Abstract
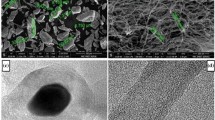
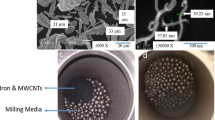
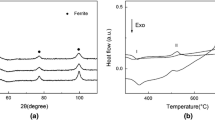
High-energy ball milling (HEBM) of mixtures of iron powder and multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) has been performed in an attempt to synthesize nano-grained steel. Even after exposure to a harsh HEBM conditions, the MWCNTs are seen to have retained their structural identity, and therefore, an MWCNT-reinforced steel matrix composite could be finally produced. Moreover, the study has revealed that the minor addition of copper leads to a significant reduction in grain size of ferrite in the so-produced steel matrix–MWCNT composite. It is also noticed that the fine grain structure of ferrite remains intact even after consolidation of the powder composite by spark plasma sintering, followed by hot forging. The micro-hardness values obtained for the composites (with/without copper) are observed as comparable with the submicron-grained steels, so far reported in the literature.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Rashad, F. Pan, A. Tang, and M. Asif, Effect of Graphene Nanoplatelets Addition on Mechanical Properties of Pure Aluminum Using a Semi-Powder Method, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 2014, 24, p 101–108
M. Rashad, F. Pan, Z. Yu, M. Asif, H. Lin, and R. Pan, Investigation on Microstructural, Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties of Aluminum Composites Reinforced with Graphene Nanoplatelets, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int., 2015, 25, p 460–470
E.T. Thostenson, Z. Rez, and T.-W. Chou, Advances in the Science and Technology of Carbon Nanotubes and Their Composites: A Review, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2001, 61, p 1899–1912
W. Zhou, T. Yamaguchi, K. Kikuchi, N. Nomura, and A. Kawasaki, Effectively Enhanced Load Transfer by Interfacial Reactions in Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Al Matrix Composites, Acta Mater., 2017, 125, p 369–376
A. Kumar, M.K. Banerjee, and U. Pandel, Development of a Novel MWCNT Reinforced Iron Matrix Nanocomposite Through Powder Metallurgy Route, Powder Technol., 2018, 331, p 41–51
N. Silvestre, State-of-the-art Review on Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Int. J. Compos. Mater., 2013, 3(6A), p 28–44
K.S. Munir, Y. Li, M. Qian, and C. Wen, Identifying and Understanding the Effect of Milling Energy on the Synthesis of Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Titanium Metal Matrix Composites, Carbon, 2016, 99, p 384–397
B. Chen, J. Shen, X. Ye, H. Imai, J. Umeda, M. Takahashi, and K. Kondoh, Solid-State Interfacial Reaction and Load Transfer Efficiency in Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)-Reinforced Aluminum Matrix Composites, Carbon, 2017, 114, p 198–208
A. Singh, T.R. Prabhu, A.R. Sanjay, and V. Koti, An Overview of Processing and Properties of CU/CNT Nano Composites, Mater. Today Proc., 2017, 4, p 3872–3881
N. Nayan, A.K. Shukla, P. Chandran, S.R. Bakshi, S.V.S.N. Murty, B. Pant, and P.V. Venkitakrishnan, Processing and Characterization of Spark Plasma Sintered Copper/Carbon Nanotube Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2017, 682(229-237), p 229–237
T. Varol and A. Canakci, Effect of the CNT Content on Microstructure, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cu-Based Electrical Contact Materials Produced by Flake Powder Metallurgy, Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2015. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1734-6
A.M.K. Esawi and M.M. Farag, Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Composites: Potential and Current Challenges, Mater. Des., 2007, 28, p 2394–2401
S.R. Bakshi, D. Lahiri, and A. Agarwal, Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites—A Review, Int. Mater. Rev., 2010, 55, p 41–64
I. Lahiri and S. Bhargava, Compaction and Sintering Response of Mechanically Alloyed Cu–Cr Powder, Powder Technol., 2009, 189, p 395–528
T. Kuzumaki, O. Ujiie, H. Ichinose, and K. Ito, Mechanical Characteristics and Preparation of Carbon Nanotube Fiber-Reinforced Ti Composite, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2000, 2, p 416–418
