Abstract
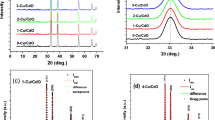
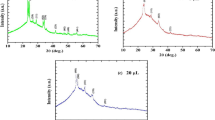
In this work, tungsten oxide (WO3) films were deposited at room temperature and annealed for 2 h at 400°C. The electrochromic and electrochemical properties were studied for two different electrolytes. The films were deposited at different oxygen flow rates of 2, 4, and 6 standard cubic centimeters per minute (SCCM). X-ray diffraction analysis revealed structural characterization of amorphous and crystalline phases. UV-visible spectroscopy optical transmittance revealed 91% transmittance, and energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis revealed the absence of impurities and the presence of W and O. An electrochemical analyzer was used to characterize the deposited and annealed WO3 films immersed in the two different electrolyte solutions (H2SO4 and LiClO4 with oxygen flow rates ranging from 2 SCCM to 6 SCCM). It was found that the H2SO4 electrolyte of an annealed WO3 thin film at 2 SCCM demonstrated high coloring efficiency of 50.18 cm2/C, and the LiClO4 electrolyte of an annealed WO3 thin film at 4 SCCM demonstrated high coloring efficiency of 20.06 cm2/C.














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article and are available from the author.
References
T. Brousse, D. Bélanger, K. Chiba, M. Egashira, F. Favier, J. Long, J.R. Miller, M. Morita, K. Naoi, P. Simon, and W. Sugimoto, Materials for electrochemical capacitors. Springer Handbooks (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46657-5_16.
R.S. Vemuri, M.H. Engelhard, and C.V. Ramana, Correlation between surface chemistry, density, and band gap in nanocrystalline WO3 thin films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 1371 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/am2016409.
C.G. Granqvist, Oxide electrochromics: an introduction to devices and materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 99, 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2011.08.021.
J. Gupta, H. Shaik, and K.N. Kumar, A review on the prominence of porosity in tungsten oxide thin films for electrochromism. Ionics (Kiel) 27, 2307 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04035-8.
J. Gutpa, H. Shaik, K.N. Kumar, and S. Abdul, Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing PVD techniques proffering avenues for fabrication of porous tungsten oxide (WO3) thin films : a review. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 143, 106534 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2022.106534.
M. Grätzel, Ultrafast colour displays. Nature 409, 575 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35054655.
C.G. Granqvist, Electrochromics for smart windows: oxide-based thin films and devices. Thin Solid Films 564, 1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2014.02.002.
G.A. Niklasson and C.G. Granqvist, Electrochromics for smart windows :thin films of tungsten oxide and nickel oxide, and devices based on these. J. Mater. Chem. 17(2), 127 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1039/b612174h.
C.G. Granqvist, Electrochromic tungsten oxide films: review of progress 1993–1998. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 60, 201 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0927-0248(99)00088-4.
H. Simchi, B.E. McCandless, T. Meng, and W.N. Shafarman, Structural, optical, and surface properties of WO3 thin films for solar cells. J. Alloy. Compd. 617, 609 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.047.
Y.A.K. Reddy, B. Ajitha, A. Sreedhar, and E. Varrla, Enhanced UV photodetector performance in bi-layer TiO2/WO3 sputtered films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 494, 575 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.07.124.
A.V. Shchegolkov, S.H. Jang, A.V. Shchegolkov, Y.V. Rodionov, A.O. Sukhova, and M.S. Lipkin, A brief overview of electrochromic materials and related devices: a nanostructured materials perspective. Nanomaterials 11, 2376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11092376.
A.R. GV, H. Shaik, K.N. Kumar, V. Madhavi, H.D. Shetty, S.A. Sattar, M. Dhananjaya, B. Daruka Prasad, G.R. Kumar, and B.H. Doreswamy, Structural and electrochemical studies of WO3 coated TiO2 nanorod hybrid thin films for electrochromic applications. Optik 277, 170694 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2023.170694.
