Abstract
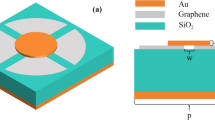
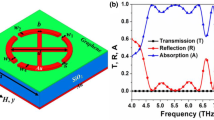
In this paper, we propose an absorber with adjustable single-layer graphene multi-band perfect absorption, which has the advantages of simple structure, polarization insensitivity, tunability, multi-band absorption, and high sensitivity. The device can achieve four perfect absorption peaks at the same time, and the absorption rate of all absorption peaks is above 99%. The absorption effect of the absorber can be efficiently adjusted and controlled by adjusting the geometric parameters of the single-layer graphene array and the thickness of the dielectric layer. In addition, by changing the strength of the applied magnetic field, the Fermi level, and the relaxation rate of graphene, the absorption of the device can be dynamically adjusted, and high absorption can be maintained in the range of 0°–70° wide incidence angle. Finally, considering the potential sensing applications of the device, we measured maximum sensitivity (S) of 3.06 THz/RIU and a maximum figure of merit (FOM) of 54.6 when exposed to different ambient refractive indices, suggesting that the device can be used as a refractive index sensor. These results show that this study provides a new idea for the design of the tunable multi-band perfect metamaterial absorber based on graphene, which has great application value in many fields and provides a new reference for future research.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Zheng, Y. Zheng, Y. Luo, Z. Yi, J. Zhang, L. Liu, Q. Song, P. Wu, Y. Yu, and J. Zhang, Terahertz perfect absorber based on flexible active switching of ultra-broadband and ultra-narrowband. Opt. Express 29, 42787 (2021).
R. Nie, C. He, R. Zhang, and Z. Song, Vanadium dioxide-based terahertz metasurfaces for manipulating wavefronts with switchable polarization. Opt. Laser Technol. 159, 109010 (2023).
W.L. Barnes, A. Dereux, and T.W. Ebbesen, Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424, 6950 (2003).
D.R. Smith, W.J. Padilla, D. Vier, S.C. Nemat-Nasser, and S. Schultz, Composite medium with simultaneously negative permeability and permittivity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 4184 (2000).
B. Spackova, P. Wrobel, M. Bockova, and J. Homola, Optical biosensors based on plasmonic nanostructures: a review. Proc. IEEE 104, 2380–2408 (2016).
J. Valentine, S. Zhang, T. Zentgraf, E. Ulin-Avila, D.A. Genov, G. Bartal, and X. Zhang, Three-dimensional optical metamaterial with a negative refractive index. Nature 455, 7211 (2008).
L. Ye, X. Chen, G. Cai, J. Zhu, N. Liu, and Q.H. Liu, Electrically tunable broadband terahertz absorption with hybrid-patterned graphene metasurfaces. Nanomater-Basel 8, 562 (2018).
Z. Zhou, Y. Chen, Y. Tian, J. Liang, and W. Yang, Ultra-broadband metamaterial perfect solar absorber with polarization-independent and large incident angle-insensitive. Opt. Laser Technol. 156, 108591 (2022).
Y. Cheng, R. Gong, and J. Zhao, A photoexcited switchable perfect metamaterial absorber/reflector with polarization-independent and wide-angle for terahertz waves. Opt. Mater. 62, 28 (2016).
S. Zhang, D.A. Genov, Y. Wang, M. Liu, and X. Zhang, Plasmon-induced transparency in metamaterials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 047401 (2008).
Z. Song, Q. Chu, and Q.H. Liu, Isotropic wide-angle analog of electromagnetically induced transparency in a terahertz metasurface. Mater. Lett. 223, 90 (2018).
Z. Zheng, Y. Luo, H. Yang, Z. Yi, J. Zhang, Q. Song, W. Yang, C. Liu, X. Wu, and P. Wu, Thermal tuning of terahertz metamaterial absorber properties based on VO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24, 8846 (2022).
A. Fardoost, F.G. Vanani, A.A. Amirhosseini, and R. Safian, Design of a multilayer graphene-based ultrawideband terahertz absorber. IEEE T. Nanotechnol. 16, 68 (2016).
Y. Cai, J. Zhu, and Q.H. Liu, Tunable enhanced optical absorption of graphene using plasmonic perfect absorbers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 043105 (2015).
Z. Li, S. Butun, and K. Aydin, Large-Area, lithography-free super absorbers and color filters at visible frequencies using ultrathin metallic films. ACS Photonics 2, 183 (2015).
F. He, B. Han, X. Li, T. Lang, X. Jing, and Z. Hong, Analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency with high-Q factor in metal-dielectric metamaterials based on bright-bright mode coupling. Opt. Express 27, 37590 (2019).
