Abstract
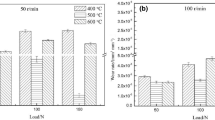
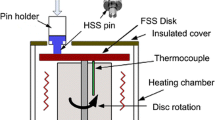
Sliding wear tests were performed for H13 steel in atmosphere, distilled water, 3.5% NaCl, and 5% NaOH water solutions under various loads on a pin-on-disk wear tester. The results showed that for different environmental media, the wear rate of H13 steel in atmosphere was the maximum and that in 3.5% NaCl solution was the minimum. The maximum wear rate in atmosphere was caused by a larger quantity of heat produced in the friction process. In this case, the adhesive wear prevailed. In three wet environments, the mild wear prevailed due to the good lubrication and cooling capacity of media as well as corrosion product film on worn surface. In distilled water, the wear mechanism was a typical fatigue wear. On the other hand, in 3.5% NaCl and 5% NaOH solutions, corrosive wear prevailed. The minimum wear rate in 3.5% NaCl solution was attributed to the protective function of corrosion product film. On the contrary, noncompact corrosion product film in 5% NaOH solution resulted in higher wear rate.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.W. Stschowiak and A.W. Batchelor, Engineering Tribology, Tribol. Ser., 1993, 24, p 872
W.J. Schumacher, Corrosive Wear Principle, Mater. Perform., 1993, 32(7), p 50
N. Diomidis, J.P. Celis, P. Ponthiaux, and F. Wenger, Tribocorrosion of Stainless Steel in Sulfuric Acid: Identification of Corrosion-wear Components and Effect of Contact Area, Wear, 2010, 269(1), p 93–103
Y.L. Huang, I.N.A. Oguocha, and S. Yannacopoulos, The Corrosion Wear Behavior of Selected Stainless Steels in Potash Brine, Wear, 2005, 258(9), p 1357–1363
X.Y. Wang and D.Y. Li, Application of An Electrochemical Scratch Technique to Evaluate Contributions of Mechanical and Electrochemical Attacks to Corrosive Wear of Materials, Wear, 2005, 259(7), p 1490–1496
F.J. He, Y.Z. Fang, and S.J. Jin, The Study of Corrosion-wear Mechanism of Ni-W-P Alloy, Wear, 2014, 311(1), p 14–20
J. Chen, Q. Zhang, Q.A. Li, S.L. Fu, and J.Z. Wang, Corrosion and Tribocorrosion Behaviors of AISI, 316 Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4 V Alloys in Artificial Seawater, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2014, 24(4), p 1022–1031
M.R. Bateni, J.A. Szpunar, X. Wang, and D.Y. Li, Wear and Corrosion Wear of Medium Carbon Steel and 304 Stainless Steel, Wear, 2006, 260(1), p 116–122
S.B. Yin and D.Y. Li, Corrosion and Corrosive Wear of Annealed, Impact-fractured and Slow Bending-fractured Surface Layers of AISI, 1045 Steel in a 3.5% NaCl Solution, Wear, 2005, 259(1), p 383–390
L. Fedrizzi, S. Rossi, F. Bellei, and F. Deflorian, Wear-corrosion Mechanism of Hard Chromium Coatings, Wear, 2002, 256(11), p 1173–1181
P.A. Dearnley and B. Mallia, The Chemical Wear of Novel Cr Based Hard Coated 316L Austenitic Stainless Steels in Aqueous Saline Solution, Wear, 2013, 306(1), p 263–275
Y. Sun and E. Haruman, Tribocorrosion Behavior of Low Temperature Plasma Carburized 316L Stainless Steel in 0.5 M NaCl Solution, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, p 4131–4140
A. Medvedeva, J. Bergstrob, S. Gunnarssona, and J. Anderssona, High-temperature Properties and Microstructural Stability of Hot-work Tool Steels, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 523(1), p 39–46
M.X. Wei, S.Q. Wang, L. Wang, X.H. Cui, and K.M. Chen, Effect of Tempering Conditions on Wear Resistance in Various Wear Mechanisms of H13 Steel, Tribol. Int., 2011, 44(7), p 898–905
S.Q. Wang, M.X. Wei, F. Wang, and Y.T. Zhao, Transition of Elevated-temperature Wear Mechanisms and the Oxidative Delamination Wear in Hot-working Die Steels, Tribol. Int., 2010, 43(3), p 577–584
S.H. Chang, Y.K. Lin, and K.T. Huang, Study on the Thermal Erosion, Wear and Corrosion Behaviors of TiAlN/oxynitriding Duplex-treated AISI, H13 Alloy Steel, Surf. Coat. Tech., 2012, 207, p 571–578
E. McCafferty, Validation of Corrosion Rates Measured by the Tafel Extrapolation Method, Corros. Sci., 2005, 47(12), p p3202–p3215
T.C. Zhang, X.X. Jiang, S.Z. Li, and X.C. Lu, A Quantitative Estimation of the Synergy Between Corrosion and Abrasion, Corros. Sci., 1994, 36(12), p 1953–1962
J.F. Achard and W. Hirst, The Wear of Metals Under Unlubricated Conditions, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A, 1956, 236, p 397–410
N.P. Suh, The Delamination Theory of Wear, Wear, 1973, 25(1), p 111–124
X.X. Jiang, Z.S. Li, and S. Li, Corrosive Wear of Metals, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2003
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the support from the Graduate Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, PR China (No. CXLX13_C652), the Natural Scientific Foundation of Education Department of Jiangsu Province, PR China (No. 13KJD430004) as well as the Scientific Research Found Project of Suqian College, PR China (No. 2015KY28).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhou, Y., Cao, H. et al. Wear Behavior and Mechanism of H13 Steel in Different Environmental Media. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 4134–4144 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2223-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2223-0