Abstract
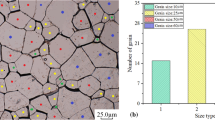
The principle objective of this research is to investigate the modeling of compression behavior and microstructural evolution of pure aluminum in the ultrasonic-assisted compression test. A dislocation density-based constitutive model was developed based on the existing frameworks and calibrated using experimental data to predict the stress-strain response of pure aluminum during UAC tests. An experimental set-up was designed to work at resonance condition with frequency of around 20 kHz and variant longitudinal vibration amplitudes at the range of 0~20 μm. The verified model and experimental samples were used for parameter studies and the study of grain formation of aluminum after conventional and ultrasonic upsetting. Results showed that the developed constitutive model was able to predict compression behavior of aluminum suitably. An increase in the flow stress drop, residual flow stress, and dislocation density occurred when the applied vibration intensity was raised. In addition, it was observed that the more homogenous microstructure with nearly equiaxed grains and also the higher microhardness values can be achieved when ultrasonic vibration is imposed on samples during compression test.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.E. Eaves, A.W. Smith, W.J. Waterhouse, and D.H. Sansome, Review of the Application of UltraSonic Vibrations to Deforming Metals, Ultrasonics, 1975, 7, p 162–170
S.H. Baker and G.S. Carpenter, Dislocation Mobility and Motion Under Combined Stresses, J. Appl. Phys., 1967, 38(4), p 1586–1591
H.O.K. Kirchner, W.K. Kromp, F.B. Prinz, and P. Trimmel, Plastic Deformation Under Simultaneous Cyclic and Unidirectional Loading at Low and Ultrasonic Frequencies, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1985, 68(2), p 197–206
B. Langenecker, Effects of Ultrasound on Deformation Characteristics of Metals, IEEE Trans. Sonics Ultrason., 1966, SU-13(1), p 1–8
G.A. Malygin, Acoustoplastic Effect and the Stress Superimposition Mechanism, Phys. Solid State, 2000, 42, p 72–78
O. Izumi, K. Oyama, and Y. Suzuki, Effects of Superimposed Ultrasonic Vibration on Compressive Deformation of Metals, Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1966, 7, p 162–166
T. Ohgaku and N. Takeuchi, The Blaha Effect of Alkali Halide Crystals, Phys. Status Solidi A, 1987, 102, p 293–299
C. Bunget and G. Ngaile, Influence of Ultrasonic Vibration on Micro-Extrusion, Ultrasonics, 2011, 51(5), p 606–616
T. Jimma, Y. Kasuga, N. Iwaki, O. Miyazawa, E. Mori, K. Ito, and H. Hatano, An Application of Ultrasonic Vibration to the Deep Drawing Process, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1998, 80-81, p 406–412
Y. Liu, S. Suslov, Q. Han, C. Xu, and L. Hua, Microstructure of the Pure Copper Produced by Upsetting with Ultrasonic Vibration, Mater. Lett., 2012, 67(1), p 52–55
K. Siegert and A. Möck, Wire Drawing with Ultrasonically Oscillating Dies, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1996, 60(1-4), p 657–660
M.A. Rasoli, A. Abdullah, M. Farzin, A.F. Tehrani, and A. Taherizadeh, Influence of Ultrasonic Vibrations on Tube Spinning Process, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2012, 212(6), p 1443–1452
J. Hung and M. Chiang, The Influence of Ultrasonic-Vibration on Double Backward-Extrusion of Aluminum Alloy, Proceeding of the World Congress on Engineering 2009 (WCE 2009), 2009, Vol II, London
S.A.A.A. Mousavi, H. Feizi, and R. Madoliat, Investigations on the Effects of Ultrasonic Vibrations in the Extrusion Process, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 188, p 657–661
Y. Ashida and H. Aoyama, Press forming Using Ultrasonic Vibration, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 188, p 118–122
M. Lucas and Y. Daud, A Finite Element Model of Ultrasonic Extrusion, J. Phys., 2009, 181, p 012027
