Abstract
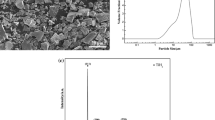
In this study, the effects of phase composition and hydrogen content on the compactibility of the titanium hydride powders are investigated. The crushing strength and the XRD patterns were performed. From the results of the green density, it is clear that the compressibility of the unsaturated hydride titanium powder is higher than that of TiH2. The results of the compression tests indicate that the crushing strength of unsaturated hydride titanium powder is markedly higher than that of the TiH2 and pure Ti. The relative mass fraction of each phase of the unsaturated hydride titanium powder was analyzed by Rietveld refinement of the XRD patterns. The phase composition with high compactibility of the unsaturated hydride titanium powder contains a lot of TiH1.5 and a small amount of α-Ti and TiH. There is a suitable range for each phase: TiH1.5 (70-73 wt.%), α-Ti (13-18 wt.%) and TiH (11-15 wt.%).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Ivasishin and V. Moxson, Low-cost titanium hydride powder metallurgy, Titanium Powder Metallurgy: Science, Technology and Applications, M. Qian and H.F. Froes, Ed., Butterworth Heinemann, Kidlington, 2015, p 117–148
V. Duz, M. Matviychuk, A. Klevtsov, and V. Moxson, Industrial Application of Titanium Hydride Powder, Met. Powder Rep., 2017, 72(1), p 30–38
Y. Zheng, X. Yao, Y. Su, and D.L. Zhang, High Strength Titanium with a Bimodal Microstructure Fabricated by Thermomechanical Consolidation of a Nanocrystalline TiH2 Powder, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2017, 686, p 11–18
I. Paulin, Synthesis and Characterization of Al Foams Produced by Powder Metallurgy Route Using Dolomite and Titanium Hydride as a Foaming Agents, Mater. Technol., 2014, 48(6), p 943–947
I.M. Robertson and G.B. Schaffer, Comparison of Sintering of Titanium and Titanium Hydride Powders, Powder Metall., 2010, 53(1), p 12–19
D.W. Lee, H.S. Lee, J.H. Park, S.M. Shin, and J.P. Wang, Sintering of Titanium Hydride Powder Compaction, Procedia Manuf., 2015, 2, p 550–557
V.V. Joshi, C. Lavender, V. Moxson, V. Duz, E. Nyberg, and K.S. Well, Development of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-1Al-8V-5Fe Alloys Using Low-Cost TiH2 Powder Feedstock, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(4), p 995–1003
Y.N. Zhang, C.M. Wang, Y.G. Zhang, P. Cheng, Y.H. Wei, S.F. Xiao, and Y.G. Chen, Fabrication of Low-Cost Ti-1Al-8V-5Fe by Powder Metallurgy with TiH2 and FeV80 Alloy, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2017, 32(16), p 1869–1873
O.M. Ivasishin, D.G. Savvakin, F.H. Froes, V.C. Mokson, and K.A. Bondareva, Synthesis of Alloy Ti-6Al-4V with Low Residual Porosity by a Powder Metallurgy Method, Powder. Metall. Met. C+, 2002, 41(7–8), p 382–390
O.M. Ivasishin, D. Eylon, V.I. Bondarchuk, and D.G. Savvakin, Diffusion During Powder Metallurgy Synthesis of Titanium Alloys, Defect. Diffus. Forum., 2008, 277, p 177–185
B. Sharma, S.K. Vajpai, and K. Ameyama, Preparation of Strong and Ductile Pure Titanium via Two-Step Rapid Sintering of TiH2 Powder, J. Alloys Compd., 2016, 683, p 51–55
C.M. Wang, Y.N. Zhang, S.F. Xiao, and Y.G. Chen, Sintering Densification of Titanium Hydride Powders, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2017, 32(5), p 517–522
C.M. Wang, L. Pan, Y.N. Zhang, S.F. Xiao, and Y.G. Chen, Deoxidization Mechanism of Hydrogen in TiH2 Dehydrogenation Process, Int. J. Hydrog. Eng., 2016, 41(33), p 14836–14841
C.M. Wang, Y.G. Zhang, Y.H. Wei, L.B. Mei, S.F. Xiao, and Y.G. Chen, XPS Study of the Deoxidization Behavior of Hydrogen in TiH2 Powders, Powder Technol., 2016, 302, p 423–425
O.D. Neikov, D.V. Lotsko, and V.G. Gopienko, Powder Characterization and Testing, Handbook of Non-ferrous Metal Powders, O.D. Neikov, S.S. Naboychenko, and G. Dowson, Ed., Elsevier, Oxford, 2009, p 7–44
S. Lampman, Compressibility and Compactibility of Metal Powders, ASM Handbook, Vol. 7—Powder Metal Technologies and Applications (ASM International, 1998), pp. 704–716
K.A. Nazari, A. Nouri, and T. Hilditch, Compressibility of a Ti-Based Alloy with Varying Amounts of Surfactant Prepared by High-Energy Ball Milling, Powder Technol., 2015, 279, p 33–41
