Abstract
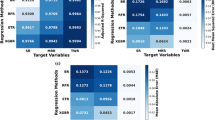
Machine learning (ML) algorithms have been proven to be effective methods in steel design and production processes. In this study, the feature analysis and prediction of slag entrapment in continuous casting process were carried out based on XGBoost model. Results show that the area under the curve (AUC) and accuracy of BO-XGBoost are 0.811 and 0.756, respectively, which are higher than PSO-XGBoost and GA-XGBoost. Feature analysis shows that mold flux, oscillation frequency, serial number, inner arc, casting speed (CS) and slab width are the key features which affect the entrapped slag defect, based on Gini coefficient and SHAP values. In addition, partial dependence plots of SHAP value suggest that it is conducive to product the qualified slabs with less entrapped slag defect, when the oscillation frequency is 60–140 cpm, inner arc is 7.5–9.5 m, CS is 0.35–1.2 m/min, serial number is less than 5, slab width is less than 1300 mm and 2# mold flux.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.K. Dhua: J. Fail. Anal. Prev., 2019, vol. 19, pp. 1023–33.
Y. Chung and A.W. Cramb: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31B, pp. 957–71.
P. Rocabois, J. Lehmann, C. Gatellier, and J.P. Teres: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2003, vol. 30, pp. 95–100.
M. Iguchi, Y. Sumida, R. Okada, and Z. Morita: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 164–70.
S.M. Cho, B.G. Thomas, and S.H. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2019, vol. 50B, pp. 52–76.
I. Okamura, K. Baba, T. Takahashi, and H. Shiomi: IECON Proc., 1991, vol. 1, pp. 37–41.
K. Son, J. Lee, H. Hwang, W. Jeon, H. Yang, I. Sohn, Y. Kim, and H. Um: J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2021, vol. 12, pp. 555–68.
J. Xiong, T.Y. Zhang, and S.Q. Shi: Sci. China: Technol. Sci., 2020, vol. 63, pp. 1247–55.
T. Chen and C. Guestrin: Proc. ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. Knowl. Discov. Data Min., 2016, vol. 13–17, pp. 785–94.
Y. Qiu, J. Zhou, M. Khandelwal, H. Yang, P. Yang, and C. Li: Eng. Comput., 2022, vol. 38, pp. 4145–62.
K. Budholiya, S.K. Shrivastava, and V. Sharma: J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci., 2022, vol. 34, pp. 4514–23.
J.H. Friedman: Ann. Stat., 2001, vol. 29, pp. 1189–1232.
K. Song, F. Yan, T. Ding, L. Gao, and S. Lu: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2020, vol. 174, 109472.
B. Shahriari, K. Swersky, Z. Wang, R.P. Adams, and N. de Freitas: Proc. IEEE, 2016, vol. 104, pp. 148–75.
L. Yang and A. Shami: Neurocomputing, 2020, vol. 415, pp. 295–316.
R. Shi, X. Xu, J. Li, and Y. Li: Appl. Soft Comput., 2021, vol. 109, 107538.
T.M. Shami, A.A. El-Saleh, M. Alswaitti, Q. Al-Tashi, M.A. Summakieh, and S. Mirjalili: IEEE Access, 2022, vol. 10, pp. 10031–61.
M. Jain, V. Saihjpal, N. Singh, and S.B. Singh: Appl. Sci., 2022, vol. 12, p. 8392.
F. Marini and B. Walczak: Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst., 2015, vol. 149, pp. 153–65.
S. Katoch, S.S. Chauhan, and V. Kumar: Multimed. Tools Appl., 2021, vol. 80, pp. 8091–8126.
D. Whitley: Stat. Comput., 1994, vol. 4, pp. 65–85.
J. Huang and C.X. Ling: IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., 2005, vol. 17, pp. 299–310.
W. Dong, Y. Huang, B. Lehane, and G. Ma: Autom. Constr., 2020, vol. 114, 103155.
Z. Xu, D. Shen, T. Nie, Y. Kou, N. Yin, and X. Han: Inf. Sci., 2021, vol. 572, pp. 574–89.
J.A. Sáez, J. Luengo, J. Stefanowski, and F. Herrera: Inf. Sci., 2015, vol. 291, pp. 184–203.
H. Cao, X. Xie, J. Shi, and Y. Wang: J. Hydrol., 2022, vol. 610, 127933.
B. Lu, W. Wang, J. Li, H. Zhao, and D. Huang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 365–77.
K.C. Mills, A.B. Fox, Z. Li, and R.P. Thackray: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2005, vol. 32, pp. 26–34.
A.B. Parsa, A. Movahedi, H. Taghipour, S. Derrible, and A. Mohammadian: Accid. Anal. Prev., 2020, vol. 136, 105405.
Y. Meng, N. Yang, Z. Qian, and G. Zhang: J. Theoret. Appl. Electron. Commer. Res., 2021, vol. 16, pp. 466–90.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province [Grant numbers 2022JJ10081], National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant number 52174327, 52374348, U1760202], and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Y., Wang, W., Zhou, L. et al. Prediction and Feature Analysis of Entrapped Slag Defect on Casting Slab Based on Optimized XGBoost Model. Metall Mater Trans B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03092-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03092-4