Abstract
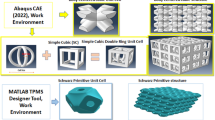
Lightweight materials with complex structures such as cellular solids (or foams) have proven to possess desirable properties, specifically in terms of its stiffness, strength, and thermal conductivity, among other mechanical and thermal performance aspects while the density is reduced. The fabrication of such attractive yet complex materials has become possible due to the witnessed advancements in fabrication techniques. However, a major challenge in adapting cellular solids in mechanical design is choosing the appropriate lattice design. Therefore, this paper focuses on studying the compressive mechanical behavior of four different types of cellular solids with topologies based on the mathematically known triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS); namely, Diamond (D), I-WP (IWP), Gyroid (G), and Fisher-Koch C(Y) (CY). These cellular materials are 3D printed using the powder bed fusion selective laser sintering technique out of Nylon thermoplastic polymer at various relative densities. The effects of the number of unit cells, type of the ligament-based TPMS architecture, and relative density on the stiffness, yield strength, ultimate strength, and toughness are thoroughly investigated. The results indicated that the effect of the architecture is stronger when the relative density is decreased. Also, the analyses showed that all the tested architectures were bending dominated implying that it could be best applied in shock absorbing and vibration mitigation applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. Gibson and M.F. Ashby, Cellular Solids: Structure And Properties, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1999
M. Ashby, The Properties of Foams and Lattices, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 2006, 364(1838), p 15–30
V. Deshpande, M. Ashby, and N. Fleck, Foam Topology: Bending Versus Stretching Dominated Architectures, Acta Mater., 2001, 49(6), p 1035–1040
S. Guessasma, P. Babin, G. Della Valle, and R. Dendievel, Relating Cellular Structure of Open Solid Food Foams to Their Young’s Modulus: Finite Element Calculation, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2008, 45(10), p 2881–2896
W. Lee, Cellular Solids, Structure and Properties, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, 16(2), p 233
M.K. Ravari, M. Kadkhodaei, M. Badrossamay, and R. Rezaei, Numerical Investigation on Mechanical Properties of Cellular Lattice Structures Fabricated by Fused Deposition Modeling, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2014, 88, p 154–161
V. Valuiskikh, Method of Stochastic Simulation Modeling of the Structure, Calculation, and Optimization of the Physicomechanical Characteristics of Foam Plastics, Mech. Compos. Mater., 1990, 25(4), p 429–435
V. Yakushin and U. Stirna, Physicomechanical Characteristics of Spray-on Rigid Polyurethane Foams at Normal and Low Temperatures, Mech. Compos. Mater., 2002, 38(3), p 273–280
R. Gümrük, R. Mines, and S. Karadeniz, Determination of Strain Rate Sensitivity of Micro-struts Manufactured Using the Selective Laser Melting Method, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27(3), p 1016–1032
M.K. Ravari and M. Kadkhodaei, A Computationally Efficient Modeling Approach for Predicting Mechanical Behavior of Cellular Lattice Structures, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(1), p 245–252
T. Lu, H. Stone, and M. Ashby, Heat Transfer in Open-Cell Metal Foams, Acta Mater., 1998, 46(10), p 3619–3635
L.R. Meza, S. Das, and J.R. Greer, Strong, Lightweight, and Recoverable Three-Dimensional Ceramic Nanolattices, Science, 2014, 345(6202), p 1322–1326
O. Al-Ketan, R. Rezgui, R. Rowshan, H. Du, N.X. Fang, and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Microarchitected Stretching-Dominated Mechanical Metamaterials with Minimal Surface Topologies, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2018, 20(9), p 1800029
X. Zheng, W. Smith, J. Jackson, B. Moran, H. Cui, D. Chen, J. Ye, N. Fang, N. Rodriguez, T. Weisgraber, and C.M. Spadaccini, Multiscale Metallic Metamaterials, Nat. Mater., 2016, 15, p 1100
