Vickers hardness and theoretical density but decreases the plastic strain. The CoCu0.5FeNiTa0.1 alloy with a single FCC solid solution structure shows the optimal balance between density and ductility. The theoretical density and tensile fracture strain can reach 8.94 g/cm3 and 36.3%, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Birkhoff, D.P. MacDougall, E.M. Pugh, and S.G. Taylor, Explosives with Lined Cavities, J. Appl. Phys., 1948, 19(6), p 563–582
S. Lee, J. Kim, S. Kim, S. Lee, J. Jeong, and C. Lee, Performance Comparison of Double-Layer Liner for Shaped Charge Fabricated Using Kinetic Spray, J. Therm. Spray. Tech., 2018, 28(3), p 484–494
H.W. He and S.Y. Jia, Direct Electrodeposition of Cu-Ni-W Alloys for the Liners for Shaped Charges, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(5), p 429–432
F. Yang, W.H. Tian, C.C. Feng, and B.S. Wang, Crystal Defects Formed in Electroformed Nickel Liners of Shaped Charges, Acta Metall. Sin., 2009, 22(5), p 383–391
F. Yang, C.H. Li, S.W. Cheng, L. Wang, and W.H. Tian, Deformation Behavior of Explosive Detonation in Electroformed Nickel Liner of Shaped Charge with Nano-Sized Grains, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2010, 20, p 1397–1402
B. Xi, J.X. Liu, S.K. Li, C.C. Cui, W.Q. Guo, and T.T. Wu, Effect of Interaction Mechanism Between Jet and Target on Penetration Performance of Shaped Charge Liner, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 553(36), p 142–148
Q. Wei, T. Jiao, K.T. Ramesh, E. Ma, L.J. Kecskes, L. Magness, R. Dowding, V.U. Kazykhanov, and R.Z. Valiev, Mechanical Behavior and Dynamic Failure of High-Strength Ultrafine Grained Tungsten Under Uniaxial Compression, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(1), p 77–87
Q. Wei, H.T. Zhang, B.E. Schuster, K.T. Ramesh, R.Z. Valiev, L.J. Kecskes, R.J. Dowding, L. Magness, and K. Cho, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Super-Strong Nanocrystalline Tungsten Processed by High-Pressure Torsion, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(15), p 4079–4089
W. Guo, S.K. Li, F.C. Wang, and M. Wang, Dynamic Recrystallization of Tungsten in a Shaped Charge Liner, Scr. Mater., 2009, 60, p 329–332
H.M. He, L.X. Wang, J. Sun, H.P. Gu, and F.W. Liu, Experiment and Numerical Simulation on Rod-Like Jet Formation by Molybdenum Liner, Explos. Shock Waves, 2013, 33, p 28–33
W. Walters, W. Gooch, and M. Burkins, The Penetration Resistance of a Titanium Alloy against Jets From Tantalum Shaped Charge Liners, Int. J. Impact Eng, 2001, 26(1), p 823–830
T.F. Guo, W.B. Li, W.B. Li, and X.W. Hong, Controlling Effect of Tantalum Liner’s Structural Parameters on EFP Formation and Penetration Performance, Chin. J. High Pressure Phys., 2018, 32(3), p 1–6
W.Q. Guo, J.X. Liu, Y. Xiao, S.K. Li, Z.Y. Zhao, and J. Cao, Comparison of Penetration Performance and Penetration Mechanism of W-Cu Shaped Charge Liner Against Three Kinds of Target: Pure Copper, Carbon Steel and Ti-6Al-4 V Alloy, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2016, 60, p 147–153
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, and A.J.B. Vincent, Microstructural Development in Equiatomic Multicomponent Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 375–377(1), p 213–218
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6(5), p 299–303
Z.M. Li, K.G. Pradeep, Y. Deng, D. Raabe, and C.C. Tasan, Metastable High-Entropy Dual-Phase Alloys Overcome the Strength–Ductility Trade-Off, Nature, 2016, 534, p 227–230
F. Zhang, Y. Wu, H.B. Lou, Z.D. Zeng, V.B. Prakapenka, E. Greeberg, Y. Ren, J.Y. Yan, J.S. Okasinski, X.J. Liu, Y. Liu, Q.S. Zeng, and Z.P. Lu, Polymorphism in a High-Entropy Alloy, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, p 15687
