Abstract
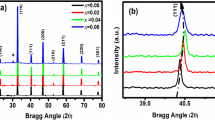
The solid-state reaction approach was used to synthesize Ba0.95Sr0.05Ca5Ti2−xMxNb8O30 (where M represents Fe and Mn and x is 0 and 0.05) in order to compare the variations in the structural and dielectric properties of the ferroelectric material. The structural investigation was carried out using x-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. The orthorhombic structure with Pbcn space group revealed by the XRD investigation was validated by Rietveld refinement. The FTIR spectroscopy results were in good agreement with the reported phase. Analysis of the electrical properties was carried out by complex impedance spectroscopy. The results of transition metal doping with both Fe and Mn with regard to the dielectric permittivity as a function of frequency showed an improvement in the dielectric characteristics, while Mn exhibited a higher dielectric constant than Fe. The pure sample showed a lower transition temperature than the Fe- and Mn-doped sample. Analysis of the magnetic characteristics obtained from vibrating-sample magnetometry (VSM) revealed that doping enhanced the magnetic properties. This approach thus shows excellent potential for high-temperature operation, achieving good temperature stability via transition metal doping.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.C. Mathai, S. Vidya, A. John, S. Solomon, and J.K. Thomas, Structural, optical, and compactness characteristics of nanocrystalline CaNb2O6 synthesized through an autoigniting combustion method. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2014, 1–6 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/735878.
P. Ganguly and A.K. Jha, Structural and electrical properties of Ba5−xCaxSmTi3Nb7O30 (x=0–5) ferroelectric ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 495, 7–12 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.01.118.
X. Zhu, M. Fu, M.C. Stennett, P.M. Vilarinho, I. Levin, C.A. Randall, J. Gardner, F.D. Morrison, and I.M. Reaney, A crystal-chemical framework for relaxor versus normal ferroelectric behavior in tetragonal tungsten bronzes. Chem. Mater. 27, 3250–3261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b00072.
A. Rotaru and F.D. Morrison, Vogel-Fulcher analysis of relaxor dielectrics with the tetragonal tungsten bronze structure: Ba6MNb9O30 (M = Ga, Sc, In). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.Calorim. 120, 1249–1259 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4355-5.
X.L. Zhu, K. Li, and X.M. Chen, Ferroelectric transition and low-temperature dielectric relaxations in filled tungsten bronzes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97, 329–338 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.12790.
X.L. Zhu, S.Y. Wu, and X.M. Chen, Dielectric anomalies in (BaxSr1−x)4Nd2Ti4Nb6O30 ceramics with various radius differences between A1- and A2-site ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2800789.
M.C. Stennett, I.M. Reaney, G.C. Miles, D.I. Woodward, A.R. West, C.A. Kirk, and I. Levin, Dielectric and structural studies of Ba2MTi2Nb3O15 (BMTNO15, M=Bi3+, La3+, Nd3+, Sm3+, Gd3+) tetragonal tungsten bronze-structured ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2205720.
P. Ganguly and A.K. Jha, Investigations of structural, dielectric and electrical behaviour of calcium substituted Ba5NdTi3Nb7O30 ferroelectric ceramics. Integr. Ferroelectr.. Ferroelectr. 115, 149–156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2010.488566.
X.L. Zhu, X.Q. Liu, and X.M. Chen, Crystal structure and dielectric properties of Sr5RTi3Nb7O30 (R=La, Nd, Sm, and Eu) tungsten bronze ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1829–1836 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04327.x.
X. Li Zhu, Y. Bai, X.Q. Liu, and X. Ming Chen, Ferroelectric phase transition and low-temperature dielectric relaxations in Sr4(La1−xSmx)2Ti4Nb6O30 ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3664857.
K. Li, X.L. Zhu, X.Q. Liu, and X.M. Chen, Effects of Ca-substitution on structural, dielectric, and ferroelectric properties of Ba5SmTi3Nb7O30 tungsten bronze ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 042906 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4739841.
R.N.P. Choudhary, S.R. Shannigrahi, and A.K. Singh, Ferroelectric phase transition in Ba5RTi3Nb7O30 [R=Nd, Eu, Gd] ceramics. Bull. Mater. Sci. 22, 975–979 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02745689.
P.P. Rao, S.K. Ghosh, and P. Koshy, Dielectric and ferroelectric properties of Ba3M3Ti5Nb5O30 (M= Sm or Y) ceramics. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electr. 12, 729–732 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012944927315.
S.R. Shannigrahi, R.N.P. Choudhary, A. Kumar, and H.N. Acharya, Phase transition in Ba5RTi3Nb7O30 (R = Dy, Sm) ferroelectric ceramics. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 59, 737–742 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3697(97)00217-5.
X.H. Zheng and X.M. Chen, Dielectric ceramics with tungsten-bronze structure in the BaO–Nd2O3–TiO2–Nb2O5 system. J. Mater. Res. 17, 1664–1670 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2002.0245.
P.R. Das, R.N.P. Choudhary, and B.K. Samantray, Diffuse ferroelectric phase transition in Na2PbSm2W2Ti4Nb4O30 ceramics. Mater. Chem. Phys. 101, 228–233 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2006.04.005.
B. Behera, P. Nayak, and R.N.P. Choudhary, Structural, dielectric and electrical properties of NaBa2X5O15 (X=Nb and Ta) ceramics. Mater. Lett. 59, 3489–3493 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2005.06.019.
J. Yeon, P.S. Halasyamani, and I.V. Kityk, Nonlinear optical effects in nano-sized ferroelectrics Sr6Ti2Nb(Ta)8O30. Mater. Lett. 62, 1082–1084 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2007.07.048.
