Abstract
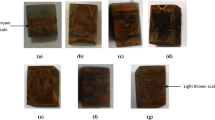
The corrosion behavior of newly developed API X120 C-steel that is commenced to be used for oil pipelines was studied in a H2S saturated 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution between 20 and 60 °C using potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy techniques. The corrosion products formed on the surface of the alloy were characterized using x-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. It has been noticed that the formation of corrosion product layer takes place at both lower and higher temperatures which is mainly comprised of iron oxides and sulfides. The electrochemical results confirmed that the corrosion rate decreases with increasing temperature up to 60 °C. This decrease in corrosion rate with increasing temperature can be attributed to the formation of a protective layer of mackinawite layer. However, cracking in the formed mackinawite layer may not be responsible for the increase in the corrosion rate. More specifically, developed pourbaix diagrams at different temperatures showed that the formed protective layer belongs to mackinawite (FeS), a group of classified polymorphous iron sulfide, which is in good agreement with the experimental results. It is also noticed that the thickness of corrosion products layer increases significantly with decrease in the corrosion rate of API X120 steel exposed to H2S environment. These findings indicate that API X120 C-steel is susceptible to sour corrosion under the above stated experimental conditions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Igi, T. Sakimoto, and S. Endo, Effect of Internal Pressure on Tensile Strain Capacity of X80 Pipeline, Proc. Eng., 2011, 10, p 1451–1456
N. Jones and R.S. Birch, Influence of Internal Pressure on the Impact Behavior of Steel Pipelines, J. Press. Vessel Technol., 1996, 118(4), p 464–471
M.-C. Zhao, B. Tang, Y.-Y. Shan, and K. Yang, Role of Microstructure on Sulfide Stress Cracking of Oil and Gas Pipeline Steels, MMTA, 2003, 34(5), p 1089–1096
A. Hernández-Espejel, M.A. Domínguez-Crespo, R. Cabrera-Sierra, C. Rodríguez-Meneses, and E.M. Arce-Estrada, Investigations of Corrosion Films Formed on API-X52 Pipeline Steel in Acid Sour Media, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(7), p 2258–2267
H.F. López, R. Raghunath, J.L. Albarran, and L. Martinez, Microstructural Aspects of Sulfide Stress Cracking in an API, X-80 Pipeline Steel, MMTA, 1996, 27(11), p 3601–3611
F. Nasirpouri, A. Mostafaei, L. Fathyunes, and R. Jafari, Assessment of Localized Corrosion in Carbon Steel Tube-Grade AISI, 1045 used in Output Oil–Gas Separator Vessel of Desalination Unit in Oil Refinery Industry, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2014, 40, p 75–88
M.A. Lucio-Garcia, J.G. Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M. Casales, L. Martinez, J.G. Chacon-Nava, M.A. Neri-Flores, and A. Martinez-Villafañe, Effect of Heat Treatment on H2S Corrosion of a Micro-alloyed C-Mn Steel, Corros. Sci., 2009, 51(10), p 2380–2386
Y. Qi, H. Luo, S. Zheng, C. Chen, Z. Lv, and M. Xiong, Effect of Temperature on the Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel in Hydrogen Sulphide Environments, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2014, 9, p 2101–2112
M. Liu, J. Wang, W. Ke, and E.-H. Han, Corrosion Behavior of X52 Anti-H2S Pipeline Steel Exposed to High H2S Concentration Solutions at 90 °C, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, 30(5), p 504–510
P.C. Okonkwo and A.M.A. Mohamed, Erosion-Corrosion in Oil and Gas Industry: A Review, Int. J. Metall. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2014, 4(3), p 7–28
Z.F. Yin, W.Z. Zhao, Z.Q. Bai, Y.R. Feng, and W.J. Zhou, Corrosion Behavior of SM 80SS Tube Steel in Stimulant Solution Containing H2S and CO2, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53(10), p 3690–3700