K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, A. Pawar, L.N. Chandrashekar, S.A. Sattar, G. Nithya, R. Imran Jafri, V. Madhavi, J. Gupta, and G.V. Ashok Reddy, Effect of annealing and oxygen partial pressure on the RF sputtered WO3 thin films for electrochromic applications. Mater. Today: Proc. 59, 339 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.11.185.
K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, L.N. Chandrashekar, P. Aishwarya, S. Abdul Sattar, G. Nithya, V. Madhavi, R. Imran Jafri, J. Gupta, and G.V. Ashok Reddy, On ion transport during the electrochemical reaction on plane and GLAD deposited WO3 thin films. Mater. Today Proc. 59, 275 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.11.113.
L. Geng, Gas sensitivity study of polypyrrole/WO3 hybrid materials to H2S. Synth. Met. 160, 1708 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2010.06.005.
M. Trapatseli, D. Vernardou, P. Tzanetakis, and E. Spanakis, Field emission properties of low-temperature, hydrothermally grown tungsten oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3, 2726 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/am200519w.
R. Mukherjee and P.P. Sahay, Improved electrochromic performance in sprayed WO3 thin films upon Sb doping. J. Alloy. Compd. 660, 336 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.11.138.
N. Naseri, R. Azimirad, O. Akhavan, and A.Z. Moshfegh, Improved electrochromical properties of sol-gel WO3 thin films by doping gold nanocrystals. Thin Solid Films 518, 2250 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2009.08.001.
J. Thangala, S. Vaddiraju, R. Bogale, R. Thurman, T. Powers, B. Deb, and M.K. Sunkara, Large-scale, hot-filament-assisted synthesis of tungsten oxide and related transition metal oxide nanowires. Small 3, 890 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200600689.
J. Zhang, X.L. Wang, X.H. Xia, C.D. Gu, Z.J. Zhao, and J.P. Tu, Enhanced electrochromic performance of macroporous WO3 films formed by anodic oxidation of DC-sputtered tungsten layers. Electrochim. Acta 55, 6953 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.06.082.
K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, Sathish, V. Madhavi, and S. Abdul Sattar, On the bonding and electrochemical performance of sputter deposited WO3 thin films. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 872, 012147 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/872/1/012147.
K.N. Kumar, S.A. Sattar, G.V. Ashok Reddy, R.I. Jafri, R. Premkumar, M.R. Meera, A.A. Ahamed, M. Muthukrishnan, M. Dhananjaya, and A.M. Tighezza, Structural, optical, and electrochromic properties of RT and annealed sputtered tungsten trioxide (WO3) thin films for electrochromic applications by using GLAD technique. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 1934 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11285-x.
K.N. Kumar, G. Nithya, H. Shaik, L.N. Chandrashekar, P. Aishwarya, and A.S. Pawar, Optical and electrochromic properties of DC magnetron sputter deposited tungsten oxide thin films at different electrolyte concentrations and vertex potentials for smart window applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 789 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10180-9.
A.R. GV, K.N. Kumar, S. Abdul, H.D. Shetty, N. Guru, R.I. Jafri, C. Devaraja, B.C. Manjunatha, C.S. Kaliprasad, R. Premkumar, and S. Ansar, Physica B: condensed Matter Effect of post annealing on DC magnetron sputtered tungsten oxide (WO3) thin films for smartwindow applications. Phys. B Condens Matter 664, 414996 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2023.414996.
K.N. Kumar, H. Shaik, J. Gupta, S. Abdul, I. Jafri, A. Pawar, V. Madhavi, A.R. GV, and G. Nithya, Sputter deposited tungsten oxide thin films and nanopillars: electrochromic perspective. Mater. Chem. Phys. 278, 125706 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.125706.
K. Naveen Kumar, G. Nithya, H. Shaik, B. Hemanth, M. Chethana, K. Kishore, V. Madhavi, R.I. Jafri, S.A. Sattar, J. Gupta, and G.V. Ashok Reddy, Simulation and fabrication of tungsten oxide thin films for electrochromic applications. Phys. B Condens Matter 640, 413932 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2022.413932.