V. Massarotti, D. Capsoni, M. Bini, C.B. Azzoni, M.C. Mozzati, P. Galinetto, and G. Chiodelli, Structural and spectroscopic properties of pure and doped Ba6Ti2Nb8O30 tungsten bronze. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 17798–17805 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp063382p.
X.H. Zheng and X.M. Chen, Crystal structure and dielectric properties of ferroelectric ceramics in the BaO-Sm2O3-TiO2-Nb2O5 system. Solid State Commun.Commun. 125, 449–454 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0038-1098(02)00709-3.
L. Fang, H. Zhang, J.B. Yan, and W.M. Yang, Synthesis and dielectric properties of a new niobate Ba5NdTi3Nb7O30. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 18(11), 1131–1134 (2002).
A. Bendahhou, P. Marchet, A. El-Houssaine, S. El Barkany, and M. Abou-Salama, Relationship between structural and dielectric properties of Zn-substituted Ba5CaTi2−xZnxNb8O30 tetragonal tungsten bronze. CrystEngComm 23, 163–173 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ce01561j.
A. Bendahhou, P. Marchet, S. El Barkany, and M. Abou-salama, Structural and impedance spectroscopic study of Zn-substituted Ba5CaTi2Nb8O30 tetragonal tungsten bronze ceramics. J. Alloy. Compd. 882, 160716 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160716.
S. Jindal, A. Vasishth, S. Devi, N. Aggarwal, and K.K. Kushwah, Investigation of structural, ferroelectric and magnetic properties of iron doped tungsten bronze multiferroic ceramics. Physica B B 595, 412341 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.412341.
S. Jindal, A. Vashishth, S. Devi, and K. Kumar Kushwah, Prospective features of multiferroic tungsten bronze ceramics and its futuristic applications. Mater. Today: Proc. 51, 1252–1258 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.07.351.
S. Jindal, N. Aggarwal, A. Vasishth, and A. Sharma, Investigation of tungsten bronze ferroelectric ceramic by conventional and mechanical activation processes. Mater. Today: Proc. 68, 886–890 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.06.424.
S. Jindal, S. Devi, A. Vasishth, K.M. Batoo, and G. Kumar, Interdependence between electrical and magnetic properties of polycrystalline cobalt-substituted tungsten bronze multiferroic ceramics. J. Adv. Dielectr.Dielectr. 08, 1850002 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/s2010135x18500029.
P. Sahoo, A. Panigrahi, S. Patri, and R. Choudhary, Structural, dielectric, electrical and piezoelectric properties of Ba4SrRTi3V7O30 (R=Sm, Dy) ceramics. Open Phys. (2008). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11534-008-0112-3.
A. Bendahhou, K. Chourti, R. El Bouayadi, S. El Barkany, and M. Abou-Salama, Structural, dielectric and impedance spectroscopy analysis of Ba5CaTi1.94Zn0.06Nb8O30ferroelectric ceramic. RSC Adv. 10, 28007–28018 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra05163b.
J.H. Joshi, D.K. Kanchan, M.J. Joshi, H.O. Jethva, and K.D. Parikh, Dielectric relaxation, complex impedance and modulus spectroscopic studies of mix phase rod like cobalt sulfide nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 93, 63–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.04.013.
Y.J. Wong, J. Hassan, and M. Hashim, Dielectric properties, impedance analysis and modulus behavior of CaTiO3 ceramic prepared by solid state reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 571, 138–144 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.03.123.
P. Kamkum, N. Atiwongsangthong, R. Muanghlua, and N. Vittayakorn, Application of chicken eggshell waste as a starting material for synthesizing calcium niobate (Ca4Nb2O9) powder. Ceram. Int. 41, S69–S75 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.03.189.
S. Chaudhary, S. Devi, and S. Jindal, Enhancing structural, optical, magnetic, dielectric and impedance properties of Ba0.95Sr0.05Ca5Ti2−xFexNb8O30 tungsten bronze ferroelectric ceramic through Fe/Ti ratio on optimization for the advanced device applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 312, 128580 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.128580.
L. Malik, G.S. Saini, and A. Tevatia, A self-sustained machine learning model to predict the in-flight mechanical properties of a rocket nozzle by inputting material properties and environmental conditions, Handbook of Sustainable Materials: Modelling, Characterization, and Optimization. (Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2023), pp. 431–456. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003297772.
L. Malik, S. Rawat, M. Kumar, and A. Tevatia, Simulation studies on aerodynamic features of Eurofighter Typhoon and Dassault Rafale combat aircraft. Mater. Today: Proc. 38, 191–197 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.536.
L. Malik, G.S. Saini, M. Malik, and A. Tevatia, Sustainability of wind turbine blade: instantaneous real-time prediction of its failure using machine learning and solution based on materials and design, Handbook of Sustainable Materials: Modelling, Characterization, and Optimization. (Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2023), pp. 399–430. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003297772.
L. Malik and A. Tevatia, Comparative analysis of aerodynamic characteristics of F16 and F22 combat aircraft using computational fluid dynamics. Def. Sci. J. 71, 137–145 (2021). https://doi.org/10.14429/dsj.71.15762.
L. Malik, Novel concept of tailorable magnetic field and electron pressure distribution in a magnetic nozzle for effective space propulsion. Propul. Power Res. 12, 59–68 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jppr.2023.02.002.
L. Malik, In-flight plume control and thrust tuning in magnetic nozzle using tapered-coils system under the effect of density gradient. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 51, 1325–1333 (2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhary, S., Devi, S., Jindal, S. et al. Impact of B-site Substitution of Transition Metal (Fe and Mn) on the Structural, Electrical, and Magnetic Properties of Tungsten Bronze Ferroelectric Ceramic. J. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11083-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11083-z