Z.Z. Fang, J.D. Paramore, P. Sun, K.S.R. Chandran, and Y. Zhang, Powder Metallurgy of Titanium—Past, Present, and Future, Int. Mater. Rev., 2017, 63, p 407–459
J. Capus, Titanium Powder Metallurgy at POWDERMET 2015: Past, Present and Future, Met. Powder Rep., 2016, 71(1), p 25–27
M. Qian, Some New Development in Titanium Powder Metallurgy, Int. J. Powder. Metall., 2011, 47(6), p 47–48
C. Machio, R. Mahaka, and H.K. Chikwanda, Consolidation of Titanium Hydride Powders During the Production of Titanium PM Parts: The Effect of Die Wall Lubricants, Mater. Des., 2016, 90, p 757–766
H. Leuenberger, The Compressibility and Compactibility of Powder Systems, Int. J. Pharm., 1982, 12(1), p 41–55
L. Bolzonia, E.M. Ruiz-Navasb, and E. Gordo, Quantifying the Properties of Low-Cost Powder Metallurgy Titanium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 687, p 47–53
L. Bolzonia, E.M. Ruiz-Navasb, and E. Gordo, Understanding the Properties of Low-Cost Iron-Containing Powder Metallurgy Titanium Alloys, Mater. Des., 2016, 110, p 317–323
W. Schatt and K.P. Wieters, Powder Metallurgy, Processing and Materials, EPMA-European Powder Metallurgy Association, Brussels, 1997, p 61–65
I. Paulin, B. Šuštaršič, V. Kevorkijan, S.D. Škapin, and M. Jenko, Synthesis of Aluminium Foams by the Powder-Metallurgy Process: Compacting of Precursors, Mater. Tehnol., 2011, 45(1), p 13–19
S. Verma, S. Rani, S. Kumar, and M.A.M. Khan, Rietveld Refinement, Micro-structural, Optical and Thermal Parameters of Zirconium Titanate Composites, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(2), p 1653–1661
X. Zhou, D. Liu, H.L. Bu, L.L. Deng, H.M. Liu, P. Yuan, P.X. Du, and H.Z. Song, XRD-Based Quantitative Analysis of Clay Minerals Using Reference Intensity Ratios, Mineral Intensity Factors, Rietveld, and Full Pattern Summation Methods: A Critical Review, Solid. Earth. Sci., 2018, 3(1), p 16–29
S.D. Luo, Y.F. Yang, G.B. Schaffer, and M. Qian, Warm Die Compaction and Sintering of Titanium and Titanium Alloy Powders, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2014, 214(3), p 660–666
A. Hadadzadeh, M.A. Whitney, M.A. Wells, and S.F. Corbin, Analysis of Compressibility Behavior and Development of a Plastic Yield Model for Uniaxial Die Compaction of Sponge Titanium Powder, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, 243, p 92–99
S. Chikosha, T.C. Shabalala, and H.K. Chikwanda, Effect of Particle Morphology and Size on Roll Compaction of Ti-Based Powders, Powder Technol., 2014, 264, p 310–319
M.T. Jia and D.L. Zhang, Warm compaction of titanium and titanium alloy powders, Titanium Powder Metallurgy: Science, Technology and Applications, M. Qian and H.F. Froes, Ed., Butterworth Heinemann, Kidlington, 2015, p 183–200
Y.G. Zhang, C.M. Wang, Y. Liu, S.P. Liu, S.F. Xiao, and Y.G. Chen, Surface Characterizations of TiH2 Powders Before and After Dehydrogenation, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 410, p 177–185
I. Paulin, C. Donik, D. Mandrino, M. Vončina, and M. Jenko, Surface Characterization of Titanium Hydride Powder, Vacuum, 2011, 86(6), p 608–613
T.M. Marcelo, V. Livramento, M.V. de Oliveira, and M.H. Carvalho, Microstructural Characterization and Interactions in Ti- and TiH2-Hydroxyapatite Vacuum Sintered Composites, Mat. Res., 2006, 9(1), p 65–71
C. Jiménez, F. Garcia-Moreno, B. Pfretzschner, M. Klaus, M. Wollgarten, I. Zizak, G. Schumacher, M. Tovar, and J. Banhart, Decomposition of TiH2 Studied In Situ by Synchrotron X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction, Acta Mater., 2011, 59(16), p 6318–6330
G. Chen, K.D. Liss, G. Auchterlonie, H. Tang, and P. Cao, Dehydrogenation and Sintering of TiH2: An In Situ Study, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, 48(6), p 2949–2959
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Wang, C., Zhang, Y. et al. The Compactibility of Unsaturated Titanium Hydride Powders. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 5752–5761 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3659-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3659-1