Abstract
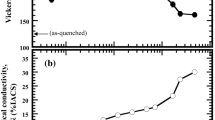
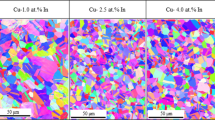
The strength and electrical conductivity of Cu-Ti alloy wires fabricated by over-aging and intense drawing were investigated as a function of Ti content (2.7 to 4.3 at. pct). The microstructure of all over-aged Cu-Ti alloys before drawing showed mainly coarse cellular components laminating the plates of a terminal Cu solid solution and a β-Cu4Ti intermetallic compound precipitated discontinuously by grain boundary reactions. The volume fraction of β-Cu4Ti plates increased with Ti content, although the compositions of the two phases remained unchanged. When the over-aged alloys were drawn to the same deformation strain, the hardness and tensile strength of the wires increased monotonically with Ti content due to strain-induced strengthening; a high volume fraction of hard β-Cu4Ti fibers formed from laminating plates during drawing promoted a high dislocation density in the matrix. The electrical conductivity of the wires decreased gradually with Ti content due to the higher volume fraction of β-Cu4Ti fibers and due decomposition of the fibers during drawing. The overall performance of the Cu-Ti alloy wires improved as the Ti content increased and was superior to that of conventional Cu-Ti alloy wires fabricated by peak-aging and drawing, and to that of commercial Cu-Be alloy wires.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Datta and W.A. Soffa: Acta Metall., 1976, vol. 24, pp. 987–1001.
S. Nagarjuna, M. Srinivas, K. Balasubramanian, and D. S. Sarma: Acta Metall., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 2285–2293.
A.A. Hameda and L. Blaz: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, vol. 254, pp. 83–89.
C. Borchers: Philos. Mag. A., 1999, vol. 79, pp.537–547.
W.A. Soffa and D. E. Laughlin: Prog. Mater. Sci., 2004, vol. 49, pp. 347–366.
D. Bozic, J. Stasic, J. Ruzic, M. Vilotijevic, and V. Rajkovic: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 8139–8144.
M. Sobhani, A. Mirhabibi, H. Arabi, and R.M.D. Brydson: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 577, pp. 16–22.
J.A. Cornie, A. Datta, and W.A. Soffa: Metal. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 727–733.
D.E. Laughlin and J.W. Cahn: Acta Metall., 1975, vol. 23, pp. 329–339.
L.A. Nesbit and D.E. Laughlin: Acta Metall., 1978, vol. 26, pp. 815–825.
W.A. Soffa and D.E. Laughlin: Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 3019–3028.
R. Markandeya, S. Nagarjuna, and D.S. Sarma: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, vol. 371, pp. 291–305.
I.S. Balta, A. Laik, G.B. Kale, G.K. Dey, and U.D. Kulkami: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 402, pp. 118–125.
S. Semboshi, T. Nishida, H. Numakura, T. Al-Kassab, and R. Kirchheim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 2136–2143.
S. Semboshi, S. Sato, M. Ishikuro, K. Wagatsuma, A. Iwase, and T. Takasugi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45A, pp. 3401–3411.
L. Si, L. Zhou, X. Zhu, L. Sanhua, S. Leinuo, and D. Qiyi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, vol. 650, pp. 345–353.
H. Wei, Y. Cui, H. Cui, Y. Wei, and L. Hou: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, vol. 707, pp. 392–398.
S. Semboshi, S. Amano, J. Fu, A. Iwase, and T. Takasugi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 1501–1511.
S. Semboshi, Y. Kaneno, T. Takasugi, and N. Masahashi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 4956–4964.
R.C. Ecob, J.V. Bee, and B. Ralph: Phys. Status Solidi, 1979, vol. 52A, pp. 201–210.
R.C. Ecob, J.V. Bee, and B. Ralph: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 1407–1414.
R.W. Fonda and G.J. Shiflet: Scr. Metall., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 2259–2262.
R.W. Fonda and G.J. Shiflet: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 2507–2518.
A.M. Elwazri, P. Wanjara, and S. Yue: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 404, pp. 91–98.
S.W. Joung, U.G. Kang, S.P. Hong, Y.W. Kim, and W.J. Nam: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 586, pp. 171–177.
Y. Li, D. Raabe, M. Herbig, P.P. Choi, S. Goto, A. Kostka, H. Yarita, C. Borchers, and R. Kirchheim: Phys. Rev. Lett., 2014, vol. 113, pp. 106104.
A. Durgaprasad, S. Giri, S. Lenkaa, S. Kundu, S. Mishra, S. Chandra, R.D. Doherty, and I. Samajdra: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 4583–4597.
C. Borchers, and R. Kirchheim: Prog. Mater.Sci., 2016, vol. 82, pp. 405–444.
D. Nikas, X.D. Zhang, and J. Ahlstrom: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, vol. 737, pp. 341–347.
Y. Sakai and H.-J. Schneider-Muntau: Acta Mater., 1997, vol. 45, pp. 1017–1023.
Y.Z. Tian, S.D. Wu, Z.F. Zhang, R.B. Figueiredo, N. Gao, and T.G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 4331–4336.
C. Biselli and D.C. Morris: Acta Mater., 1996, vol. 44, pp. 493–504.
Q. Feng, L. Song, Y. Zeng, Y. Fang, L. Meng, J. Liu, and H. Wang: J. Alloys Compd., 2015, vol. 640, pp. 45–50.
J.Y. Brun, S.J. Hamar-Thibault, and C.H. Allibert: Z. Metallk., 1983, vol. 74, pp. 525–529.
H. Doi, S. Suzuki, K. Mimura, K. Isshiki, and Y. Waseda: J. Japan Inst. Met., 2004, vol. 68, pp. 78–81.
S. Semboshi and T.J. Konno: J. Mater. Res., 2008, vol. 23, pp. 473–477.
M.A. Turchanin, P.G. Agraval, and A.R. Abdulov: Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 2008, vol. 47, pp. 344–360.
S. Semboshi, M. Ishikuro, S. Sato, K. Wagatsuma, and T. Takasugi: Mater. Charact., 2013, vol. 82, pp. 23–31.
S. Chen, Y.H. Duan, B. Huang, and W.C. Hu: Philos. Mag., 2015, vol. 95, pp. 3535–53.
R. Landauer: J. Appl. Phys., 1952, vol. 23, pp. 779–784.
J. Miyake and M.E. Fine: Acta Metall., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 733–741.
S. Suzuki, K. Hirabayashi, H. Shibata, K. Mimura, M. Isshiki, and Y. Waseda: Scr. Mater., 2003, vol. 48, pp. 431–435.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. I. Nakayoshi of Tokusen Kogyo Co. for sample preparation. The authors are grateful to Dr. E.A. Choi of the Korea Institute of Materials Science for useful discussions and comments. The authors also thank Dr. M. Ishikuro, Mr. E. Aoyagi, Mr. I. Nagano, Ms. Y. Matsuda, and Mr. Y. Kadoi of the Institute for Materials Research (IMR) of Tohoku University and Professor Iwase and Mr. T. Teshima of Osaka Prefecture University for their experimental assistance. This work was supported by a cooperative program of Collaborative Research and Development Center for Advanced Materials (CRDAM) in IMR (No. 18G0421). We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science via a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (No. 18H01743) and from the Japan Copper and Brass Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 1, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semboshi, S., Kaneno, Y., Takasugi, T. et al. Effect of Composition on the Strength and Electrical Conductivity of Cu-Ti Binary Alloy Wires Fabricated by Aging and Intense Drawing. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 1389–1396 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-5088-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-5088-z