H. Vedage, T.A. Ramanarayanan, J.D. Mumford, and S.N. Smith, Electrochemical Growth of Iron Sulfide Films in H2S-Saturated Chloride Media, Corrosion, 1993, 49(2), p 114–121
P. Bai, S. Zheng, and C. Chen, Electrochemical Characteristics of the Early Corrosion Stages of API, X52 Steel Exposed to H2S Environments, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2015, 149–150, p 295–301
M. Schulte and M. Schutze, The Role of Scale Stresses in the Sulfidation of Steels, Oxid. Met., 1999, 51(1–2), p 55–77
P.C. Okonkwo, E. Ahmed, and A.M.A. Mohamed, Effect of Temperature on the Corrosion Behavior of API, X80 Steel Pipeline, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2015, 10(12), p 10246–10260
E. Sosa, R. Cabrera-Sierra, M.E. Rincón, M.T. Oropeza, and I. González, Evolution of Non-stoichiometric Iron Sulfide Film Formed by Electrochemical Oxidation of Carbon Steel in Alkaline Sour Environment, Electrochim. Acta, 2002, 47(8), p 1197–1208
R.A. Carneiro, R.C. Ratnapuli, and V. de Freitas Cunha Lins, The Influence of Chemical Composition and Microstructure of API, Linepipe Steels on Hydrogen Induced Cracking and Sulfide Stress Corrosion Cracking, Mat. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 357(1–2), p 104–110
N.s. TM0284-2003, Evaluation of Pipeline and Pressure Vessel Steels for Resistance to Hydrogen-induced Cracking. NACE International
A. Davoodi, M. Pakshir, M. Babaiee, and G.R. Ebrahimi, A Comparative H2S Corrosion Study of 304L and 316L Stainless Steels in Acidic Media, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53(1), p 399–408
A.B. Radwan, A.M.A. Mohamed, A.M. Abdullah, and M.A. Al-Maadeed, Corrosion Protection of Electrospun PVDF–ZnO Superhydrophobic Coating, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2016, 289, p 136–143
H.-H. Huang, W.-T. Tsai, and J.-T. Lee, Electrochemical Behavior of the Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of A516 Carbon Steel in H2S Solution, Electrochim. Acta, 1996, 41(7–8), p 1191–1199
J. Tang, Y. Shao, J. Guo, T. Zhang, G. Meng, and F. Wang, The Effect of H2S Concentration on the Corrosion Behavior of Carbon Steel at 90 °C, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(6), p 2050–2058
B. Rutkowski, A. Gil, and A. Czyrska-Filemonowicz, Microstructure and Chemical Composition of the Oxide Scale Formed on the Sanicro 25 Steel Tubes After Fireside Corrosion, Corros. Sci., 2016, 102, p 373–383
W. Zhao, Y. Zou, K. Matsuda, and Z. Zou, Characterization of the Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide on the Corrosion of X80 Pipeline Steel in Saline Solution, Corros. Sci., 2016, 102, p 455–468
P. Bai, H. Zhao, S. Zheng, and C. Chen, Initiation and Developmental Stages of Steel Corrosion in Wet H2S Environments, Corros. Sci., 2015, 93, p 109–119
P. Atempa-Rosiles, M. Díaz-Cruz, J.L. González-Velázquez, J.G. Godínez-Salcedo, Y.A. Rodríguez-Arias, and R. Macías-Salinas, Simulation of Turbulent Flow of a Rotating Cylinder Electrode and Evaluation of its Effect on the Surface of Steel API, 5L X-56 During the Rate of Corrosion in Brine Added with Kerosene and H2S, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2014, 9, p 4805–4815
H. Tamura, The Role of Rusts in Corrosion and Corrosion Protection of Iron and Steel, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50(7), p 1872–1883
D.W. Shoesmith, P. Taylor, M.G. Bailey, and D.G. Owen, The Formation of Ferrous Monosulfide Polymorphs during the Corrosion of Iron by Aqueous Hydrogen Sulfide at 21 °C, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1980, 127(5), p 1007–1015
R.A. King, J.D.A. Miller, and J.S. Smith, Corrosion of Mild Steel by Iron Sulphides, Br. Corros. J., 1973, 8(3), p 137–141