B.L.F. Blaha, Tensile Deformation of Zinc Crystal Under Ultrasonic Vibration, Nature, 1955, 42, p 556
J.-C. Hung and C. Hung, The Influence of Ultrasonic-Vibration on Hot Upsetting of Aluminum Alloy, Ultrasonics, 2005, 43(8), p 692–698
Y. Daud, M. Lucas, and Z. Huang, Modelling the Effects of Superimposed Ultrasonic Vibrations on Tension and Compression Tests of Aluminium, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 186(1-3), p 179–190
A. Siddiq and E. Ghassemieh, Thermomechanical Analyses of Ultrasonic Welding Process Using Thermal and Acoustic Softening Effects, Mech. Mater., 2008, 40(12), p 982–1000
S. AbdulAziz, M. Lucas, F. Chinesta, Y. Chastel, and M. ElMansori, A Study of an Ultrasonically Assisted Metal Forming Test, AIP Conf. Proc., 2011, 733(1), p 733–738
A. Rusinko, Analytical Description of Ultrasonic Hardening and Softening, Ultrasonics, 2011, 51(6), p 709–714
K.W. Siu, A.H.W. Ngan, and I.P. Jones, New Insight on Acoustoplasticity—Ultrasonic Irradiation Enhances Subgrain Formation During deformation, Int. J. Plast, 2011, 27(5), p 788–800
Z. Yao, G.-Y. Kim, L. Faidley, Q. Zou, D. Mei, and Z. Chen, Experimental Study of High-Frequency Vibration Assisted Micro/Mesoscale Forming of Metallic Materials, J. Manuf. Sci. Eng., 2011, 133(6), p 061009
Z. Yao, G.-Y. Kim, L. Faidley, Q. Zou, D. Mei, and Z. Chen, Effects of Superimposed High-Frequency Vibration on Deformation of Aluminum in Micro/Meso-Scale Upsetting, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2012, 212(3), p 640–646
Z. Yao, G.-Y. Kim, Z. Wang, L. Faidley, Q. Zou, D. Mei, and Z. Chen, Acoustic Softening and Residual Hardening in Aluminum: Modeling and Experiments, Int. J. Plast, 2012, 39, p 75–87
F. Barlat, M.V. Glazov, J.C. Brem, and D.J. Lege, A Simple Model for Dislocation Behavior, Strain and Strain Rate Hardening Evolution in Deforming Aluminum Alloys, Int. J. Plast, 2002, 18, p 919–939
Y. Estrin, Dislocation-Density-Related Constitutive Modeling, Academic Press Inc., New York, 1966
H.J. Forest and M.F. Ashby, Deformation mechanisms Maps: The Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics, 1st ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford shire, Oxford, New York, 1982
U.F. Kocks, Constitutive Behavior Based on Crystal Plasticity: Unified Constitutive Equations for Creep and Plasticity, Elsevier Applied Science, London; New York, 1987
A. Siddiq and T. El Sayed, Acoustic Softening in Metals During Ultrasonic Assisted Deformation Via CP-FEM, Mater. Lett., 2011, 65(2), p 356–359
C. Tome, G.R. Canova, U.F. Kocks, N. Christodoulou, and J.J. Jonas, The Relation Between Macroscopic and Microscopic Strain Hardening in F.C.C. Polycrystals, Acta Metall., 1984, 32(10), p 1637–1653
J.I. Taylor, Plastic Strain in Metals, J. Inst. Met., 1938, 62, p 307–324
J. Blitz, Ultrasonics Methods and Applications, Newnes-Butterworth, London, 1971
Y. Liu, S. Suslov, Q. Han, L. Hua, and C. Xu, Comparison Between Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Upsetting and Conventional Upsetting, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, 44(7), p 3232–3244
ASM, Metallography and Microstructures, Vol 9, ASM Handbook, New York, 1992
Acknowledgment
The authors thankfully acknowledge the financial support of University of Tehran and the provision of the research facilities used in this work. Also, the sincere collaboration of Dr. M. R. Karafi (Assistance professor of Tarbiat Modares University) during designing of ultrasonic equipments in this research is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagherzadeh, S., Abrinia, K. Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration on Compression Behavior and Microstructural Characteristics of Commercially Pure Aluminum. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 4364–4376 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1730-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1730-8