Abstract
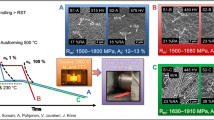
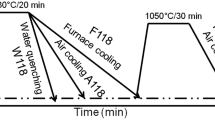
A systematic study has been carried out to ascertain the effect of cooling rate on structure and mechanical properties of eutectoid steel subjected to a novel incomplete austenitization-based cyclic heat treatment process up to 4 cycles. Each cycle consists of a short-duration holding (6 min) at 775 °C (above A1) followed by cooling at different rates (furnace cooling, forced air cooling and ice-brine quenching). Microstructure and properties are found to be strongly dependent on cooling rate. In pearlitic transformation regime, lamellar disintegration completes in 61 h and 48 min for cyclic furnace cooling. This leads to a spheroidized structure possessing a lower hardness and strength than that obtained in as-received annealed condition. On contrary, lamellar disintegration does not occur for cyclic forced air cooling with high air flow rate (78 m3 h−1). Rather, a novel microstructure consisting of submicroscopic cementite particles in a ‘interweaved pearlite’ matrix is developed after 4 cycles. This provides an enhancement in hardness (395 HV), yield strength (473 MPa) and UTS (830 MPa) along with retention of a reasonable ductility (%Elongation = 19) as compared to as-received annealed condition (hardness = 222 HV, YS = 358 MPa, UTS = 740 MPa, %Elongation = 21).












Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Grange, Strengthening by Austenite Grain Refinement, Trans. Am. Soc. Met., 1966, 1, p 26–29
A. Anashkin et al., Heat Cycling of Carbon Steel Wire, Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 1987, 2, p 10–14
O.E. Cullen, Continuous Short-Cycle Anneal for Spheroidization of Cartridge-Case Steel, Met. Prog., 1953, 64, p 79–82
P. Payson, W.L. Hadapp, and J. Leeder, The Spheroidizing of Steel by Isothermal Transformation, Trans. Am. Soc. Met., 1940, 28, p 306–332
Y.L. Tian and R.W. Kraft, Mechanisms of Pearlite Spheroidization, Metall. Trans. A, 1987, 18A, p 1403–1414
D.K. Mondal and R.M. Dey, Effect of Structures on the Response to Spheroidization in a Eutectoid Plain Carbon Steel, Trans. IIM, 1984, 37, p 351–356
V. Sista, P. Nash, and S.S. Sahay, Accelerated Bainitic Transformation During Cyclic Austempering, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42, p 9112–9115
A. Saha, D.K. Mondal, K. Biswas, and J. Maity, Microstructural Modifications and Changes in Mechanical Properties During Cyclic Heat Treatment of 0.16% Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 534, p 465–475
A. Saha, D.K. Mondal, and J. Maity, Effect of Cyclic Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 0.6 wt% Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 4001–4007
A. Saha, D.K. Mondal, and J. Maity, An Alternate Approach to Accelerated Spheroidization in Steel by Cyclic Annealing, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2011, 20, p 114–119
J. Maity, A. Saha, D.K. Mondal, and K. Biswas, Mechanism of Accelerated Spheroidization of Steel During Cyclic Heat Treatment Around Upper Critical Temperature, Philos. Mag. Lett. Taylor & Francis, 2013, 93, p 231–237
A. Saha, D.K. Mondal, K. Biswas, and J. Maity, Development of High Strength Ductile Hypereutectoid Steel by Cyclic Heat Treatment Process, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 541, p 204–215
A. Mishra and J. Maity, Structure-Property Correlation of AISI, 1080 Steel Subjected to Cyclic Quenching Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 646, p 169–181
H.L. Yi, Z.Y. Hou, Y.B. Xu, D. Wu, and G.D. Wang, Acceleration of Spheroidization in Eutectoid Steels by the Addition of Aluminum, Scr. Mater., 2012, 67, p 645–648
Z.Q. Lv, B. Wang, Z.H. Wang, S.H. Sun, and W.T. Fu, Effect of Cyclic Heat Treatments on Spheroidizing Behavior of Cementite in High Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 574, p 143–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maji, S., Subhani, A.R., Show, B.K. et al. Effect of Cooling Rate on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Eutectoid Steel Under Cyclic Heat Treatment. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 3058–3070 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2779-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2779-3