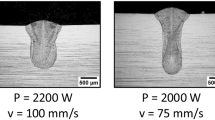
Abstract
Type 316L(N) stainless steel (SS) weld joints were made by employing advanced welding processes such as laser, hybrid laser-MIG (HLM) and hybrid laser-TIG (HLT). First, the welding parameters were identified and full penetration joints were fabricated using 5.6-mm-thick plates. To understand the residual stresses and distortion in weld joints, thermomechanical analysis of advanced welding processes has been performed. The validation of model predictions was carried out experimentally. The hybrid double ellipsoidal heat source coupled with a conical heat source model was used to analyze hybrid welding processes, and the conical model with a cylindrical shell was used for laser welding process. The heat source parameters were fine-tuned by matching the simulated weld profile with the experimentally obtained profile. Thermocouple measurements verified the simulated thermal cycles. Then the predicted temperature distribution was sequentially coupled to the mechanical analysis considering the isotropic hardening model. The simulated residual stresses were confirmed by experimental measurements employing an ultrasonic technique with longitudinally critically refracted (LCR) waves. The hybrid heat source model was found to be accurate for the thermomechanical analysis of the laser and hybrid laser welding of 316L(N) SS. Spot analysis showed that the HAZ of the weld joints exhibited higher residual stresses than the weld metal. The longitudinal tensile residual stress values are lower for the TIG/MIG part than the laser part in the through-thickness direction for the hybrid welds. The weld joint’s measured distortion values are generally low and found to correlate with the weld metal volume.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.B. Vogt, J. Foct, C. Regnard, G. Robert, and J. Dhers: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22, pp. 2385–92.
P. Aubert, F. Tavassoli, M. Rieth, E. Diegele, and Y. Poitevin: J. Nucl. Mater., 2011, vol. 417, pp. 43–50.
C. Casavola and C. Pappalettere: in Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series., Springer, New York, NY, 2004.
S. Grünenwald, T. Seefeld, and M. Kocak: Phys. Procedia, 2010, vol. 5, pp. 77–87.
M. Gao, C. Chen, S. Mei, L. Wang, and X. Zeng: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2014, vol. 74, pp. 199–208.
J.-N. Yang, L.-J. Zhang, J. Ning, Q.-L. Bai, X.-Q. Yin, and J.-X. Zhang: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2017, vol. 91, pp. 3749–73.
S.A. Tsirkas: Opt. Laser Technol., 2018, vol. 100, pp. 45–56.
E.W. Reutzel, S.M. Kelly, R.P. Martukanitz, M.M. Bugarewicz, and P. Michaleris: ASM Proc. Int. Conf. Trends Weld. Res., 2005, vol. 2005, pp. 143–8.
W. Piekarska and M. Kubiak: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2011, vol. 54, pp. 4966–74.
H.S. Bang, H.S. Bang, Y.C. Kim, and I.H. Oh: Mater. Des., 2011, vol. 32, pp. 2328–33.
D. Li, H. Ji, Y. Liu, G. Gou, H. Chen, J. Liu, and L. Meng: Adv. Mater. Res., 2012, vol. 399–401, pp. 2040–3.
G.X. Xu, C.S. Wu, G.L. Qin, X.Y. Wang, and S.Y. Lin: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2011, vol. 57, pp. 245–55.
T. Zhang, C.S. Wu, G.L. Qin, X.Y. Wang, and S.Y. Lin: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2010, vol. 47, pp. 848–56.
N. Yazdian, E.D. Derakhshan, and R. Kovacevic: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, vol. 98, pp. 2725–35.
X. Zhan, Y. Wu, Y. Kang, X. Liu, and X. Chen: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, vol. 101, pp. 1611–22.
L. Chen, G. Mi, X. Zhang, and C. Wang: Mater. Des., 2019, vol. 168, p. 107653.
E.D. Derakhshan, N. Yazdian, B. Craft, S. Smith, and R. Kovacevic: Opt. Laser Technol., 2018, vol. 104, pp. 170–82.
M. Ragavendran and M. Vasudevan: Mater. Manuf. Process., 2020, 24:1–13.
J.J. Dike and G.C. Johnson: NDT E Int., 1995, vol. 2, p. 118.
D.E. Bray and W. Tang: Nucl. Eng. Des., 2001, vol. 207, pp. 231–40.
H. Lu, X.S. Liu, J.G. Yang, S.P. Zhang, and H.Y. Fang: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2008, vol. 13, pp. 70–4.
H. Zhang: IEEE Int. Ultrason. Symp. IUS, 2014, pp. 1352–5.
P. Palanichamy, M. Vasudevan, and T. Jayakumar: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2009, vol. 14, pp. 166–71.
D. Deng, C. Zhang, X. Pu, and W. Liang: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, vol. 26, pp. 1494–505.
F. Kong, J. Ma, and R. Kovacevic: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2011, vol. 211, pp. 1102–11.
A.R. Lawrence and P. Michaleris: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2011, vol. 16, pp. 215–20.
P. Michaleris: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2011, vol. 16, pp. 363–8.
P. Colegrove, C. Ikeagu, A. Thistlethwaite, S. Williams, T. Nagy, W. Suder, A. Steuwer, and T. Pirling: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2009, vol. 14, pp. 717–25.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the ARCI-Hyderabad, India, for extending their facility to carry out the work. Special thanks are due to Laser Material Processing Lab ARCI-Hyderabad, India, for their tremendous help and support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted December 23, 2020; accepted April 23, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ragavendran, M., Vasudevan, M. Effect of Laser and Hybrid Laser Welding Processes on the Residual Stresses and Distortion in AISI Type 316L(N) Stainless Steel Weld Joints. Metall Mater Trans B 52, 2582–2603 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02202-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-021-02202-w