A.H. Schoen, Infinite Periodic Minimal Surfaces Without Self-Intersections, NASA Report D5541, 1970
D. Cvijović and J. Klinowski, The Computation of the Triply Periodic I-WP Minimal Surface, Chem. Phys. Lett., 1994, 226(1), p 93–99
S.C. Kapfer, S.T. Hyde, K. Mecke, C.H. Arns, and G.E. Schröder-Turk, Minimal Surface Scaffold Designs for Tissue Engineering, Biomaterials, 2011, 32(29), p 6875–6882
M. Afshar, A.P. Anaraki, H. Montazerian, and J. Kadkhodapour, Additive Manufacturing and Mechanical Characterization of Graded Porosity Scaffolds Designed Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Architectures, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2016, 62, p 481–494
J. Kadkhodapour, H. Montazerian, A.C. Darabi, A. Zargarian, and S. Schmauder, The Relationships Between Deformation Mechanisms and Mechanical Properties of Additively Manufactured Porous Biomaterials, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2017, 70, p 28–42
I. Maskery, A.O. Aremu, L. Parry, R.D. Wildman, C.J. Tuck, and I.A. Ashcroft, Effective Design and Simulation of Surface-Based Lattice Structures Featuring Volume Fraction and Cell Type Grading, Mater. Des., 2018, 155, p 220–232
I. Maskery, L. Sturm, A.O. Aremu, A. Panesar, C.B. Williams, C.J. Tuck, R.D. Wildman, I.A. Ashcroft, and R.J.M. Hague, Insights into the Mechanical Properties of Several Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Lattice Structures Made by Polymer Additive Manufacturing, Polymer, 2018, 152, p 62–71
D.W. Abueidda, M. Bakir, R.K. Abu Al-Rub, J.S. Bergström, N.A. Sobh, and I. Jasiuk, Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Polymeric Cellular Materials with Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Architectures, Mater. Des., 2017, 122, p 255–267
O. Al-Ketan, R. Rowshan, and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Topology-Mechanical Property Relationship of 3D Printed Strut, Skeletal, and Sheet Based Periodic Metallic Cellular Materials, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 19, p 167–183
O. Al-Ketan, R.K. Abu Al-Rub, and R. Rowshan, The Effect of Architecture on the Mechanical Properties of Cellular Structures Based on the IWP Minimal Surface, J. Mater. Res., 2018, 33(03), p 343–359
C. Yan, L. Hao, A. Hussein, and P. Young, Ti-6Al-4 V Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Structures for Bone Implants Fabricated via Selective Laser Melting, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2015, 51, p 61–73
D.W. Abueidda, R.K. Abu Al-Rub, A.S. Dalaq, D.-W. Lee, K.A. Khan, and I. Jasiuk, Effective Conductivities and Elastic Moduli of Novel Foams with Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces, Mech. Mater., 2016, 95, p 102–115
D.W. Abueidda, A.S. Dalaq, R.K. Abu Al-Rub, and H.A. Younes, Finite Element Predictions of Effective Multifunctional Properties of Interpenetrating Phase Composites with Novel Triply Periodic Solid Shell Architectured Reinforcements, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2015, 92, p 80–89
A.S. Dalaq, D.W. Abueidda, and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Mechanical Properties of 3D Printed Interpenetrating Phase Composites with Novel Architectured 3D Solid-Sheet Reinforcements, Compos. A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2016, 84, p 266–280
O. Al-Ketan, M. Adel Assad, and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Mechanical Properties of Periodic Interpenetrating Phase Composites with Novel Architected Microstructures, Compos. Struct., 2017, 176, p 9–19
O. Al-Ketan, R.K. Abu Al-Rub, and R. Rowshan, Mechanical Properties of a New Type of Architected Interpenetrating Phase Composite Materials, Adv. Mater. Technol., 2017, 2(2), p 1600235
O. Al-Ketan, A. Soliman, A.M. AlQubaisi, and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Nature-Inspired Lightweight Cellular Co-Continuous Composites with Architected Periodic Gyroidal Structures, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2018, 20(2), p 1700549