R.P. Bustamante, I.E. Guel, W.A. Flores, M.M. Yoshida, P.J. Ferreira, and R.M. Sánchez, Novel Al-Matrix Nanocomposites Reinforced with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, 450, p 323–326
W.J. Kim and S.H. Lee, High Temperature Deformation Behavior of Carbon Nanotube (CNT)-Reinforced Aluminum Composites and Prediction of Their High-Temperature Strength, Compos. A, 2014, 67, p 308–315
A. Kumar, U. Pandel, and M.K. Banerjee, Effect of High Energy Ball Milling on the Structure of Iron—Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNT) Composite, Adv. Mater. Res., 2017, 6, p 245–255
C. Edtmaier, E. Wallnoefer, A. Koeck, in Proceedings of PM 2004, Vienna, Austria, 2004
Z. Tao, H. Geng, K. Yu, Z. Yang, and Y. Wang, Effect of High-Energy Ball Milling on the Morphology and the Field Emission Property of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58, p 3410–3413
C.F. Deng, D.Z. Wang, X.X. Zhang, and A.B. Li, Processing and Properties of Carbon Nanotubes Reinforced Aluminum Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2007, 444, p 138–145
S. Praveen, B.S. Murty, and R.S. Kottada, Alloying Behavior in Multi-Component AlCoCrCuFe and NiCoCrCuFe High Entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 534, p 83–89
K.S. Munir, M. Qian, Y. Li, D.T. Oldfield, P. Kingshott, D.M. Zhu, and C. Wen, Quantitative Analyses of MWCNT-Ti Powder Mixtures Using Raman Spectroscopy: The Influence of Milling Parameters on Nanostructural Evolution, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2015, 17, p 1660–1669
S. Simões, F. Viana, M.A.L. Reis, and M.F. Vieira, Improved Dispersion of Carbon Nanotubes in Aluminum Nanocomposites, Compos. Struct., 2014, 108, p 992–1000
A.A. Tohidi, M. Ketabchi, and A. Hasannia, Nanograined Ti–Nb Microalloy Steel Achieved by Accumulative Roll Bonding (ARB) Process, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, 577, p 43–47
Y. Fukuda, K. Oh-ishi, Z. Horita, and T.G. Langdon, Processing of a Low-Carbon Steel by Equal Channel Angular Pressing, Acta Mater., 2002, 50, p 1359–1368
F. Saba, S.A. Sajjadi, M.H. Sabzevar, and F. Zhang, Formation Mechanism of Nano Titanium Carbide on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube and Influence of the Nanocarbides on the Load-Bearing Contribution of the Nanotubes Inner-Walls in Aluminum-Matrix Composites, Carbon, 2017, 115, p 720–729
M. Barzegar and A.A. Vishlaghi, Investigation on Solid Solubility and Physical Properties of Cu–Fe/CNT Nano-Composite Prepared via Mechanical Alloying Route, J. Ultrafine Grained Nanostruct. Mater., 2014, 47, p 37–42
P. Delhaes, M. Couzi, M. Trinquecoste, J. Dentzer, H. Hamidou, and C. Vix-Guterl, A Comparison Between Raman Spectroscopy and Surface Characterizations of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon, 2006, 44, p 3005–3013
J.H. Lehman, M. Terrones, E. Mansfield, K.E. Hurst, and V. Meunier, Evaluating the Characteristics of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes, Carbon, 2011, 49, p 2581–2602
N.S. Anas, R.K. Dash, T.N. Rao, and R. Vijay, Effect of Carbon Nanotubes as Reinforcement on the Mechanical Properties of Aluminum-Copper-Magnesium Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(7), p 3376–3386
L. Wu, R. Wu, L. Hou, J. Zhang, J. Sun, and M. Zhang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CNT-Reinforced AZ31 Matrix Composites Prepared Using Hot-Press Sintering, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(11), p 5495–5500
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Materials Research Centre (Malaviya National Institute of Technology, Jaipur, India) for providing the characterization facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P., Kumar, A. & Banerjee, M.K. Structural Evolution in Mechanically Alloyed and Spark Plasma Sintered Iron–0.15 wt.% MWCNT Composite. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 4740–4748 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3547-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3547-8