Abstract
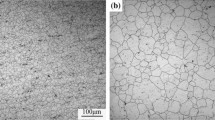
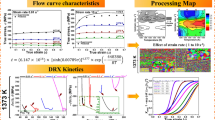
Hot compression tests were performed to study the hot deformation characteristics of 13Cr-4Ni stainless steel. The tests were performed in the strain rate range of 0.001-10 s−1 and temperature range of 900-1100 °C using Gleeble® 3800 simulator. A constitutive equation of Arrhenius type was established based on the experimental data to calculate the different material constants, and average value of apparent activation energy was found to be 444 kJ/mol. Zener-Hollomon parameter, Z, was estimated in order to characterize the flow stress behavior. Power dissipation and instability maps developed on the basis of dynamic materials model for true strain of 0.5 show optimum hot working conditions corresponding to peak efficiency range of about 28-32%. These lie in the temperature range of 950-1025 °C and corresponding strain rate range of 0.001-0.01 s−1 and in the temperature range of 1050-1100 °C and corresponding strain rate range of 0.01-0.1 s−1. The flow characteristics in these conditions show dynamic recrystallization behavior. The microstructures are correlated to the different stability domains indicated in the processing map.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.F. Santa, L.A. Espitia, J.A. Blanco, S.A. Romo, and A. Toro, Slurry and Cavitation Erosion Resistance of Thermal Spray Coatings, Wear, 2009, 267, p 160–167
D.C. Wen, Improvement of Slurry Erosion Resistance of Martensitic/Ferritic Duplex Stainless Steel by Hot Rolling, Met. Mater. Int. J., 2010, 16, p 13–19
H.J. Amarendra, P. Kalhan, G.P. Chaudhari, S.K. Nath, and S. Kumar, Slurry Erosion Response of Heat-Treated 13Cr-4Ni Martensitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2012, 710, p 500–505
H.S. Grewal, H.S. Arora, H. Singh, and A. Agrawal, Surface Modification of Hydro Turbine Steel Using Friction Stir Processing, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 268, p 547–555
B. Kishor, G.P. Chaudhari, and S.K. Nath, Cavitation Erosion of Thermomechanically Processed 13/4 Martensitic Stainless Steel, Wear, 2014, 319, p 150–159
B. Kishor, G.P. Chaudhari, and S.K. Nath, Slurry Erosion of Thermo-Mechanically Processed 13Cr4Ni Stainless Steel, Tribol. Int., 2016, 93, p 50–57
Y.H. Xiao and C. Guo, Constitutive Modelling for High Temperature Behavior of Cr12Ni3Mo2VNbN Martensitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 5081–5087
S.K. Rajput, M. Dikovits, G.P. Chaudhari, C. Poletti, F. Warchomicka, V. Pancholi, and S.K. Nath, Physical Simulation of Hot Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of AISI, 1016 Steel Using Processing Map, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 587, p 291–300
S.K. Rajput, G.P. Chaudhari, and S.K. Nath, Physical Simulation of Hot Deformation of Low-Carbon Ti-Nb Microalloyed Steel and Microstructural Studies, J. Mater. Eng. Perform, 2014, 23, p 2930–2942
Z. Shi, X. Yan, and C. Dan, Characterization of Hot Deformation Behaviour of GH925 Super Alloy Using Constitutive Equation, Processing Map And Microstructure Observation, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 652, p 30–38
G. E. Dieter, H. A. Kuhn, and S. L. Semiatin, Handbook of Workability and Process Design, ISBN: 0-87170-778-0, Materials Park, OH: USA, 2003, p 151–152
P. Suikkanen, Development and Processing of Low Carbon Bainitic Steels, Academic Dissertation, Acta Univ. Oul. C 340, Oulun Yliopisto, Oulu, 2009
T. Gladman, The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels, Book 615, The Institute of Materials, London, 1997, p 176–184
D. Samantaray, S. Mandal, and A.K. Bhaduri, Optimization of Hot Working Parameters for Thermo-Mechanical Processing of Modified 9Cr–1Mo (P91) Steel Employing Dynamic Materials Model, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 5204–5211
S. Venugopal, P. Venugopal, and S.L. Mannan, Optimisation of Cold and Warm Workability of Commercially Pure Titanium Using Dynamic Materials Model (DMM) Instability Maps, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 202, p 201–215
A. Momeni, K. Dehghani, M. Heidari, and M. Vaseghi, Modeling the Flow Curve of AISI, 410 Martensitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, 21, p 2238–2243
A. Momeni and K. Dehghani, Characterization of Hot Deformation Behavior of 410 Martensitic Stainless Steel Using Constitutive Equations and Processing Maps, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 5467–5473
S. Venugopal and P.V. Sivaprasad, A Journey with Prasad’s Processing Maps, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2003, 12, p 674–686
P.V. Sivaprasad and S. Venugopal, Instability Maps: An Aid to Tool Design, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2003, 12, p 656–660
A. Marchattiwar, A. Sarkar, J.K. Chakravartty, and B.P. Kashyap, Dynamic Recrystallization during Hot Deformation of 304 Austenitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 2168–2175
S.V.S.N. Murty, B.N. Rao, and B.P. Kashyap, Identification of Flow Instabilities in the Processing Maps of AISI, 304 Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2005, 166, p 268–278
