Abstract
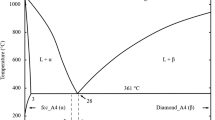
Joining delicate electronic components for high-temperature applications is challenging. Regular soldering with lead-free or lead-based materials is typically not suitable for high-temperature applications due to their low melting points. Using off-eutectic compounds for joints offer an easy and gentle process creating joints that can be formed at a lower process temperature than the final operation temperature. Microstructural evolution near the eutectic melting point is key to be able to form reliable joints. A layered Au/eutectic Au-Ge/Au structure was used to form Au-rich off-eutectic Au-Ge joints. Columnar-like structures of primary \( \alpha \)-phase (Au) protruded through a Ge-rich off-eutectic Au-Ge mixture at the center of the joint. These structures connect the joined pieces with a single solid phase with a melting point of ca. 1064 °C. The microstructure coarsened when exposed to temperatures between 300 °C and 380 °C, i.e., near the eutectic melting point at 361 °C. Ge diffused and accumulated along grain boundaries between Au grains. Annealing above the eutectic melting point, Ge rapidly diffused and formed larger colonies of pure Ge surrounded by a Au matrix. This accords well with our previously published results demonstrating shear strength capacity of similar joints at temperatures well above the eutectic temperature.









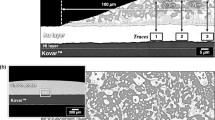
Reproduced with permission from Ref. [20]

Reproduced with permission from Ref. [20]








Similar content being viewed by others
References
1 V.R. Manikam and K.Y. Cheong: Components, Packag. Manuf. Technol. IEEE Trans., 2011, vol. 1, pp. 457–478.
F. Roccaforte, P. Fiorenza, G. Greco, R. Lo-Nigro, F. Giannazzo, F. Iucolano, M. Saggio, R. Lo, F. Giannazzo, F. Iucolano, and M. Saggio: Microelectron. Eng., 2018, vol. 187–188, pp. 66–77.
3 W.D. MacDonald and T.W. Eagar: Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1992, vol. 22, pp. 23–46.
W.D. MacDonald and T.W. Eagar: Met. Sci. Join., 1992, pp. 93–100.
5 W.D. MacDonald and T.W. Eagar: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 315–25.
6 W.F. Gale and D.A. Butts: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2004, vol. 9, pp. 283–300.
7 G.O. Cook and C.D. Sorensen: J. Mater. Sci., 2011, vol. 46, pp. 5305–23.
8 L. Bernstein: J. Electrochem. Soc., 1966, vol. 113, pp. 1282–9.
9 L. Bernstein and H. Bartholomew: Trans. Metall. Soc. Aime, 1966, vol. 236, pp. 405–12.
10 H. Liu, K. Wang, K.E. Aasmundtveit, and N. Hoivik: J. Electron. Mater., 2012, vol. 41, pp. 2453–62.
11 K.S. Siow: J. Electron. Mater., 2014, vol. 43, pp. 947–61.
12 F. Yu, J. Cui, Z. Zhou, K. Fang, R.W. Johnson, and M.C. Hamilton: IEEE Trans. Power Electron., 2017, vol. 32, pp. 7083–95.
13 S.A. Paknejad and S.H. Mannan: Microelectron. Reliab., 2017, vol. 70, pp. 1–11.
14 V. Chidambaram, H.B. Yeung, and G. Shan: J. Electron. Mater., 2012, vol. 41, pp. 2107–17.
15 A. Drevin-Bazin, F. Lacroix, and J.F. Barbot: J. Electron. Mater., 2014, vol. 43, pp. 695–701.
S. Tanimoto, K. Matsui, Y. Murakami, H. Yamaguchi, and H. Okumura: in IMAPS Int. Conf. High Temp. Election. (HiTEC), IMAPS, Albuquerque, NM, 2010.
17 H. Okamoto and T.B. Massalski: Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1983, vol. 4, pp. 190–8.
18 H. Okamoto and T.B. Massalski: Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1984, vol. 5, pp. 601–10.
19 H. Okamoto: J. Phase Equilibria Diffus., 2004, vol. 25, pp. 197–8.
20 A. Larsson, T.A. Tollefsen, and K.E. Aasmundtveit: Microelectron. Reliab., 2019, vol. 99, pp. 31–43.
A. Larsson, T.A. Tollefsen, O.M. Løvvik, and K.E. Aasmundtveit: in Eur. Microelectron. Packag. Conf. (EMPC), IMAPS, Warsaw, 2017.
A. Larsson, C.B. Thoresen, and T. Aamli: in Proc. Tech. Program—Pan Pac. Microelectron. Symp. (Pan Pacific), IEEE, Kauai, HI, 2019.
A. Larsson and C.B. Thoresen: IEEE Trans. Compon., Packag. Manuf. Technol., 2019, p. 11.
24 R.M. Waghorne, V.G. Rivlin, and G.I. Williams: J. Phys. F Met. Phys., 1976, vol. 6, pp. 147–56.
25 R.P. Elliott and F.A. Shunk: Bull. Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1980, vol. 1, pp. 51–4.
26 J. Wang, C. Leinenbach, and M. Roth: J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, vol. 481, pp. 830–6.
MIL-STD-883H, 2010.
28 F.C. Campbell: Elements of Metallurgy and Engineering Alloys, ASM International, 2008.
29 R.J.D. Tilley: Understanding Solids : The Science of Materials, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Chichester, UK, 2004.
30 H. Okamoto: Desk Handbook: Phase Diagrams for Binary Alloys, 2nd edn., ASM International, United States of America, 2010.
31 G. Humpston and D.M. Jacobson: Principles of Soldering, ASM International, 2004.
J.D. Verhoeven: Fundamentals of Physical Metallurgy. Wiley, Hoboken, 1975, pp. 169-215.
M.E. Glicksman: Principles of Solidification, Springer, New York, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-7344-3
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Christian Thoresen (USN). The authors would also like to acknowledge Torleif A. Tollefsen (TEGma AS) and Ole Martin Løvvik (SINTEF) for their support in the project. We would like to thank TECHNI AS, TEGma AS, and The Norwegian Research Council for financial support of the project (Project No.: 244915).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted June 23, 2019.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsson, A., Aamundtveit, K.E. On the Microstructure of Off-Eutectic Au-Ge Joints: A High-Temperature Joint. Metall Mater Trans A 51, 740–749 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05530-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05530-4