Abstract
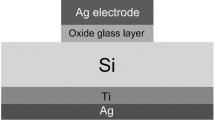
The development of high-efficiency n-type crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cells primarily depends on the application of silver–aluminum (Ag–Al) paste metallization. To deeply reveal and clarify the formation mechanism of the ohmic contact between Ag–Al paste and the p+-Si emitter, the microstructure of the Ag/Si contact interface and the migration of Al to the interface during sintering were investigated. The results showed that the sintered Ag/Si interface contained a glass phase layer with a thickness less than 500 nm, in which a large number of Ag colloids were embedded. This is the same as the Ag/Si contact interface formed by Ag paste metallization on p-type c-Si cells. Compared with Ag paste, Ag–Al paste provides a considerably lower contact resistance with the p+ emitter. Electrical tests revealed a smaller Ag/Si contact resistance and higher Ag electrode resistance with increasing Al concentrations in the Ag–Al paste. In the study of the action mechanism of Al, scanning electron microscopy images illustrated that during sintering, Al powder dissolves in the glass melt at ~ 600°C and reaches the contact interface with the flowing glass melt. As the temperature exceeded 700°C, the mutual diffusion of Al-Si across the Ag/Si contact interface enables Al to enter the Si substrate. The electrochemical capacitance–voltage test results confirmed that the p-type doping concentration of Al in the Si surface significantly increased, leading to a reduction in the shunt resistance. Consequently, the formation of Ag/Si ohmic contact with significantly low contact resistance was completed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Mat Desa, S. Sapeai, A.W. Azhari, K. Sopian, M.Y. Sulaiman, N. Amin, and S.H. Zaidi, Silicon back Contact Solar Cell Configuration: A Pathway Towards Higher Efficiency. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 60, 1516 (2016).
M. Taguchi, A. Yano, S. Tohoda, K. Matsuyama, Y. Nakamura, T. Nishiwaki, K. Fujita, and E. Maruyama, 24.7% Record Efficiency HIT Solar Cell on Thin Silicon Wafer. IEEE J. Photovolt. 4L, 96 (2014).
R. Guerrero-Lemus, R. Vega, T. Kim, A. Kimm, and L.E. Shephard, Bifacial Solar Photovoltaics: A Technology Review. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 60, 1533 (2016).
F. Feldmann, M. Bivour, C. Reichel, M. Hermle, and S.W. Glunz, Passivated Rear Contacts for High-Efficiency n-type Si Solar Cells Providing High Interface Passivation Quality and Excellent Transport Characteristics. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 120, 270 (2014).
K. Yoshikawa, W. Yoshida, T. Irie, H. Kawasaki, K. Konishi, H. Ishibashi, T. Asatani, D. Adachi, M. Kanematsu, H. Uzu, and K. Yamamoto, Exceeding Conversion Efficiency of 26% by Heterojunction Interdigitated Back Contact Solar Cell with thin Film Si Technology. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 173, 37 (2017).
H. Kerp, S. Kim, R. Lago, F. Recart, I. Freire, L. Pérez, K. Albertsen, J.C. Jiméno, A. Shaikh, Development of screenprintable contacts for p+ emitters in bifacial solar cells, in Proceedings of the 21st European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference (2006), p.393
R. Lago, L. Pérez, H. Kerp, I. Freire, I. Hoces, N. Azkona, F. Recart, and J.C. Jimeno, Screen Printing Metallization of Boron Emitters. Prog. Photovolt. Res. Appl. 18, 20 (2010).
R. Kopecek, T. Buck, J. Libal, R. Petres, I. Rover, K. Wambach, R. Kinderman, L.J. Geerligs, P. Fath, Large Area N-Type Multicrystalline Silicon Solar Cells with B-Emitter: Efficiencies Exceeding 14%, in 15th International Photovoltaic Science and Engineering Conference (2005)
S. Riegel, F. Mutter, T. Lauermann, B. Terheiden, and G. Hahn, Review on Screen Printed Metallization on p-type Silicon. Energy Procedia 21, 14 (2012).