S. Tan, Z. Wang, S. Cheng, Z. Liu, J. Han, and W. Fu, Processing Maps and Hot Workability of Super304H Austenitic Heat-Resistant Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 517, p 312–315
G.R. Ebrahimi, H. Keshmiri, M. Mazinani, A. Maldar, and M. Haghshenas, Multi-Stage Thermomechanical Behaviour of AISI, 410 Martensitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559, p 520–527
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, H.L. Gegel, S.M. Doraivelu, J.C. Malas, J.T. Morgan, K.A. Lork, and D.R. Barker, Modelling of Dynamic Material Behaviour in Hot Deformation: Forging of Ti-6242, Metall. Trans. A, 1984, 15, p 1883–1892
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Processing Maps: A Status Report, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22, p 2867–2874
ASTM E209, Annual Board of ASTM Standards. ASTM International 3, 2010
L. Backe, Modeling the Microstructural Evolution During Hot Deformation of Microalloyed Steels, PhD. Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology Stockholm, 2009
F. Ren, J. Chen, and F. Chen, Constitutive Modelling of Hot Deformation Behavior of X20Cr13 Martensitic Stainless Steel with Strain Effect, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2014, 24, p 1407–1413
H. Zhou, Hot Deformation and Processing Maps of As-Extruded Mg-9.8Gd-2.7Y-0.4Zr Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 576, p 101–107
A. Momeni, S.M. Abbasi, and H. Badri, Hot Deformation Behavior and Constitutive Modelling of VCN200 Low Alloy Steel, Appl. Math. Model., 2012, 36, p 5624–5632
H. Dehghani, S.M. Abbasi, A. Momeni, and A.K. Taheri, On the Constitutive Modelling and Microstructural Evolution of Hot Compressed A286 Iron-Base Super Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 564, p 13–19
C.M. Sellars and W.J. McTegart, On the Mechanism of Hot Deformation, Acta Metall., 1966, 14, p 1136–1138
C. Zener and J.H. Hollomon, Effect of Strain upon Plastic Flow of Steel, J. Appl. Phys., 1944, 15, p 22–32
H. Ziegler, Progress in Solid Mechanics, 4th ed., Wiley, New York, 1963, p 93
H.G. Sheng, H. Guangojier, W.L. Yun, and P. Fursheng, Processing Map for Hot Working of As Extruded AZ31B Magnesium Alloy, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2005, 15, p 813–817
Y. Ninga, Z. Yaoa, H. Li, H. Guoa, Y. Taob, and Y. Zhang, High Temperature Deformation Behavior of Hot Isostatically Pressed P/M FGH4096 Super Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 961–966
Q.L. Pan, B. Li, Y. Zhang, and Z. Yin, Characterization of Hot Deformation Behavior Of Ni-Base Super Alloy Rene’41 Using Processing Map, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 585, p 371–378
Y.C. Lin and X.M. Chen, A Critical Review of Experimental Results and Constitutive Descriptions for Metals and Alloys in Hot Working, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 1733–1759
C.H. Park, Y.G. Ko, C.S. Lee, K.T. Park, D.H. Shin, and H.S. Lee, High Temperature Deformation Behaviour of ELI, Grade Ti-6Al-4V Alloy with Martensite Microstructure, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2007, 551–552, p 365–372
E. Pu, W. Zheng, J. Xiang, Z. Song, and J. Li, Hot Deformation Characteristic and Processing Map of Superaustenitic Stainless Steel S32654, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 598, p 174–182
A.S. Taylor and P.D. Hodgson, Dynamic Behaviour of 304 Stainless Steel During High Z Deformation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 3310–3320
N.D. Ryan and H.J. McQueen, Hot Strength and Microstructural Evolution of 316 Stainless Steel During Simulated Multistage Deformation by Torsion, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1993, 36, p 103–123
D. Zou, Y. Han, D. Yan, D. Wang, W. Zhang, and G. Fan, Hot Workability of 00Cr13Ni5Mo2 Supermartensitic Stainless Steel, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 4443–4448
A.M.J. Junior, Prediction of Steel Flow Stresses under Hot Working Conditions, Mater. Res., 2005, 3, p 1980–5373
G. Liu, Y. Han, Z. Shi, J. Sun, D. Zou, and G. Qiao, Hot Deformation and Optimization of Process Parameters of an As-Cast 6Mo Superaustenitic Stainless Steel: A Study with Processing Map, Mater. Des., 2014, 53, p 662–672
F. Chen, Z.S. Cui, and D.S. Sui, Recrystallization of 30Cr2Ni4MoV Ultra-Super Critical Rotor Steel during Hot Deformation, Part III: Metadynamic Recrystallization, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 540, p 46–54
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India (Grant Number SR/S3/ME/0029/2009-(G)) for the research funding and FIST grant (Grant number SR/FST/ETI-216/2007) for procuring Gleeble® 3800. M/s. Vaishnav Steel Pvt. Ltd. Muzzafarnagar India is acknowledged for providing the steel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kishor, B., Chaudhari, G.P. & Nath, S.K. Hot Deformation Characteristics of 13Cr-4Ni Stainless Steel Using Constitutive Equation and Processing Map. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 2651–2660 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2159-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-2159-4