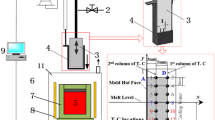
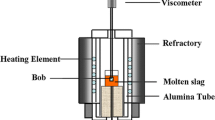
Abstract
To compensate the negative effect caused by the absorption of chromium oxide inclusions during the casting process of Cr-contained steels, a new mold flux system has been designed and investigated. The melting temperature range of the newly designed mold flux system is from [1124 K to 1395 K (851 °C to 1122 °C)]. The viscosity at 1573 K (1300 °C) and the break temperature increase with the addition of MnO and Cr2O3 but decrease with the addition of B2O3. The crystalline fraction of mold flux decreases from 81 to 42.1 pct with the addition of MnO and Cr2O3, and then further decreases to 25.3 pct with the addition of B2O3; however, it improves from 54.4 to 81.5 pct when the basicity increases. Besides, the heat-transfer ability of mold flux is inverse to the crystallization ratio of the slag. The comprehensive study of the properties for the four designed mold fluxes suggests that the mold flux with 1.15 basicity-3.01 pct B2O3-1.10 pct MnO-2.10 pct Cr2O3 shows the best properties for the continuous casting of Cr-contained steels.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Yan, S. Huang, L. Pandelaers, J.V. Dyck, M. Guo, and B. Blanpain: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 1105–19.
T. Nakasuga, K. Nakashima, and K. Mori: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 665–72.
Y. Okabe, I. Tajima, and K. Ito: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 19B, pp. 131–36.
L. Zhang: JOM, 2012, vol. 64, pp. 1059–62.
B.G. Thomas, Q. Yuan, S. Mahmood, R. Liu, and R. Chaudhary: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45B, pp. 22–35.
H. Arai, K. Matsumoto, S. Shimasaki, and S. Taniguchi: ISIJ Int., 2009, vol. 49, pp. 965–74.
G.A. Khater and M.H. Idris: Ceram. Int., 2009, vol. 35, pp. 69–75.
V.K. Marghussian and S. Arjomandnia: Phys. Chem. Glasses, 1999, vol. 40, pp. 311–13.
M.A. Bin Hussain, M.H. Idrees, and M.M. Khan: J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2002, vol. 67, pp. 563–77.
L. Barbieri, C. Leonelli, T. Manfredini, G.C. Pellacani, G.C. Pellacani, E. Tondello, and R. Bertoncello: J. Mater. Sci., 1994, vol. 29, pp. 6273–80.
C. Xu, W. Wang, L. Zhou, S. Xie, and C. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 882–92.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, F. Ma, J. Li, J. Wei, H. Matsuura, and F. Tsukihashi: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 354–62.
W. Wang, X. Yan, L. Zhou, S. Xie, and D. Huang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47B, pp. 963–73.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, D. Huang, J. Wei, and J. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 925–36.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, R. Liu, and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44B, pp. 1264–79.
L. Zhou, W. Wang, and K. Zhou: Metals, 2016, vol. 6, pp. 139–53.
W. Wang and A.W. Cramb: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 1864–70.
W. Wang, K. Blazek, and A. Cramb: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 66–74.
J.V. Beck: 1HCP1D: Version 5.31, Beck Engineering Consultants Company, Houston, TX, 1997.
A. Muan and S. Omiya: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1960, vol. 43, pp. 204–09.
A.B. Fox, M.E. Valdez, J. Gisby, R.C. Atwood, P.D. Lee, and S. Sridhar: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol. 44, pp. 836–45.
H. Kim and I. Sohn: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1–8.
K.C. Mills, A.B. Fox, Z. Li, and R.P. Thackray: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2005, vol. 32, pp. 26–34.
G. Kim, C. Kim, and I. Sohn: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 170–76.
S. Ozawa, M. Susa, T. Goto, R. Endo, and K.C. Mills: ISIJ Int., 2006, vol. 46, pp. 413–19.
J. Cho, H. Shibata, T. Emi, and M. Suzuki: ISIJ Int., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 834–42.
Acknowledgments
The financial support from the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51504294 and U1760202) is great acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 28, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Yu, J., Zhou, L. et al. Optimization of Mold Flux for the Continuous Casting of Cr-Contained Steels. Metall Mater Trans B 49, 1580–1587 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1279-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1279-7