Abstract
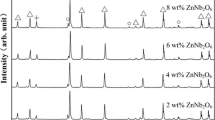
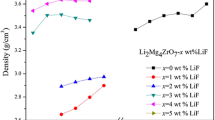
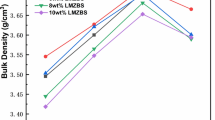
The microstructure, sintering behavior, and microwave dielectric properties of LiZn1−xCoxPO4 (x = 0.00–0.10) ceramics were investigated. All these materials were synthesized by the traditional solid-state reaction method. Component and microstructure of the ceramics were verified by x-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), respectively. The substitution of Co2+-ion to Zn2+-ion would improve the densification level of composite ceramics, and the microwave dielectric properties would be changed accordingly. An excellent microwave dielectric property of LiZn1−xCoxPO4 (x = 0.00–0.10) was achieved when x = 0.07 (ɛr = 5.43, Q × f = 35,446 GHz at 15 GHz, τf = − 77.4 ppm/°C). In order to achieve reliable thermal stability, Pb1.5Nb2O6.5 was used to adjust its τf value. The LiZn0.93Co0.07PO4 ceramics with 6 vol.% Pb1.5Nb2O6.5 sintered at 750°C for 4 h shows a near-zero τf value of − 4.4 ppm/°C, ɛr = 6.09, Q × f = 14,305 GHz (at 15 GHz), and there was no chemical reaction between Pb1.5Nb2O6.5 and LiZn0.93Co0.07PO4. The composite ceramics are promising materials for millimeter-wave device applications in the field of low temperature co-fired ceramics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Ohsato, T. Tsunooka, A. Kan, Y. Ohishi, Y. Miyauchi, Y. Tohdo, T. Okawa, K. Kakimoto, and H. Ogawa, Key Eng. Mater. 269, 195 (2004).
X.-C. Wang, W. Lei, R. Ang, and W.-Z. Lu, Ceram. Int. 39, 1707 (2013).
S.-H. Kweon, M.-R. Joung, J.-S. Kim, B.-Y. Kim, S. Nahm, J.-H. Paik, Y.-S. Kim, and T.-H. Sung, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1995 (2011).
H.-W. Chen, H. Su, H.-W. Zhang, T.-C. Zhou, B.-W. Zhang, J.-F. Zhang, and X.-L. Tang, Ceram. Int. 40, 14655 (2014).
A. Feteira and D.C. Sinclair, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 1338 (2008).
G.-G. Yao, P. Liu, H.-W. Zhang, and J. Calame, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 1691 (2013).
S. George, P.S. Anjana, V.N. Deepu, P. Mohanan, and M.T. Sebastian, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 1244 (2009).
J.-S. Kim, N.-H. Nguyen, J.-B. Lim, D.-S. Paik, S. Nahm, J.-H. Paik, J.-H. Kim, and H.-J. Lee, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 671 (2008).
Z. Cheng, X. Hu, Y. Li, Z. Ling, and N. Alford, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 99, 2688 (2016).
Z.W. Dong, Y. Zheng, P. Cheng, X.P. Lv, and W. Zhou, Ceram. Int. 40, 12983 (2014).
K. Fukuda, R. Kitoh, and I. Awai, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 32, 4584 (1993).
Z.W. Dong, Y. Zheng, P. Cheng, X.P. Lv, W.Y. Zhang, W. Zhou, and W.H. Xiong, Ceram. Int. 40, 14865 (2014).
C.C. Xia, D.H. Jiang, G.H. Chen, Y. Luo, B. Li, C.L. Yuan, and C.R. Zhou, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 12026 (2017).
C. Zhang, R. Zuo, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, and J. Jones, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 98, 702 (2015).
M.B. Bechir, A.B. Rhaiem, and K. Guidara, Bull. Mater. Sci. 37, 473 (2014).
T. Sugiyama, T. Tsunooka, K.-I. Kakimoto, and H. Ohsato, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 26, 2097 (2006).
R.D. Shannon, J. Appl. Phys. 73, 348 (1993).
R. Ubic and I.M. Reaney, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 85, 2472 (2010).
B.W. Hakki and P.D. Coleman, IRE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 8, 402 (2003).
H. Zhuang, Z. Yue, F. Zhao, J. Pei, and L. Li, J. Alloys Compd. 472, 411 (2009).
Y. Lv, R. Zuo, Y. Cheng, C. Zhang, and P. Davies, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 3862 (2013).
M. Guo, G. Dou, S. Gong, and D. Zhou, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 883 (2012).
V.L. Gurevich and A.K. Tagantsev, Adv. Phys. 40, 719 (1991).
S.J. Penn, N.M. Alford, A. Templeton, X. Wang, M. Xu, M. Reece, and K. Schrapel, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 80, 1885 (1997).
Y.-N. Wang, Y.-C. Chen, S.-L. Yao, and C.-Y. Wu, Ceram. Int. 40, 2641 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank National key R&D program No. 2017YFB0406300, Sichuan science and technology supporting program Nos. 2016GZ0245 and 2016GZ0261, Guizhou science and technology major projects [2016] No. 3011, and the Dongguan entrepreneurial talent program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, R., Li, Y., Yu, G. et al. Effect of Co2+ Substitution on the Microwave Dielectric Properties of LiZnPO4 Ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 47, 7281–7287 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6665-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6665-z