Abstract
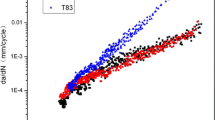
The texture evolution and fatigue crack propagation (FCP) of 2000 series alloys were investigated, respectively, by using scanning electron microscopy and x-ray diffraction. Results showed that the intensity change in different textures (such as Goss, Copper, S and Brass) abides by a linear evolution law, and a new model for texture evolution is proposed to predict the texture intensity during different heat treatments. With increasing annealing temperature, the FCP rate increased, but the damage tolerance decreased. The intensity of P texture was the key to affecting FCP rate and damage tolerance of the alloys. A new model based on the average grain diameter and P texture volume fraction was proposed to predict FCP rate and damage tolerance, and the predicted FCP rates agree very well with the experimental FCP rates of the alloys after different T83 treatments.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.I. Rodgers and P.B. Prangnell, Quantification of the Influence of Increased Pre-stretching on Microstructure-strength Relationships in the Al-Cu-Li Alloy AA2195, Acta Mater., 2016, 108, p 55–67
Y.J. Chen, J. Zhou, C.C. Liu, and F.S. Wang, Effect of Pre-deformation on the Pre-Corrosion Multiaxial Fatigue Behaviors of 2024-T4 Aluminum Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2018, 108, p 35–46
S.F. Zhang, W.D. Zeng, W.H. Yang, C.L. Shi, and H.J. Wang, Ageing Response of a Al-Cu-Li 2198 Alloy, Mater. Des., 2014, 63, p 368–374
M.R. Joyce, M.J. Starink, and I. Sinclair, Assessment of Mixed Mode Loading on Macroscopic Fatigue Crack Paths in Thick Section Al-Cu-Li Alloy Plate, Mater. Des., 2016, 93, p 379–387
N. Nayan, S.V.S.N. Murty, S. Chhangani, A. Prakash, M.J.N.V. Prasad, and I. Samajdar, Effect of Temperature and Strain Rate on Hot Deformation Behavior and Microstructure of Al-Cu-Li Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 723, p 548–558
P.S. De, R.S. Mishra, and J.A. Baumann, Characterization of High Cycle Fatigue Behavior of a New Generation Aluminum Lithium Alloy, Acta Mater., 2011, 59, p 5946–5960
F.D. Li, Z.Y. Liu, W.T. Wu, P. Xia, P.Y. Ying, Y.R. Zhou, W.J. Liu, L.Q. Lu, and A. Wang, Enhanced Fatigue Crack Propagation Resistance of Al-Cu-Mg Alloy by Intensifying Goss Texture and Refining Goss Grains, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 679, p 204–214
F.D. Li, Z.Y. Liu, W.T. Wu, Q. Zhao, Y.R. Zhou, S. Bai, X.H. Wang, and G.H. Fan, Slip Band Formation in Plastic Deformation Zone at Crack Tip in Fatigue Stage II, of 2xxx Aluminum Alloys, Int. J. Fatigue, 2016, 91, p 68–78
F.D. Li, Z.Y. Liu, W.T. Wu, P. Xia, P.Y. Ying, Q. Zhao, J.L. Li, S. Bai, and C.W. Ye, On the Role of Texture in Governing Fatigue Crack Propagation Behavior of 2524 Aluminum Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 669, p 367–378
Z.Y. Liu, F.D. Li, P. Xia, S. Bai, Y.X. Gu, D.E. Yu, and S.M. Zeng, Mechanisms for Goss-grains Induced Crack Deflection and Enhanced Fatigue Crack Propagation Resistance in Fatigue Stage II, of An A2524 Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 625, p 271–277
M. Liu, Z.Y. Liu, S. Bai, P. Xia, P.Y. Ying, and A. Wang, Analysis on the Dissolution Behavior of Various Size Cu-Mg Co-Clusters Near a Fatigue Crack Tip of Underaged Al-Cu-Mg Alloy During Cyclic Loading, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 699, p 119–125
M. Liu, Z.Y. Liu, S. Bai, P. Xia, P.Y. Ying, and S.M. Zeng, Solute Cluster Size Effect on the Fatigue Crack Propagation Resistance of an Underaged Al-Cu-Mg Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2016, 84, p 104–112
D.J. Morrison and J.C. Moosbrugger, Effects of Grain Size on Cyclic Plasticity and Fatigue Crack Initiation in Nickel, Int. J. Fatigue, 1997, 19, p 51–59
L. Venning, S.C. Hogg, I. Sinclair, and P.A.S. Reed, Fatigue Crack Growth and Closure in Fine-grained Aluminium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 428, p 247–255
Y. Estrin and A. Vinogradov, Fatigue Behaviour of Light Alloys with Ultrafine Grain Structure Produced by Severe Plastic Deformation: An Overview, Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, 32, p 898–907
