Abstract
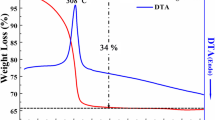
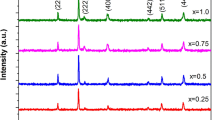
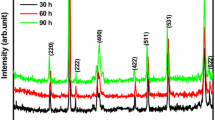
This paper reports a series of investigations on the frequency and temperature dependent dielectric and magnetic properties of manganese doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. The investigated samples were prepared via solid state reaction using planetary ball milling. The nature in the variation of the relative dielectric constant of the investigated sample with Mn content (x) = 0.375 and 0.5 as a function of frequency demonstrates the normal behavior for the selected temperature at 77 K and 300 K. However, the relaxation single peaks are noted at 100 kHz for selected temperatures of 148 K, 165 K, and 236 K, which mark the ferrimagnetic-to-ferromagnetic phase transition. This transition may have originated from the dominance of anisotropy energy at a lower temperature. The values of relative dielectric constant for the samples are found to be higher than that at room temperature, which shows the relative dielectric constant to be strongly dependent on temperature. Their D-factor values are observed to be much lower in the low temperature region (below room temperature) and exhibit normal variation with an increase of frequency. The higher values of relative dielectric constant may make the samples suitable to be used in spaceborne applications. The enhanced saturation magnetization is observed due to calcination at elevated temperature (900°C). The effect of Mn content (x) is found to lessen the saturation magnetization due to the substitution of Fe3+ cation in the B site according to Neel’s two-sublattice model. The decreasing nature in the real part of permeability matches the spin-glass of the materials of the investigated system due to the tendency of their frozen spins in the lower temperature region. In addition, the decreasing trend in the Weiss constant with Mn content is also the signature of the spin-glass of the materials in the lower temperature region due to the decreased magnetic exchange interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Bawawaje, M. Hashi, and I. Ismail, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 1433 (2011).
R. Ahmad, H.I. Gul, M. Zarrar, H. Anwar, M.B. Khan, and A. Khan, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 405, 28 (2016).
Y.D. Kolekar, L. Sanchez, E.J. Rubio, and C.V. Ramana, Solid State Commun. 184, 34 (2014).
N. Sivakumar, A. Narayanasamy, C.N. Chinnasamy, and B. Jeyadevan, J. Phys. Condens. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/38/386201.
N. Ponpandian, P. Balaya, and A. Narayanasami, J. Phys. Condens 14, 3221 (2002).
J.P. Singh, H. Kumar, A. Singhal, N. Sarin, R.C. Srivastava, and K.H. Chae, Appl. Sci. Lett. (2016). https://doi.org/10.17571/appslett.2016.02001.
H. Kumar, R.C. Srivastava, J.P. Singh, P. Negi, H.M. Agrawal, D. Das, and K. HwaChae, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 16 (2016).
M.Z. Ahsan and F.A. Khan, Mater SciNanotechnol. 2, 1 (2018).
M.Z. Ahsan, F.A. Khan, M.A. Islam, T. Tanzina, and M.K. Alam, J. Phys. Commun. 2, 105008 (2018).
M.Z. Ahsan, F.A. Khan, and M.A. Islam, Results Phys. 14, 102484 (2019).
M.Z. Ahsan and F.A. Khan, J. Phys. Sci. Appl. (2017). https://doi.org/10.17265/2159-5348/2017.06.005.
M.N. Akhtar and M.A. Khan, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 421, 260 (2017).
S.P. Yadav, S.S. Shinde, A.A. Kadam, and K.Y. Rajpure, J. Semicond. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/093002.
A.A. Khadem, S.S. Shinde, S.P. Yadv, P.S. Patil, and K.Y. Rajpur, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329, 59 (2013).
G.H. Jonker, J PhysChem Solids. 9, 165 (1959).
R. Nongjai, S. Khan, K. Asokan, H. Ahmed, and I. Khan, Appl. Phys. 112, 084321 (2012).
I.C. NlebedimY and C.Jiles Melikhov, J. Appl. Phys. 15, 043903 (2014).
M.Z. Ahsan, F.A. Khan, and M.A. Islam, Int. J. Mat. Sci. Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ijmsa.20180706.11.
A. Saini, P. Kumar, B. Ravelo, S. Lallechere, A. Thakur, and P. Thakur, Eng. Sci. Technol. 19, 911 (2016).
S. Tapdiya, Adv. Mat. Proc. 2, 547 (2017).
Koferstein, J. Mater. Sci. 48, 6509 (2013).
Rashed, J. Mater. Sci. 42, 5248 (2007).
A. Hossain, M.S.I. Sarker, and M.K.R. Khan, Appl. Phys. A (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-2042-2.
S. Roy and J. Ghose, J. Appl. Phys. 87, 6226 (2000).
Y. Melikhov, J.E. Snyder, D.C. Jiles, A.P. Ring, J.A. Paulsen, C.C.H. Lo, and K.W. Dennis, J. Appl. Phys. 99, 08R102 (2006).
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the International Science Programme (ISP), Uppsala University, Sweden, for financial and technical support, and also to the department of physics, Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology and the department of physics, Military Institute of Science and Technology for experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahsan, M.Z., Khan, F.A. & Islam, M.A. Frequency and Temperature Dependent Dielectric and Magnetic Properties of Manganese Doped Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 7721–7729 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07583-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07583-y