H.W. Yao, J.W. Qiao, J.A. Hawk, H.F. Zhou, M.W. Chen, and M.C. Gao, Mechanical Properties of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys: Experiments and Modeling, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 696, p 1139–1150
J.W. Qiao, M.L. Bao, Y.J. Zhao, H.J. Yang, Y.C. Wu, Y. Zhang, J.A. Hawk, and M.C. Gao, Rare-Earth High Entropy Alloys with Hexagonal Close-Packed Structure, J. Appl. Phys., 2018, 124, p 195101
Y. Zhang, T.T. Zuo, Z. Tang, M.C. Gao, K.A. Dahmen, P.K. Liaw, and Z.P. Lu, Microstructures and Properties of High-Entropy Alloys, Prog. Mater Sci., 2014, 61, p 1–93
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, and P.K. Liaw, Solid-Solution Phase Formation Rules for Multi-Component Alloys, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2008, 10(6), p 534–538
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, E.H. Chang, E.P. George, and R.O. Ritchie, A Fracture-Resistant High-Entropy Alloy for Cryogenic Applications, Science, 2014, 345(6201), p 1153–1158
S.M. Oh and S.I. Hong, Microstructural Stability and Mechanical Properties of Equiatomic CoCrCuFeNi, CrCuFeMnNi, CoCrCuFeMn Alloys, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2018, 210, p 120–125
T.T. Shun and Y.C. Du, Microstructure and Tensile Behaviors of FCC Al03CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 479(1), p 157–160
M.C. Gao, J.W. Yeh, P.K. Liaw, and Y. Zhang, High-Entropy Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed., Springer, Cham, 2016
H. Jiang, K.M. Han, D.X. Qiao, Y.P. Lu, Z.Q. Cao, and T.J. Li, Effects of Ta Addition on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2018, 210, p 43–48
L. Jiang, Y.P. Lu, Y. Dong, T.M. Wang, Z.Q. Cao, and T.J. Li, Effects of Nb Addition on Structural Evolution and Properties of the CoFeNi2V0.5 High-Entropy Alloy, Appl. Phys. A, 2015, 119(1), p 291–297
P. Cui, Y.M. Ma, L.J. Zhang, M.D. Zhang, J.T. Fan, W.Q. Dong, P.F. Yu, and G. Li, Microstructure and Mechanical Behaviors of CoFeNiMnTixAl1-x High Entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 731, p 124–130
D.B. Miracle and O.N. Senkov, A Critical Review of High Entropy Alloys and Related Concepts, Acta Mater., 2017, 122, p 448–511
D. Yong, Y.P. Lu, J.R. Kong, J.J. Zhang, and T.J. Li, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multi-Component AlCrFeNiMox High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 573(10), p 96–101
S. Guo, C. Ng, and C.T. Liu, Anomalous Solidification Microstructures in Co-Free AlxCrCuFeNi2 High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 557(10), p 77–81
W.Y. Huo, H. Zhou, F. Fang, X.F. Zhou, Z.H. Xie, and J.Q. Jiang, Microstructure and Properties of Novel CoCrFeNiTax Eutectic High-Entropy Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2018, 735, p 897–904
N. Yurchenko, N. Stepanov, and G. Salishchev, Laves-Phase Formation Criterion for High-Entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33(1), p 17–22
S. Guo and C.T. Liu, Phase Stability in High Entropy Alloys: Formation of Solid-Solution Phase or Amorphous Phase, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 2011, 21, p 433–446
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51671044, 51822402 and 51574058), Dalian Support Plan for Innovation of High-level Talents (Top and Leading Talents, 2015R013), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Dalian Support Plan for Innovation of High-level Talents (Youth Technology Stars, 2016RQ005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, T., Lu, Y., Cao, Z. et al. Effects of Ta Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCu0.5FeNi High-Entropy Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 7642–7648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04463-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04463-8