K.A. Khan and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Time Dependent Response of Architectured Neovius Foams, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 2017, 126, p 106–119
K.A. Khan and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Modeling Time and Frequency Domain Viscoelastic Behavior of Architectured Foams, J. Eng. Mech., 2018, 144(6), p 04018029
D.-W. Lee, K.A. Khan, and R.K. Abu Al-Rub, Stiffness and Yield Strength of Architectured Foams Based on the Schwarz Primitive Triply Periodic Minimal Surface, Int. J. Plast., 2017, 95, p 1–20
F. Bobbert, K. Lietaert, A. Eftekhari, B. Pouran, S. Ahmadi, H. Weinans, and A. Zadpoor, Additively Manufactured Metallic Porous Biomaterials Based on Minimal Surfaces: A Unique Combination of Topological, Mechanical, and Mass Transport Properties, Acta Biomater., 2017, 53, p 572–584
I. Maskery, N.T. Aboulkhair, A.O. Aremu, C.J. Tuck, and I.A. Ashcroft, Compressive Failure Modes and Energy Absorption in Additively Manufactured Double Gyroid Lattices, Addit. Manuf., 2017, 16, p 24–29
L. Zhang, S. Feih, S. Daynes, S. Chang, M.Y. Wang, J. Wei, and W.F. Lu, Energy Absorption Characteristics of Metallic Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Sheet Structures Under Compressive Loading, Addit. Manuf., 2018, 23, p 505–515
A. Ataee, Y. Li, D. Fraser, G. Song, and C. Wen, Anisotropic Ti-6Al-4 V Gyroid Scaffolds Manufactured by Electron Beam Melting (EBM) for Bone Implant Applications, Mater. Des., 2018, 137, p 345–354
C. Han, Y. Li, Q. Wang, S. Wen, Q. Wei, C. Yan, L. Hao, J. Liu, and Y. Shi, Continuous Functionally Graded Porous Titanium Scaffolds Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting for Bone Implants, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater., 2018, 80, p 119–127
C. Yan, L. Hao, A. Hussein, S.L. Bubb, P. Young, and D. Raymont, Evaluation of Light-Weight AlSi10 Mg Periodic Cellular Lattice Structures Fabricated via Direct Metal Laser Sintering, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2014, 214(4), p 856–864
C. Yan, L. Hao, A. Hussein, and D. Raymont, Evaluations of Cellular Lattice Structures Manufactured Using Selective Laser Melting, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf, 2012, 62, p 32–38
C. Yan, L. Hao, A. Hussein, P. Young, and D. Raymont, Advanced Lightweight 316L Stainless Steel Cellular Lattice Structures Fabricated via Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Des., 2014, 55, p 533–541
A. Yánez, A. Cuadrado, O. Martel, H. Afonso, and D. Monopoli, Gyroid Porous Titanium Structures: A Versatile Solution to be Used as Scaffolds in Bone Defect Reconstruction, Mater. Des., 2018, 140, p 21–29
K. Michielsen and J. Kole, Photonic Band Gaps in Materials with Triply Periodic Surfaces and Related Tubular Structures, Phys. Rev. B, 2003, 68(11), p 115107
S. Van Bael, G. Kerckhofs, M. Moesen, G. Pyka, J. Schrooten, and J.-P. Kruth, Micro-CT-Based Improvement of Geometrical and Mechanical Controllability of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4 V Porous Structures, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528(24), p 7423–7431
M.E. Ashby, A.G. Evans, N.A. Fleck, L.J. Gibson, J.W. Hutchinson, H.N.G. Wadley, Chapter 3: Characterization Methods 2000, Metal Foams, p 24–39
I. Maskery, N.T. Aboulkhair, A.O. Aremu, C.J. Tuck, I.A. Ashcroft, R.D. Wildman, and R.J.M. Hague, A Mechanical Property Evaluation of Graded Density Al-Si10-Mg Lattice Structures Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 670, p 264–274
Acknowledgment
Experimental parts were printed using Core Technology Platform resources at NYU Abu Dhabi. We thank Khulood Alawadi and Jumaanah Elhashemi from NYU Abu Dhabi for assistance with 3D printing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abou-Ali, A.M., Al-Ketan, O., Rowshan, R. et al. Mechanical Response of 3D Printed Bending-Dominated Ligament-Based Triply Periodic Cellular Polymeric Solids. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 2316–2326 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-03982-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-03982-8