F. Huster, Investigation of the alloying process of screen printed aluminum pastes for the BSF formation on silicon solar cells, in Proceedings of the 20th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference (2005), p.4
C. Park, S. Chung, N. Balaji, S. Ahn, S. Lee, J. Park, and J. Yi, Analysis of Contact Reaction Phenomenon between Aluminum-Silver and p+ Diffused Layer for n-Type c-Si Solar Cell Applications. Energies 13, 4537 (2020).
E. Lohmüller, S. Werner, R. Hoenig, J. Greulich, and F. Clement, Impact of Boron Doping Profiles on the Specific Contact Resistance of Screen Printed Ag–Al Contacts on Silicon. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 142, 2 (2015).
L. Liang, Z. Li, L.K. Cheng, N. Takeda, R.J.S. Young, and A. Carroll, Current Conduction Mechanism of Front-Side Contact of N-Type Crystalline Si Solar Cells With Ag/Al Pastes. IEEE J. Photovolt. 4, 549 (2014).
L. Liang, Z.G. Li, L.K. Cheng, N. Takeda, and A.F. Carroll, Microstructural Characterization and Current Conduction Mechanisms of Front-Side Contact of n-type Crystalline Si Solar Cells with Ag/Al Pastes. J. Appl. Phys. 117, 215102 (2015).
P. Kumar, M. Pfeffer, B. Willsch, O. Eibl, L.J. Koduvelikulathu, V.D. Mihailetchi, and R. Kopecek, N-type Single-Crystalline Si Solar Cells: Front Side Metallization for Solar Cells Reaching 20% efficiency. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 157, 200 (2016).
P. Kumar, Z. Aabdin, M. Pfeffer, and O. Eibl, High-Efficiency, Single-Crystalline, p- and n-type Si Solar Cells: Microstructure and Chemical Analysis of the Glass Layer. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 178, 52 (2018).
S. Fritz, S. Riegel, S. Gloger, D. Kohler, M. König, M. Hörtheis, and G. Hahn, Influence of Emitter Properties on Contact Formation to P+ Silicon. Energy Procedia 38, 720 (2013).
S. Riegel, F. Mutter, G. Hahn, and B. Terheiden, Influence of the Dopant on the Contact Formation to p+-type Silicon. Energy Procedia 8, 533 (2011).
F.D. Heinz, M. Breitwieser, P. Gundel, M. König, M. Hörteis, W. Warta, and M.C. Schubert, Microscopic Origin of the Aluminium Assisted Spiking Effects in n-type Silicon Solar Cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 131, 105 (2014).
T. Aoyama, M. Aoki, I. Sumita, Y. Yoshino, and A. Ogura, Effects of Aluminum in Metallization Paste on the Electrical Losses in Bifacial N-type Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells. Energy Procedia 98, 106 (2016).
T. Urban, K. Krügel, and J. Heitmann, Formation of Ag-Al Alloy in Context of PERC Solar Cell Metallization. Energy Procedia 124, 930 (2017).
L.K. Cheng, L. Liang, Z. Li, Ieee, Nano-Ag Colloids Assisted Tunneling Mechanism for Current Conduction in Front Contact of Crystalline Si Solar Cells, in 34th Ieee Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (2009), p.2402
S. Körner, F. Kiefer, R. Peibst, F. Heinemeyer, J. Krügener, and M. Eberstein, Basic Study on the Influence of Glass Composition and Aluminum Content on the Ag/Al Paste Contact Formation to Boron Emitters. Energy Procedia 67, 20 (2015).
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Xing, J., Yang, Y. et al. Ohimc Contact Formation Mechanism of Silver–Aluminum Paste Metallization on the p+ Emitter of n-Type Crystalline Silicon Solar Cells. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 5717–5722 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09821-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-09821-2