K.N. Kumar, S.A. Sattar, H. Shaik, A.R. GV, R.I. Jafri, M. Dhananjaya, A.S. Pawar, N.G. Prakash, R. Premkumar, S. Ansar, L.N. Chandrashekar, and P. Aishwarya, Effect of partial pressure of oxygen, target current, and annealing on DC sputtered tungsten oxide (WO3) thin films for electrochromic applications. Solid State Ion 399, 116275 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2023.116275.
G.V. Ashok Reddy, H. Shaik, K. Naveen Kumar, R. Imran Jafri, S.A. Sattar, J. Gupta, and B.H. Doreswamy, Thickness dependent tungsten trioxide thin films deposited using DC magnetron sputtering for electrochromic applications. Mater. Today Proc. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.11.134.
K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, V. Madhavi, R. Imran Jafri, J. Gupta, G. Nithya, S.A. Sattar, and G.V. Ashok Reddy, Glancing angle sputter deposited tungsten trioxide (WO3) thin films for electrochromic applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 128, 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-06124-5.
G. Nithya, K.N. Kumar, R. Sai Yashwanth, W. Baig, S.V. Sai Ganesh, S. Hanvish Kumar, Simulation, deposition, and characterization of WO3 and multilayered WO3/Ag thin film structure for smart window applications, in: 2023 International Conference on Recent Advances in Science and Engineering Technology (ICRASET, IEEE, 2023), pp. 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRASET59632.2023.10420072.
V. Madhavi, P. Kondaiah, H. Shaik, K.N. Kumar, T.S.S. Kumar Naik, G.M. Rao, and P.C. Ramamurthy, Fabrication of porous 1D WO3 NRs and WO3/BiVO4 hetero junction photoanode for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting. Mater. Chem. Phys. 274, 125095 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125095.
K.N. Kumar, G. Nithya, H. Shaik, L.N. Chandrashekar, P. Aishwarya, and A.S. Pawar, Optical and electrochromic properties of DC magnetron sputter deposited tungsten oxide thin films at different electrolyte concentrations and vertex potentials for smart window applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 789 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10180-9.
J. Gupta, H. Shaik, K.N. Kumar, S.A. Sattar, and G.V.A. Reddy, Optimization of deposition rate for E-beam fabricated tungsten oxide thin films towards profound electrochromic applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 128, 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05609-7.
J. Gutpa, H. Shaik, K. Naveen Kumar, and S.A. Sattar, Optimization of GLAD angle for E-beam-fabricated Tungsten oxide (WO3) thin films towards novel electrochromic behavior. J. Electron. Mater. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10036-8.
J.Z. Ou, S. Balendhran, M.R. Field, D.G. McCulloch, A.S. Zoolfakar, R.A. Rani, S. Zhuiykov, A.P. O’Mullane, and K. Kalantar-Zadeh, The anodized crystalline WO3 nanoporous network with enhanced electrochromic properties. Nanoscale 4, 5980 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2nr31203d.
J. Zhang, J.P. Tu, X.H. Xia, X.L. Wang, and C.D. Gu, Hydrothermally synthesized WO3 nanowire arrays with highly improved electrochromic performance. J. Mater. Chem. 21, 5492 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm04361c.
A.R. GV, K. Naveen Kumar, H. Shaik, H.D. Shetty, R. Imran Jafri, S. Abdul Sattar, K. Kamath, and B.H. Doreswamy, Growth of cerium oxide nanorods by hydrothermal method and electrochromic properties of CeO2/WO3 hybrid thin films for smart window applications. Mater. Today Proc. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.11.316.
G.V. Ashok Reddy, S.A. Sattar, K. Naveen Kumar, C.S. KaliPrasad, C. Devaraja, R. Imran Jafri, and B.H. Doreswamy, Effect of tungsten oxide thin films deposited on cerium oxide nano rods for electrochromic applications. Opt. Mater. 134, 113220 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.113220.
A.R. GV, K.N. Kumar, H. Shaik, R.I. Jafri, R. Naik, and B.H. Doreswamy, Optical and electrochromic properties of CeO2/WO3 hybrid thin films prepared by hydrothermal and sputtering. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 70, 1 (2022).
