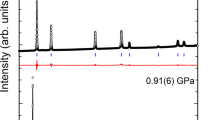
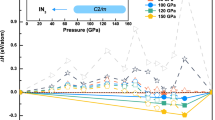
Abstract
In regards to the crystal structure of the halogen compound iodine chloride (ICl), only the experimental and theoretical structure P21/c under ambient pressure is known up to now. However, the insulator material under ambient pressure may have a metal phase transition under high pressure, resulting in more excellent properties. Here, by employing the first-principles computations and the Crystal structure AnaLYsis with Particle Swarm Optimization (CALYPSO) structure prediction technique, we studied the structure and electronic properties of ICl under high pressure. The phase sequence of ICl was established, and two high-pressure phases (Imma and P4/mmm) with six and eight coordinations, respectively, were proposed. The structure optimization demonstrated that ICl sustained the following phase transitions at high pressure: P21/c→Imma→P4/mmm, which occurred at ~14 GPa and ~46 GPa, respectively. We also found that the P21/c phase was a mixed compound containing both covalent and ionic bonds, and the Imma and P4/mmm phases were ionic compounds. Finally, the mechanical and dynamical stabilities of all phases were confirmed by the calculations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.M. Ma, M. Eremets, A.R. Oganov, Y. Xie, I. Trojan, S. Medvedev, A.O. Lyakhov, M. Valle, and V. Prakapenka, Transparent dense sodium. Nature 458, 182 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07786.
L. Wang, H. Wang, and Y. Wang, Substitutional alloy of Bi and Te at high pressure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 145501 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.106.145501.
W. Yanchao, X. Meiling, Y. Liuxiang, and Y. Bingmin, Pressure-stabilized divalent ozonide CaO3and its impact on Earth’s oxygen cycles. Nat. Commun. 11, 1–7 (2020).
L.J. Zhang, Y.C. Wang, J. Lv, and Y. Ma, Materials discovery at high pressures. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2, 17005 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/natrevmats.2017.5.
Y. Ma, M. Eremets, A.R. Oganov, Y. Xie, I. Trojan, S. Medvedev, A.O. Lyakhov, M. Valle, and V. Prakapenka, A hypervalent and cubically coordinated molecular phase of IF8predicted at high pressure. Chem. Sci. 10, 2543 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SC04635B.
C. Wang, Y.X. Liu, X. Chen, P. Lv, H.R. Sun, and X.B. Liu, Pressure-induced unexpected 2 oxidation states of bromine and superconductivity in magnesium bromide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22, 3066 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cp05627k.
F. Tian, K. Luo, C.L. Xie, B. Liu, X.W. Liang, L.Y. Wang, G.A. Gamage, H.R. Sun, H. Ziyaee, J.Y. Sun, Z.S. Zhao, B. Xu, G.Y. Gao, and X.F. Zhou, Mechanical properties of boron arsenide single crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 114, 131903 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5093289.
A.G. Sharpe, Interhalogen compounds and polyhalides. Rev. Chem. Soc. 4, 115 (1950). https://doi.org/10.1039/QR9500400115.
K.H. Boswijk, J. Heide, A. Vos, and E.H. Wiebenga, The Crystal Structure of α-ICl. Acta Cryst. 9, 274 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0365110X56000760.
R. Minkwitz, M. Berkei, Neuuntersuchung der Kristall-strukturvon α-ICl,Zeitschrift F¨ur Naturforschung B, 54,1615 (1999) https://doi.org/10.1515/znb-1999-1224
A. Jain, S.Y. Ping, G. Hautier, W. Chen, W.D. Richards, S. Dacek, S. Cholia, D. Gunter, D. Skinner, G. Ceder, and K.A. Persson, Commentary: The Materials Project: A materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation. APL Mater. 1, 011002 (2013).
F.D. Murnaghan, The compressibility of media under extreme pressures. Proc. N. A. S. 30, 244 (1944). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.30.9.244.
A.D. Becke, and K.E. Edgecombe, A simple measure of electron localization in atomic and molecular systems. J. Chem. Phys. 92, 5397 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.458517.
S. Baroni, S. Gironcoli, A.D. Corso, and P. Giannozzi, Phonons and related crystal properties from density-functionalperturbation theory. Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 515 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.73.515.
Q.C. Tong, J. Lv, P.Y. Gao, and Y.C. Wang, The CALYPSO methodology for structure prediction. Chin. Phys. B 28, 106105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab4174.
Y.C. Wang, J. Lv, L. Zhu, and Y.M. Ma, CALYPSO: a method for crystals tructure prediction. Comput. Phys. Commun. 183, 2063 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2012.05.008.
Y.C. Wang, J. Lv, L. Zhu, and Y.M. Ma, Crystal structure prediction via particle-swarm optimization. Phys. Rev. B 82, 094116 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.82.094116.
J. Kennedy and R. Eberhart, MHS’95. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Micro Machine and Human Science, 39-43.IEEE, Nagoya, Japan (2002) https://doi.org/10.1109/MHS.1995.494215
C. A. Coello and M. S. Lechuga, Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. CEC’02(Cat. No.02TH8600), 1051-1056.IEEE, Honolulu, HI,USA (2002) https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2002.1004388
C. Tang, G. Kour, and A.J. Du, Recent progress on the prediction of two-dimensional materials using CALYPSO. Chin. Phys. B 28, 107306 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab41ea.
