Abstract
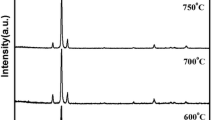
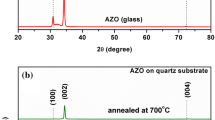
Aluminum-doped zinc oxide (ZnO:Al) thin films were synthesized by atomic layer deposition on silicon, quartz and sapphire substrates and characterized by x-ray diffraction (XRD), high-resolution scanning electron microscopy, optical spectroscopy, conductivity mapping, Hall effect measurements and positron annihilation spectroscopy. XRD showed that the as-grown films are of single-phase ZnO wurtzite structure and do not contain any secondary or impurity phases. The type of substrate was found to affect the orientation and degree of crystallinity of the films but had no effect on the defect structure or the transport properties of the films. High conductivity of 10−3 Ω cm, electron mobility of 20 cm2/Vs and carrier density of 1020 cm−3 were measured in most films. Thermal treatments in various atmospheres induced a large effect on the thickness, structure and electrical properties of the films. Annealing in a Zn and nitrogen environment at 400°C for 1 h led to a 16% increase in the thickness of the film; this indicates that Zn extracts oxygen atoms from the matrix and forms new layers of ZnO. On the other hand, annealing in a hydrogen atmosphere led to the emergence of an Al2O3 peak in the XRD pattern, which implies that hydrogen and Al atoms compete to occupy Zn sites in the ZnO lattice. Only ambient air annealing had an effect on film defect density and electrical properties, generating reductions in conductivity and electron mobility. Depth-resolved measurements of positron annihilation spectroscopy revealed short positron diffusion lengths and high concentrations of defects in all as-grown films. However, these defects did not diminish the electrical conductivity in the films.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Chen, Z.L. Pei, C. Sun, J. Gong, R.F. Huang, and L.S. Wen, Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid 85, 212 (2001).
P.R. Chalker, P.A. Marshall, S. Romani, J.W. Roberts, S.J.C. Irvine, D.A. Lamb, A.J. Clayton, and P.A. Williams, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 31, 01A120 (2013).
J.K. Srivastava, L. Agrarwal, and A.B. Bhattacharyya, J. Electrochem. Soc. 136, 3414 (1989).
K. Hazra and S. Basu, Solid State Electron. 49, 1158 (2005).
K.L. Chopra, S. Major, and D.K. Pandya, Thin Solid Films 102, 1 (1983).
H. Li, L.K. Schirra, J. Shim, H. Cheun, B. Kippelen, O.L.A. Monti, and J.L. Bredas, Chem. Mater. 24, 3044 (2012).
F.A. Selim, M.C. Tarun, D.E. Wall, L.A. Boatner, and M.D. McCluskey, Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 202109 (2011).
Y. Liu, L. Zhao, and J. Lian, Vacuum 81, 1 (2006).
L. Znaidi, T. Touman, D. Vrel, N. Souded, S.B. Yahia, O. Brinza, A. Fischer, and A. Boudrioua, Coatings 3, 126 (2013).
H. Gómez, A. Maldonado, R. Castanedo-Pérez, G. Torres-Delgado, and M.D.L.L. Olvera, Mater. Charact. 58, 708 (2007).
H. Mondragón-Suárez, A. Maldonado, M.D.L.L. Olvera, A. Reyes, R. Castanedo-Pérez, G. Torres-Delgado, and R. Asomoza, Appl. Surf. Sci. 193, 52 (2002).
D. Kim, I. Yun, and H. Kim, Curr. Appl. Phys. 10, S459 (2010).
A.C. Jones and M.L. Hitchman, Chemical Vapour Deposition: Precursors, Processes and Applications (Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry, 2009).
T. Nam, C.W. Lee, H.J. Kim, and H. Kim, Appl. Surf. Sci. 295, 260 (2014).
Y. Geng, L. Guo, S.S. Xu, Q.Q. Sun, S.J. Ding, H.L. Lu, and D.W. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 12317 (2011).
N.P. Dasgupta, N. Sebastian, L. Wonyoung, O. Trejo, J.R. Lee, and F.B. Prinz, Chem. Mater. 22, 4769 (2010).
G. Luka, T.A. Krajewski, B.S. Witkowski, G. Wisz, I.S. Virt, E. Guziewicz, and M. Godlewski, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 22, 1810 (2011).
R. Krause-Rehberg and H. Leipner, Positron Annihilation in Semiconductors (NewYork: Springer, 1999).
F.A. Selim, C.R. Varney, M.C. Tarun, M.C. Rowe, G.S. Collins, and M.D. McCluskey, Phys. Rev. B 88, 174102 (2013).
F.A. Selim, D. Winarski, C.R. Varney, M.C. Tarun, J. Ji, and M.D. McCluskey, Results Phys. 5, 28 (2015).
J. Čížek, J. Valenta, P. Hruška, O. Melikhova, I. Procházka, M. Novotný, and J. Bulíř, Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 251902 (2015).
L.J. Brillson, Z. Zhang, D.R. Doutt, D.C. Look, B.G. Svensson, AYu Kuznetsov, and F. Tuomisto, Phys. Status Solidi B 250, 2110 (2013).
F.A. Selim, M.H. Weber, D. Solodovnikov, and K.G. Lynn, Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 085502 (2007).
P. Hautojaervi, Positrons in Solids (Heidelberg: Springer, 1979).
P. Schultz and K.G. Lynn, Rev. Mod. Phys. 60, 701 (1988).
F.A. Selim, D.P. Wells, J.F. Harmon, and J. Williams, J. Appl. Phys. 97, 113539 (2005).
R. Kuzel, J. Czek, and M. Novotny, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 44A, 45 (2013).
D.J. Winarski, W. Anwand, A. Wagner, P. Saadatkia, F.A. Selim, M. Allen, B. Wenner, K. Leedy, J. Allen, S. Tetlak, and D.C. Look, AIP Adv. 6, 095004 (2016).
O. Byeong-Yun, M.-C. Jeong, D.-S. Kim, W. Lee, and J.-M. Myoung, J. Cryst. Growth 281, 475 (2005).
W.R. Saleh, N.M. Saeed, W.A. Twej, and M. Alwan, Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2, 1 (2012).
C.X. Xu, G.P. Zhu, X. Li, Y. Yang, S.T. Tan, X.W. Sun, C. Lincoln, and T.A. Smith, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 9 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR-SFFP-2015). Work at Bowling Green State University was funded by a 2016 CURS award (Cordula Mora), BGSU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haseman, M., Saadatkia, P., Winarski, D.J. et al. Effects of Substrate and Post-Growth Treatments on the Microstructure and Properties of ZnO Thin Films Prepared by Atomic Layer Deposition. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 6337–6345 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5025-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-5025-0