N.I. Landy, S. Sajuyigbe, J.J. Mock, D.R. Smith, and W.J. Padilla, Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 207402 (2008).
H. Chen, Z. Chen, H. Yang, L. Wen, Z. Yi, Z. Zhou, B. Dai, J. Zhang, X. Wu, and P. Wu, Multi-mode surface plasmon resonance absorber based on dart-type single-layer graphene. RSC Adv. 12, 7821 (2022).
F. Qin, X. Chen, Z. Yi, W. Yao, H. Yang, Y. Tang, Y. Yi, H. Li, and Y. Yi, Ultra-broadband and wide-angle perfect solar absorber based on TiN nanodisk and Ti thin film structure. Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C. 211, 110535 (2020).
K.T. Lin, H. Lin, T. Yang, and B. Jia, Structured graphene metamaterial selective absorbers for high efficiency and omnidirectional solar thermal energy conversion. Nat. commun. 11, 1389 (2020).
K.S. Novoselov, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S.V. Dubonos, I.V. Grigorieva, and A.A. Firsov, Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666 (2004).
S. Bae, H. Kim, Y. Lee, X. Xu, J.S. Park, Y. Zheng, J. Balakrishnan, T. Lei, H. Ri Kim, and Y. Song, Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 574 (2010).
K.F. Mak, M.Y. Sfeir, Y. Wu, C.H. Lui, J.A. Misewich, and T.F. Heinz, Measurement of the optical conductivity of graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 196405 (2008).
M.D. Kapetanakis, W. Zhou, M.P. Oxley, J. Lee, M.P. Prange, S.J. Pennycook, J.C. Idrobo, and S.T. Pantelides, Low-loss electron energy loss spectroscopy: an atomic-resolution complement to optical spectroscopies and application to graphene. Phys. Rev. B 92, 125147 (2015).
M. Islam, J. Sultana, M. Biabanifard, Z. Vafapour, M. Nine, A. Dinovitser, C. Cordeiro, B.H. Ng, and D. Abbott, Tunable localized surface plasmon graphene metasurface for multiband superabsorption and terahertz sensing. Carbon 158, 559 (2020).
S. Thongrattanasiri, F.H. Koppens, and F.J.G. De Abajo, Complete optical absorption in periodically patterned graphene. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 047401 (2012).
G. Yao, F. Ling, J. Yue, C. Luo, J. Ji, and J. Yao, Complete optical absorption in periodically patterned graphene. Opt. Express 24, 1518 (2016).
X. Luo, Z.Q. Cheng, X. Zhai, Z.M. Liu, S.Q. Li, J.P. Liu, L.L. Wang, Q. Lin, and Y.H. Zhou, A tunable dual-band and polarization-insensitive coherent perfect absorber based on double-layers graphene hybrid waveguide. Nano Express 14, 1 (2019).
W. Yin, Z. Shen, S. Li, L. Zhang, and X. Chen, A three-dimensional dual-band terahertz perfect absorber as a highly sensitive sensor. Front. Phys-Lausanne 9, 665280 (2021).
Z. Liu, S. Zhuo, F. Zhou, X. Zhang, Y. Qin, X. Luo, C. Ji, and G. Yang, Double narrowband induced perfect absorption photonic sensor based on graphene–dielectric–gold hybrid metamaterial. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 17, 85 (2022).
M. Liu, X. Yin, and X. Zhang, Double-layer graphene optical modulator. Nano Lett. 12, 1482 (2012).
C.H. Gan, H.S. Chu, and E.P. Li, Synthesis of highly confined surface plasmon modes with doped graphene sheets in the midinfrared and terahertz frequencies. Phys. Rev. B 85, 125431 (2012).
W. Zhu, I.D. Rukhlenko, F. Xiao, C. He, J. Geng, X. Liang, M. Premaratne, and R. Jin, Multiband coherent perfect absorption in a water-based metasurface. Opt. Express 25, 15737 (2017).
F. Liu, M. He, Z. Dong, Y. Wang, and B. Ni, Design of tunable dual-band terahertz perfect absorber base on graphene. Results Phys. 40, 105860 (2022).
P. Zamzam, P. Rezaei, and S.A. Khatami, Quad-band polarization-insensitive metamaterial perfect absorber based on bilayer graphene metasurface. Phys. E 128, 114621 (2021).
Y. Cai, Y. Guo, H. Zhang, Y. Wang, C. Chen, F. Lin, S. Zuo, and Y. Zhou, Tunable and polarization-sensitive graphene-based terahertz absorber with eight absorption bands. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 54, 195106 (2021).
M. Liu, H.Y. Hwang, H. Tao, A.C. Strikwerda, K. Fan, G.R. Keiser, A.J. Sternbach, K.G. West, S. Kittiwatanakul, and J. Lu, Terahertz-field-induced insulator-to-metal transition in vanadium dioxide metamaterial. Nature 487, 345 (2012).