G.V. Ashok Reddy, K.N. Kumar, S.A. Sattar, N.G. Prakash, B. Daruka Prasad, M. Dhananjaya, G.R. Kumar, H.S. Yogananda, S.M. Hunagund, and S. Ansar, Structural, optical, and electrochromic properties of rare earth material (CeO2)/transitional metal oxide (WO3) thin film composite structure for electrochromic applications. Ionics (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-023-05078-9.
G.F. Cai, J.P. Tu, D. Zhou, X.L. Wang, and C.D. Gu, Growth of vertically aligned hierarchical WO3 nano-architecture arrays on transparent conducting substrates with outstanding electrochromic performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 124, 103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2014.01.042.
V. Madhavi, P. Kondaiah, O.M. Hussain, and S. Uthanna, Structural, optical, and luminescence properties of reactive magnetron sputtered tungsten oxide thin films. Int. Scholar. Res. Not. 2012, 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/801468.
S.H. Mohamed, H.A. Mohamed, and H.A. Abd El Ghani, Development of structural and optical properties of WOx films upon increasing oxygen partial pressure during reactive sputtering. Phys. B 406, 831 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2010.12.005.
S.H. Lee, H.M. Cheong, C.E. Tracy, A. Mascarenhas, D.K. Benson, and S.K. Deb, Raman spectroscopic studies of electrochromic a-WO3. Electrochim. Acta 44, 3111 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(99)00027-4.
J. Gabrusenoks, A. Veispals, A. Von Czarnowski, and K.H. Meiwes-Broer, Infrared and Raman spectroscopy of WO3 and CdWO4. Electrochim. Acta 46, 2229 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(01)00364-4.
R. Chandra, A.K. Chawla, and P. Ayyub, Optical and structural properties of sputter-deposited nanocrystalline Cu2O films: effect of sputtering gas. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 6, 1119 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2006.176.
A.K. Chawla, S. Singhal, H.O. Gupta, and R. Chandra, Effect of sputtering gas on structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline tungsten oxide films. Thin Solid Films 517, 1042 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2008.06.068.
M.B. Babu and K.V. Madhuri, Synthesis and electrochromic properties of nanocrystalline WO3 thin films. Phys. B Condens. Matter 584, 412068 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.412068.
C.K. Wang, D.R. Sahu, S.C. Wang, C.K. Lin, and J.L. Huang, Structural evolution and chemical bonds in electrochromic WO3 films during electrochemical cycles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 45, 225303 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/45/22/225303.
K.J. Patel, G.G. Bhatt, S.S. Patel, R.R. Desai, J.R. Ray, C.J. Panchal, P. Suryavanshi, V.A. Kheraj, and A.S. Opanasyuk, Thickness-dependent electrochromic properties of amorphous tungsten trioxide thin films. J. Nano Electron. Phys. 9, 03040 (2017). https://doi.org/10.21272/jnep.9(3).03040.
V. Madhavi, P. Kondaiah, O.M. Hussain, and S. Uthanna, Structural, optical and electrochromic properties of RF magnetron sputtered WO3 thin films. Phys. B 454, 141 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2014.07.029.
C.S. Hsu, C.C. Chan, H.T. Huang, C.H. Peng, and W.C. Hsu, Electrochromic properties of nanocrystalline MoO3 thin films. Thin Solid Films 516, 4839 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2007.09.019.
B. Wen-Cheun Au, A. Tamang, D. Knipp, and K.Y. Chan, Post-annealing effect on the electrochromic properties of WO3 films. Opt. Mater. 108, 110426 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2020.110426.
X. Sun, Z. Liu, and H. Cao, Electrochromic properties of N-doped tungsten oxide thin films prepared by reactive DC-pulsed sputtering. Thin Solid Films 519, 3032 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2010.12.017.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Nitte Meenakshi Institute of Technology, Bengaluru, India, for providing facilities, and the work was supported by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSPD2023R765), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K.N., Reddy, G.V.A., Sattar, S.A. et al. Effect of Oxygen Flow Rate, Post-annealing Temperature, and Different Electrolyte Concentrations on WO3 Thin Films Deposited by DC Magnetron Sputtering For Electrochromic Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 53, 2351–2366 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11000-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-024-11000-4