Abstract
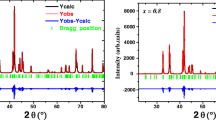
The Sm-Ni-Fe ternary system has been investigated at 773 K by means of powder x-ray diffraction, metallography and scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy. The isothermal section consists of 16 single-phase regions, 29 two-phase regions and 14 three-phase regions. The influence of Fe-doping on the structure and the microwave absorption properties of the SmNi5 compound has been systematically studied. The homogeneity range in Sm16.67Ni83.33−x Fe x was determined as x = 16.67. The lattice parameters were found to gradually increase and the particle size become much finer with the increase of Fe concentration. All the samples exhibited good microwave absorption properties in the X-band (8–12 GHz). The highest reflection loss of the Sm16.67Ni83.33−x Fe x (x = 0.0, 5.0, 10.0,15.0, 16.67) alloys are −10.12 dB, −10.39 dB, −16.44 dB, −20.69 dB, and −43.05 dB at 6.96 GHz, 7.92 GHz, 8.56 GHz, 10.04 GHz, and 11.08 GHz, respectively. The absorption peak shifted towards the higher frequency region with the increasing amount of Fe substitution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Liu, F. Luo, J.B. Su, W.C. Zhou, and D.M. Zhu, J. Electron. Mater. 44, 867 (2015).
A.L. Gaeta, M. Gruneisen, and R.W. Boyd, IEEE. J. Quantum Electron. 22, 1095 (1986).
X.H. Ren and G.L. Xu, Magn. Magn. Mater. 354, 44 (2014).
J. Zhan, Y.L. Yao, C.F. Zhang, and C.J. Li, J. Alloys Compd. 585, 240 (2014).
G.Z. Xie, P. Wang, B.S. Zhang, L.K. Yuan, Y. Shi, P.H. Lin, and H.X. Lu, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 1026 (2008).
X.X. Wang, M.M. Lu, W.Q. Cao, B. Wen, and M.S. Cao, Mater. Lett. 125, 107 (2014).
S.Y. Zhang and Q.X. Cao, Mater. Sci. Eng., B 177, 678 (2012).
X. Wang, R.Z. Gong, P.G. Li, L.Y. Liu, and W.M. Cheng, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 466, 178 (2007).
G.B. Sun, B.X. Dong, M.H. Cao, B.Q. Wei, and C.W. Hu, Chem. Mater. 23, 1587 (2011).
L. Wei, R. Che, Y. Jiang, and B. Yu, J. Environ. Sci.-China 25, S27 (2013).
W. Xie, H.F. Cheng, Z.Y. Chu, Z.H. Chen, Y.J. Zhou, and C.G. Long, Adv. Mater. Res. 150, 1336 (2010).
H.Y. Zhou, Y.G. Zhu, J.Q. Liu, Y.H. Zhuang, and S.L. Yuan, J. Alloys. Compd. 345, 167 (2002).
J.Q. Liu, J. Alloys. Compd. 232, 269 (1996).
J.X. Zheng, H.Y. Zhou, and J. Chin, Soc. Rare Earths. 4, 79 (1986).
D.X. Lü, C.P. Guo, C.R. Li, and Z.M. Du, Phys. Proc. 50, 383 (2013).
S.K. Pan, J.L. Xiong, Q.R. Yao, G.H. Rao, L.C. Cheng, and H.Y. Zhou, J. Alloys Compd. 646, 399 (2015).
K. Nouri, M. Jemmali, S. Walha, K. Zehani, L. Bessais, and A.B. Salah, J. Alloys Compd. 661, 508 (2016).
Y.Y. Pan and J.X. Zhang, Acta. Phys. Sin. 32, 92 (1983).
S. Takeda, Y. Kitano, and Y. Komura, J. Less. Comm. Metals. 84, 317 (1982).
L.I. Duarte, U.E. Klotz, C. Leinenbach, M. Palm, F. Stein, and J.F. Löffler, Intermetallics 18, 374 (2010).
L.C. Cheng, J.L. Xiong, H.Y. Zhou, S.K. Pan, and H.H. Huang, J. Electron. Mater. 45, 1023 (2016).
E. Michielssen, J.M. Sajer, S. Ranjithan, and R. Mittra, IEEE. Trans. Microw. Theory 41, 1024 (1993).
S.B. Liao, Ferromagnetic (Part II) (Beijing: Science Press, 1988), pp. 3–90.
K. Yanagimoto, K. Majima, S. Sunada, and Y. Aikawa, J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder. Metal. 51, 293 (2004).
A. Paoluzi, F. Albertini, and L. Pareti, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 212, 183 (2000).
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 51361007, Nos. 51371061, 2016YFB0700901,) and Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 2014GXNSFAA11833, 2016GXNSFGA38001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Q., Shen, Y., Yang, P. et al. The Sm-Ni-Fe System: Isothermal Section and Microwave Absorption Properties. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 1971–1976 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5313-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5313-3