S.S. Zhang, J.L. He, Z.S. Zhao, D.L. Yu, and Y.J. Tian, Discovery of superhard materials via CALYPSO methodology. Chin. Phys. B 28, 1061 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab4179.
Y.C. Wang, M.S. Miao, J. Lv, L. Zhu, K.T. Yin, H.Y. Liu, and Y.M. Ma, An effective structure prediction method for layered materials based on 2D particle swarm optimization algorithm. J. Chem. Phys. 137, 224108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4769731.
A. Hermann, Geoscience material structures prediction via CALYPSO methodology. Chin. Phys. B 28, 106105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab43bc.
W.W. Cui, and Y.W. Li, The role of CALYPSO in the discovery of high-Tchydrogen-rich superconductors. Chin. Phys. B 28, 107104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/ab4253.
S. Baroni, P. Giannozzi, and A. Testa, Green’s-function approach to linear response in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 1861 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.1861.
R.D. King-Smith, and R.J. Needs, A new and efficient scheme for first-principles calculations of phonon spectra. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2, 3431 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/2/15/001.
G. Kresse, and J. Furthmüller, Efficient iterative schemes forab initiototal-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 54, 11169 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169.
J.P. Perdew, J.A. Chevary, S.H. Vosko, K.A. Jackson, M.P. Pederson, D.J. Singh, and C. Fiolhais, Atoms, molecules, solids, and surfaces: applications of the generalized gradient approximation for exchange and correlation. Phys. Rev. B 46, 6671 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.46.6671.
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof, Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.3865.
J. Hao, Y.W. Li, Q. Zhou, D. Liu, M. Li, F.F. Li, W.W. Lei, X.H. Chen, Y.M. Ma, Q.L. Cui, G.T. Zou, J. Liu, and X.D. Li, Structural phase transformations of Mg3N2 at high pressure: experimental and theoretical studies. Inorg. Chem. 48, 9737 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/ic901324n.
A.V. Krukau, O.A. Vydrov, A.F. Izmaylov, and G.E. Scuseria, Influence of the exchange screening parameter on the performance ofscreened hybrid functionals. J. Chem. Phys. 125, 224106 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2404663.
J. Heyd, G.E. Scuseria, and M. Ernzerhof, Hybrid functionals based on a screened Coulomb potential. J. Chem. Phys. 118, 8207 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1564060.
P.E. Blochl, Project oraugmented-wave method. Phys. Rev. B 50, 17953 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.50.17953.
K. G and J. D, From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method, Phys. Rev. B, 59, 1758 (1999) https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758
D.J. Chadi, Special points for Brilloofn-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 16, 1746 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.16.1746.
V. Wang, N. Xu, J.C. Liu, G. Tang, and W.T. Geng, V ASPKIT: a user-friendly interface facilitating high-throughput computing and analysis using V ASP code. Comput. Phys. Commun. 267, 108033 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2021.108033.
J.Y. Lin, Z.Y. Zhao, C.Y. Liu, J. Zhang, X. Du, G.C. Yang, and Y.M. Ma, IrF8 molecular crystal under high pressure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 141, 5409 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b00069.
L.J. Zhang, X. Bao, Y. Sun, X.J. Ma, T.J. Ou, and P.F. Li, High-pressure crystal structure and properties of BrCl. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 33, 095401 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-648X/abcc10.
X. Zhong, L.H. Yang, X. Qu, Y.C. Wang, J.H. Yang, and Y.M. Ma, Crystal structures and electronic properties of oxygen-rich titanium oxides at high pressure. Inorg. Chem. 57, 3254 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b03263.
J.Y. Lin, S.T. Zhang, W. Guan, G.C. Yang, and Y.M. Ma, Gold with +4 and +6 oxidation states in AuF4 and AuF6. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 9545 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b04563.
F.X. Ma, Y.L. Jiao, G.P. Gao, Y.T. Gu, A. Bilic, Z.F. Chen, and A.J. Du, Graphene-like two-dimensional ionic boron with double dirac cones at ambient condition. Nano Lett. 15, 3022 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b05292.
F. Mouhat, and F.X. Coudert, Necessary and sufficient elastic stability conditionsin variouscrystal systems. Phys. Rev. B 90, 224104 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.90.224104.
S.F. Pugh, XCII Relations between the elastic moduli and the plastic properties of polycrystalline pure metals. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philosophical Mag. J. Sci. 45, 823 (1954). https://doi.org/10.1080/14786440808520496.
V. Kanchana, G. Vaitheeswaran, Y. Ma, Y. Xie, A. Svane, and O. Eriksson, Density functional study of elastic and vibrational properties of the Heusler-type alloys Fe2V Al and Fe2VGa. Phys. Rev. B 80, 125108 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.125108.
C.M. Blair Jr., and D.M. Yost, The thermodynamic constants of iodine monochloride, iodine monobromide and bromine monochloride in carbon tetrachloride solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 55, 4489–4496 (1933). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01338a026.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11964026), the Natural Science Basic Research plan in Shaanxi Province of China (No. 2020JM-621), the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia (Nos. 2019MS01010, 2020BS01001, 2020BS01009), the Scientific Research Projects in Colleges and Universities in Inner Mongolia (No. NJZZ19145), the Projects in Inner Mongolia Minzu University (Nos. BS511, NMDYB18021, BS531, BS439).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, X., Feng, L., Zhang, X. et al. Study on New High-Pressure Phases and Electronic Properties of Iodine Chloride Employing Ab Initio Calculations. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 1632–1638 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09424-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09424-3