Z. Song, Y. Deng, Y. Zhou, and Z. Liu, Terahertz toroidal metamaterial with tunable properties. Opt. Express 27, 5792 (2019).
Y. Liu, M. Bo, X. Yang, P. Zhang, C.Q. Sun, and Y.J. Huang, Size modulation electronic and optical properties of phosphorene nanoribbons: DFT–BOLS approximation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 5304 (2017).
W. Wei, J. Wu, S. Cui, Y. Zhao, W. Chen, and L. Mi, α-Ni (OH)2/NiS1.97 heterojunction composites with excellent ion and electron transport properties for advanced supercapacitors. Nanoscale 11, 6243 (2019).
G. Li, T. Sang, H. Qi, X. Wang, X. Yin, Y. Wang, and L. Hu, Flexible control of absorption enhancement of circularly polarized light via square graphene disks. OSA Continuum. 3, 1999 (2020).
Y. Li, M. Li, P. Xu, S. Tang, and C. Liu, Efficient photocatalytic degradation of acid orange 7 over N-doped ordered mesoporous titania on carbon fibers under visible-light irradiation based on three synergistic effects. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 524, 163 (2016).
X. Zeng, M. Gao, L. Zhang, G. Wan, and B. Hu, Design of a triple-band metamaterial absorber using equivalent circuit model and interference theory. Microw. Opt. Techn. Let. 60, 1676 (2018).
H. Cheng, S. Chen, P. Yu, X. Duan, B. Xie, and J. Tian, Dynamically tunable plasmonically induced transparency in periodically patterned graphene nanostrips. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 203112 (2013).
F.H. Koppens, D.E. Chang, and F.J. Garcia de Abajo, Graphene plasmonics: a platform for strong light–matter interactions. Nano Lett. 11, 3370 (2011).
A. Bhattacharya, K.M. Devi, T. Nguyen, and G. Kumar, Actively tunable toroidal excitations in graphene based terahertz metamaterials. Opt. Commun. 459, 124919 (2020).
J. Li, X. Chen, Z. Yi, H. Yang, Y. Tang, Y. Yi, W. Yao, J. Wang, and Y. Yi, Broadband solar energy absorber based on monolayer molybdenum disulfide using tungsten elliptical arrays. Mater. Today Energy 16, 100390 (2020).
Z.D. Yan, X. Lu, W. Du, Z. Lv, C. Tang, P. Cai, P. Gu, J. Chen, and Z. Yu, Ultraviolet graphene ultranarrow absorption engineered by lattice plasmon resonance. Nanotechnology 32, 465202 (2021).
M. Vaughan, The Fabry-Perot interferometer: history, theory, practice and applications (Milton Park: Routledge, 2017).
H.T. Chen, Interference theory of metamaterial perfect absorbers. Opt. Express 20, 7165 (2012).
B. Jan, T. Andreas, J. Arpad, H. Ulrich, and S. Carsten, The optimal aspect ratio of gold nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5, 161 (2010).
W. Wang, K.J. Wang, Z.G. Yang, and J.S. Liu, Experimental demonstration of an ultra-flexible metamaterial absorber and its application in sensing. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 13, 135108 (2017).
J.P. Tian, R.J. Ke, R.C. Yang, and W.H. Pei, Tunable quad-band perfect metamaterial absorber on the basis of monolayer graphene pattern and its sensing application. Results Phys. 26, 104447 (2021).
B.X. Wang, G.Z. Wang, and T. Sang, Simple design of novel triple-band terahertz metamaterial absorber for sensing application. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 49, 165307 (2016).
R. Cheng, Y. Zhou, H. Liu, J. Liu, G. Sun, X. Zhou, H. Shen, Q. Wang, and Y. Zha, Tunable graphene-based terahertz absorber via an external magnetic field. Opt. Mater. Express 10, 501 (2020).
H.F. Liu, J.X. Wu, J.R. Yuan, and X.H. Deng, Dynamically tunable perfect THz absorption in graphene-based metamaterial structures. Europhys. Lett. 134, 57003 (2021).
Funding
This study was funded by the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Materials Synthesis and Processing (Wuhan University of Technology) (Grant Number: 2022-KF-15), the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Millimeter Waves (Grant Number: K201606), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 11664025), and the Chongqing Natural Science Foundation (Grant Number: CSTB2023NSCQ-MSX0730).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have taken full responsibility for the content of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for Publication
The authors consent to publication of the article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Deng, XH., Zhang, P. et al. Graphene-Based Metamaterial Absorber with Perfect Multi-band Absorption. J. Electron. Mater. 53, 4049–4058 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11108-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11108-7