Abstract
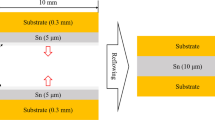
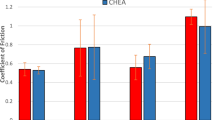
The effect of reflow time on wetting behavior of Sn-2.5Ag-0.5Cu lead-free solder on bare and nickel-coated copper substrates has been investigated. The solder alloy was reflowed at 270°C for various reflow times of 10 s, 100 s, 300 s, and 500 s. On bare copper substrate, the intermetallic compound (IMC) thickness increased with increase in reflow time, whereas on Ni-coated Cu substrate, the IMC thickness increased up to 300 s followed by a drop for solder alloy reflowed for 500 s. The spreading behavior of the solder alloy was categorized into capillary, gravity (diffusion), and viscous zones. Gravity zone was obtained from 3.8 ± 0.43 s to 38.97 ± 3.38 s and from 5.99 ± 0.5 s to 77.82 ± 8.84 s for the Sn-2.5Ag-0.5Cu/Cu and Sn-2.5Ag-0.5Cu/Ni/Cu system, respectively. Sn-2.5Ag-0.5Cu solder alloy was also reflowed for the period corresponding to the end of the gravity zone (40 s and 80 s on bare and Ni-coated Cu, respectively). The joint strength was maximum at reflow time of 40 s and 80 s for the Sn-2.5Ag-0.5Cu/Cu and Sn-2.5Ag-0.5Cu/Ni/Cu system, respectively. The dynamic contact angle at the end of the gravity (diffusion) zone (θ gz) was found to be a better parameter compared with the stabilized contact angle (θ f) to assess the effect of the wettability of the liquid solder on the microstructure and joint strength. The present investigation reveals the significance of the gravity zone in assessment of optimum reflow time for lead-free solder alloys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Tsukamoto, T. Nishimura, S. Suenaga, and K. Nogita, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 171, 162 (2010).
D.Q. Yu, J. Zhao, and L. Wang, J. Alloys Compd. 376, 170 (2004).
C.Y. Ho and J.G. Duh, Mater. Lett. 92, 278 (2013).
Satyanarayan and K.N. Prabhu, Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 166, 87 (2011).
B.L. Silva, N. Cheung, A. Garcia, and J.E. Spinelli, Mater. Lett. 142, 163 (2015).
M. Arra, D. Shangguan, E. Ristolainen, and T. Lepisto, Solder Surf. Mt. Tech. 14, 18 (2002).
M.S. Park, M.K. Stephenson, C. Shannon, L.A.C. Diaz, K.A. Hudspeth, S.L. Gibbons, M.J. Saldana, and R. Arroyave, Acta Mater. 60, 5125 (2012).
M. Sona and K.N. Prabhu, Trans. Indian Inst. Met. (2015). doi:10.1007/s12666-015-0590-0.
S. Amore, E. Ricci, G. Borzone, and R. Novakovic, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 495, 108 (2008).
M. Sona and K.N. Prabhu, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. El. 24, 3149 (2013).
A. Choubey, H. Yu, M. Osterman, M. Pecht, F. Yun, L. Yonghong, and X. Ming, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 1130 (2008).
A.A.E. Daly and A.M.E. Taher, Mater. Des. 47, 607 (2013).
T. Laurila and V. Vuorinen, Materials 2, 1796 (2009).
D. Mu, H. Huang, and K. Nogita, Mater. Lett. 86, 46 (2012).
J. Pan, J. Wang, and D.M. Shaddock, Proceedings of the 37th International Symposium on Microelectronics, (2004).
M.N. Islam, Y.C. Chan, A. Sharif, and M.O. Alam, Microelectron. Reliab. 43, 2031 (2003).
T. You, Y. Kim, W. Jung, J. Moon, and H. Choe, J. Alloys Compd. 486, 242 (2009).
C.M. Chen and H.C. Lin, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1937 (2006).
M. Sona and K.N. Prabhu, SMTA J. 28, 36 (2015).
Z. Dariavach, P. Callahan, J. Liang, and R. Fournelle, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1581 (2006).
C.K. Wong, J.H.L. Pang, J.W. Tew, B.K. Lok, H.J. Lu, F.L. Ng, and Y.F. Sun, Microelectron. Reliab. 48, 611 (2008).
A. Zribi, A. Clark, L. Zavalij, P. Borgesen, and E.J. Cotts, J. Electron. Mater. 30, 1157 (2001).
M. Schaefer, R. Fournelle, and J. Liang, J. Electron. Mater. 27, 1167 (1998).
J.M. Song, C.W. Su, Y.S. Lai, and Y.T. Chiu, J. Mater. Res. 25, 629 (2010).
Q.K. Zhang, J. Tan, and Z.F. Zhang, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 014502 (2011).
D. Mu, H. Yasuda, H. Huang, and K. Nogita, J. Alloys Compd. 536, 38 (2012).
D. Mu, H. Huang, S.D. McDonald, J. Read, and K. Nogita, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 566, 126 (2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sona, M., Prabhu, K.N. Effect of Reflow Time on Wetting Behavior, Microstructure Evolution, and Joint Strength of Sn-2.5Ag-0.5Cu Solder on Bare and Nickel-Coated Copper Substrates. J. Electron. Mater. 45, 3744–3758 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4504-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4504-7