Abstract
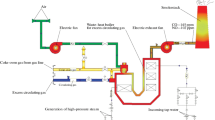
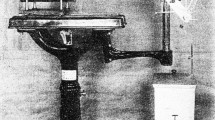
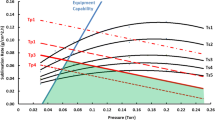
Quench probes have been used effectively to characterize the quality of quenchants for many years. For this purpose, a variety of commercial probes, as well as the necessary data acquisition system for determining the time-temperature data for a set of standardized test conditions, are available for purchase. The type of information obtained from such probes provides a good basis for comparing media, characterizing general cooling capabilities, and checking media condition over time. However, these data do not adequately characterize the actual production quenching process in terms of heat transfer behavior in many cases, especially when high temperature gradients are present. Faced with the need to characterize water quenching practices, including conventional and intensive practices, a quench probe was developed. This paper describes that probe, the data collection system, the data gathered for both intensive quenching and conventional water quenching, and the heat transfer coefficients determined for these processes. Process sensitivities are investigated and highlight some intricacies of quenching.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Ma, Characterization of the Performance of Mineral Oil Based Quenchants Using CHTE Quench Probe System, Master’s Degree Thesis, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, June 27, 2002
S. Segerberg and J. Bodin, Variation in the Heat Transfer Coefficient Around Components of Different Shapes During Quenching, Quenching and Distortion Control, G.E. Totten, Ed., ASM International, 1992, p 165–170
H.S. Hasan and M.J. Peet, Heat Transfer Coefficient and Latent Heat of Martensite in a Medium-Carbon Steel, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., 2012, 39(10), p 1519–1521
B. Liščić and T. Filetin, Measurement of Quenching Intensity, Calculation of Heat Transfer Coefficient and Global Database of Liquid Quenchants, Mater. Eng. J., 2012, 19, p 52–63 (ISSN 1338-6174)
N.I. Kobasko, Intensive Steel Quenching Methods, Quenching Theory and Technology, CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 2010, p 485–508
M.A. Aronov, N.I. Kobasko, and J.A. Powell, Basic Principals, Properties and Metallurgy of Intensive Quenching, SAE Technical Paper 02OH-48, 2002
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge sponsorship of this project by the US Army Aviation Technology Directorate under Contract W911W6-09-D-0016-0003. Mr. Clay Ames was the program liaison. The authors also acknowledge Drs. Michael Aronov and Nikolai Kobasko of Intensive Quenching Technologies, Inc. for many discussions about temperature measurement, quenching technologies, and most importantly for use of their participation in the single part intensive quenching experiments, using the system located at Euclid Heat Treating, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the 27th ASM Heat Treating Society Conference, held September 16-18, 2013, in Indianapolis, IN, and has been expanded from the original presentation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferguson, B.L., Li, Z. & Freborg, A.M. Characterizing Water Quenching Systems with a Quench Probe. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 4197–4201 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1276-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-1276-1