D. Rickard, Metastable Sedimentary Iron Sulfides, Dev. Sedimentol., 2012, 65(1), p 195–231
P. Bai, S. Zheng, C. Chen, and H. Zhao, Investigation of the Iron–Sulfide Phase Transformation in Nanoscale, Cryst. Growth Des., 2014, 14(9), p 4295–4302
A. Solehudin, I. Nurdin, M. Agma, and W. Suratno, EIS Study of Temperature and H2S Concentration Effect on API, 5LX65 Carbon Steel Corrosion in Chloride Solution, J. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2011, 1.4(A), p 496–505
H. Ma, X. Cheng, G. Li, S. Chen, Z. Quan, S. Zhao, and L. Niu, The Influence of Hydrogen Sulfide on Corrosion of Iron Under Different Conditions, Corros. Sci., 2000, 42(10), p 1669–1683
A.G. Wikjord, T.E. Rummery, F.E. Doern, and D.G. Owen, Corrosion and Deposition During the Exposure of Carbon Steel to Hydrogen Sulphide–Water Solutions, Corros. Sci., 1980, 20(5), p 651–671
B.W.A. Sherar, I.M. Power, P.G. Keech, S. Mitlin, G. Southam, and D.W. Shoesmith, Characterizing the Effect of Carbon Steel Exposure in Sulfide Containing Solutions to Microbially Induced Corrosion, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53(3), p 955–960
R.T. Lowson, Aqueous Oxidation of Pyrite by Molecular Oxygen, Chem. Rev., 1982, 82(5), p 461–497
M. Bonis and J.-L. Crolet, Practical Aspects of the Influence of in situ pH on H2S-Induced Cracking, Corros. Sci., 1987, 27(10–11), p 1059–1070
N. Yaakob, S. Marc, and D. Young, Top of the Line Corrosion Behavior in Highly Sour Environments: Effect of the Gas/Steel Temperature. CORROSION/2014ed., 2014
J.Y. Wang, Q.C. Guan, J.Q. Wei, M. Wang, and Y.G. Liu, Growth and Characterization of Cubic KTa1-x Nb x O3 Crystals. J. Cryst. Growth, 1992, 116(1), p 27–36
J. Chivot, L. Mendoza, C. Mansour, T. Pauporté, and M. Cassir, New Insight in the Behaviour of Co–H2O System at 25-150 °C, Based on REVISED POURBAIX Diagrams, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50(1), p 62–69
A. Rojas-Hernández, M.T. Ramírez, J.G. Ibáñez, and I. González, Construction of Multicomponent Pourbaix Diagrams Using Generalized Species, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1991, 138(2), p 365–371
P. Marcus and E. Protopopoff, Potential-pH Diagrams for Adsorbed Species: Application to Sulfur Adsorbed on Iron in Water at 25° and 300 °C, J. Electrochem. Soc., 1990, 137(9), p 2709–2712
J. Li and P.W. Carr, Effect of Temperature on the Thermodynamic Properties, Kinetic Performance, and Stability of Polybutadiene-Coated Zirconia, Anal. Chem., 1997, 69(5), p 837–843
Y. Li, R.A. van Santen, and T. Weber, High-Temperature FeS–FeS2 Solid-State Transitions: Reactions of Solid Mackinawite with Gaseous H2S, J. Solid State Chem., 2008, 181(11), p 3151–3162
J. Ning, Y. Zheng, B. Brown, D. Young, and S. Nesic, Construction and Verification of Pourbaix Diagrams for Hydrogen Sulfide Corrosion of Mild Steel. NACE International Corrosion ed., 2015
D. Abayarathna , A.R. Naraghi, and S. Wang, The Effect of Surface Films on Corrosion of Carbon Steel in a CO2–H2S–H2O System, Corrosion/2005.Houston:NACE, 2005
J. Ning, Y. Zheng, B. Brown, D. Young, and S. Nesic, Construction and Verification of Pourbaix Diagrams for Hydrogen Sulfide Corrosion of Mild Steel. In NACE International Corrosion 2015 Conference and Expo, 2015, p. 5507
Acknowledgment
This publication was made possible by NPRP Grant 6-027-2-010 from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of the Qatar Foundation). Statements made herein are solely the responsibility of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okonkwo, P.C., Sliem, M.H., Shakoor, R.A. et al. Effect of Temperature on the Corrosion Behavior of API X120 Pipeline Steel in H2S Environment. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 3775–3783 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2834-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2834-0