X. Chen, Z.Y. Liu, M. Lin, A.L. Ning, and S.M. Zeng, Enhanced Fatigue Crack Propagation Resistance in An Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy by Retrogression and Reaging Treatment, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, 21, p 2345–2353
C. Watanabe, R. Monzen, and K. Tazaki, Effects of Al 3 Sc Particle Size and Precipitate-Free Zones on Fatigue Behavior and Dislocation Structure of an Aged Al-Mg-Sc Alloy, Int. J. Fatigue, 2008, 30, p 635–641
T.T. Huang, Q. Zhao, Z.Y. Liu, and S. Bai, Enhanced Damage Tolerance Through Reconstructing Residual Stress and Cu-Mg Co-Clusters by Pre-rolling in An Al-Cu-Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 700, p 241–249
W.T. Wu, Z.Y. Liu, Y.C. Hu, F.D. Li, S. Bai, P. Xia, A. Wang, and C.W. Ye, Goss Texture Intensity Effect on Fatigue Crack Propagation Resistance in an Al-Cu-Mg Alloy, J. Alloy. Compd., 2018, 730, p 318–326
C.L. Dong, H.C. Yu, Z.H. Jiao, F.T. Kong, and Y.Y. Chen, Low Cycle Fatigue, Creep and Creep-fatigue Interaction Behavior of a TiAl Alloy at High Temperatures, Scr. Mater., 2018, 144, p 60–63
Q. Zhao, Z.Y. Liu, T.T. Huang, P. Xia, and F.D. Li, Enhanced Fracture Toughness in an Annealed Al-Cu-Mg Alloy by Increasing Goss/Brass Texture Ratio, Mater. Charact., 2016, 119, p 47–54
Q. Zhao, Z.Y. Liu, S.S. Li, T.T. Huang, P. Xia, and L.Q. Lu, Evolution of the Brass Texture in An Al-Cu-Mg Alloy During Hot Rolling, J. Alloy. Compd., 2017, 691, p 786–799
F. Liu, Z.Y. Liu, M. Liu, Y.C. Hu, Y. Chen, and S. Bai, Analysis of Empirical Relation between Microstructure, Texture Evolution and Fatigue Properties of An Al-Cu-Li Alloy during Different Pre-deformation Processes, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, 726, p 309–319
J. Hjelen, R. Ørsund, and E. Nes, On the Origin of Recrystallization Textures in Aluminum, Acta Metall., 1991, 39, p 1377–1404
O. Engler, J. Hirsch, and K. Lücke, Texture Development in Al-1.8 wt.% Cu Depending on the Precipitation State—II. Recrystallization Textures, Acta Metall., 1995, 43, p 121–138
O. Daaland, P.E. Dronen, H.E. Vatne, S.E. Naess, and E. Nes, On the Growth Rate of Cube-, Rotated Cube- and Rotated Goss-Grains in Commercial Aluminium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Forum, 1993, 113, p 115–120
R. Becker and J.F. Butler, Analysis of an Aluminum Single Crystal with Unstable Initial Orientation (001) [110] in Channel Die Compression, Metall. Trans. A, 1991, 22, p 45–51
T. Leffers and R.K. Ray, The Brass-type Texture and Its Deviation from the Copper-type Texture, Prog. Mater Sci., 2009, 54, p 351–396
I.L. Dillamore and H. Katoh, The Mechanisms of Recrystallization in Cubic Metals with Particular Reference to Their Orientation-dependence, Met. Sci., 1974, 8, p 73–83
F.J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly, Recrystallization and Related Annealing Phenomena, Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 2004
F.J. Humphreys, The Nucleation of Recrystallization at Second Phase Particles in Deformed Aluminium, Acta Metall., 1977, 25, p 1323–1344
J. Hirsch, Texture and Anisotropy in Industrial Applications of Aluminum Alloys, Arch. Metall. Mater., 2005, 50, p 21–34
E.O. Hall, The Deformation and Ageing of Mild Steel: II, Characteristics of the Lüders Deformation, Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. B, 1951, 64, p 742–747
N.J. Petch, The Cleavage Strength of Polycrystals, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1953, 174, p 25–28
P. Paris and F. Erdogan, A Critical Analysis of Crack Propagation Laws, Trans. ASME Ser. D, 1963, 85, p 528–533
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0300900), the National Key Fundamental Research Project of China (2012CB619506-3) and Natural Science Foundation of China (51171209).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Liu, Z., Liu, M. et al. Texture Evolution and Its Effect on Fatigue Crack Propagation in Two 2000 Series Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 1324–1336 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-03894-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-03894-7