Abstract
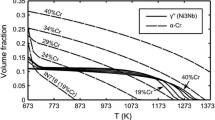
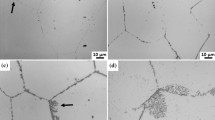
In this study, the morphology and development of precipitate-free zones (PFZs) near grain boundaries (GBs) in low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) Ni-Mo-Cr-W alloys (based on Haynes 244) have been investigated as a function of thermal history and composition using electron microscopy techniques. It is shown that the formation of wide, continuous PFZs adjacent to GBs can be largely attributed to a vacancy depletion mechanism. It is proposed that variations in the vacancy distributions that develop after solution heat treatment (SHT) and subsequent quenching and aging greatly influence the development of the γ′-Ni2(Mo,Cr) precipitates during the aging process and result in the development of PFZs of varying sizes. The relatively large (5 to 10 μm) PFZs are distinct from the smaller, more common PFZs that result from solute depletion due to GB precipitation that are typically observed after prolonged aging. During the course of this investigation, heat treatment parameters, such as aging time, SHT temperature, cooling rate after SHT, and heating rate to the aging temperature—all of which change vacancy concentration and distribution adjacent to GBs—were investigated and observed to have significant influence on both the size and morphology of the observed PFZs. In contrast to results from other Ni-based alloys studied previously, PFZ development in the current alloys was observed across a broad range of aging temperatures. This appears to be due to the high misfit strain energy of the γ′ precipitates, resulting in a nucleation process that is sensitive to vacancy concentration. It is also shown that a slightly modified alloy with higher Mo concentrations develops smaller, more typical PFZs; this is presumably due to an increased driving force for γ′ precipitation which overshadows the influence of misfit strain energy, thereby decreasing the sensitivity of precipitation on vacancy concentration.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
It should be noted that these samples are not truly solution treated at these lower temperatures due to the fact that grain boundary precipitation occurs.
References
[1] T. Krol, D. Baither, E. Nembach, Scripta Mater., 2003, Vol. 48, pp. 1189-94.
S. Hossein Nedjad, M. Nili Ahmadabadi, T. Furuhara: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 490, pp. 105–12.
[3] M. Styczyńska, W. Łojkowski, Scripta Metall., 1985, Vol. 19, pp. 1409-13.
[4] Y.J. Bi, M.H. Loretto, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1991, Vol. 134, pp. 1188-92.
[5] T. Ogura, S. Hirosawa, A. Cerezo, T. Sato, Acta Mater., 2010, Vol. 58, pp. 5714-23.
[6] T.F. Morgeneyer, M.J. Starink, S.C. Wang, I. Sinclair, Acta Mater., 2008, Vol. 56, pp. 2872-84.
[7] N. Ryum, Acta Metall., 1968, Vol. 16, pp. 327-32.
[8] V. Radmilovic, A.G. Fox, R.M. Fisher, G. Thomas, Scripta Metall., 1989, Vol. 23, pp. 75-79.
[9] S.C. Jha, T.H. Sanders, M.A. Dayananda, Acta Metall., 1987, Vol. 35, pp. 473-82.
[10] T.S. Srivatsan, Mater. Lett., 1986, Vol. 4, pp. 201-06.
[11] S. Chang, J.E. Morral, Acta Metall., 1975, Vol. 23, pp. 685-89.
[12] R. Maldonado, E. Nembach, Acta Mater., 1997, Vol. 45, pp. 213-24.
[13] J.D. Embury, R.B. Nicholson, Acta Metall., 1965, Vol. 13, pp. 403-17.
[14] W.F. Smith, N.J. Grant, Asm Trans. Quarterly, 1969, Vol. 62, pp. 724-28.
[15] A. Tolley, D. Mitlin, V. Radmilovic, U. Dahmen, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, Vol. 412, pp. 204-13.
[16] P.R. Sperry, Metall. Trans., 1970, Vol. 1, pp. 2650.
[17] G. Xie, J. Zhang, L.H. Lou, Scripta Mater., 2008, Vol. 59, pp. 858-61.
[18] T.D. Nguyen, K. Sawada, H. Kushima, M. Tabuchi, K. Kimura, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, Vol. 591, pp. 130-35.
[19] D.P. Yao, Y.Z. Zhang, Z.Q. Hu, Y.Y. Li, C.X. Shi, Scripta Metall., 1989, Vol. 23, pp. 537-41.
[20] P.N.T. Unwin, G.W. Lorimer, R.B. Nicholson, Acta Metall., 1969, Vol. 17, pp. 1363-77.
[21] M. Dollar, Scripta Metall., 1986, Vol. 20, pp. 1059-60.
[22] M. Dollar, H. Gleiter, Scripta Metall., 1985, Vol. 19, pp. 481-84.
[23] R.W. Siegel, S.M. Chang, R.W. Balluffi, Acta Metall., 1980, Vol. 28, pp. 249-57.
[24] C. Gottschalk, K. Smidoda, H. Gleiter, Acta Metall., 1980, Vol. 28, pp. 1653-56.
[25] W. Hahn, H. Gleiter, Acta Metall., 1981, Vol. 29, pp. 601-06.
[26] Y.-C. Tzeng, C.-T. Wu, S.-L. Lee, Mater. Lett., 2015, Vol. 161, pp. 340-42.
[27] T. Ogura, S. Hirosawa, T. Sato, Sci. and Tech. Adv. Mater., 2004, Vol. 5, pp. 491-96.
[28] D. Baither, T. Krol, E. Nembach, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, Vol. 387–389, pp. 163-66.
[29] T. Krol, D. Baither, E. Nembach, Acta Mater., 2004, Vol. 52, pp. 2095-108.
[30] D.H. Bechetti, J.N. Dupont, J.A. Siefert, J.P. Shingledecker, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, Vol. 47A, pp. 4502-18.
[31] S. Gardner, W. Li, M. Coleman, R. Johnston, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, Vol. 668, pp. 263-70.
[32] K.A. Rozman, J.J. Kruzic, J.A. Hawk, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, Vol. 24, pp. 2841-46.
[33] J.G. Yoon, H.W. Jeong, Y.S. Yoo, H.U. Hong, Mater. Charact., 2015, Vol. 101, pp. 49-57.
[34] H.M. Tung, K. Mo, J.F. Stubbins, J. Nucl. Mater., 2014, Vol. 447, pp. 28-37.
E. Stepniowska and S. Dymek: Electron Microscopy Xiv, 2012, pp. 156–59.
[36] S. Dymek, M. Wrobel, M. Dollar, M. Blicharski, J. Microscopy-Oxford, 2006, Vol. 224, pp. 24-26.
[37] M.G. Fahrmann, S.K. Srivastava, L.M. Pike, MATEC Web of Conferences, 2014, Vol. 14, pp. 17004.
[38] U.D. Kulkarni, G.K. Dey, S. Banerjee, Scripta Metall., 1988, Vol. 22, pp. 437-40.
J. Song, R. Field, and M. Kaufman: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 702, pp. 687-92.
[40] J.W. Cahn, J.D. Pan, R.W. Balluffi, Scripta Metall., 1979, Vol. 13, pp. 503-09.
[41] R.W. Balluffi, J.W. Cahn, Acta Metall., 1981, Vol. 29, pp. 493-500.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Haynes International Inc. for supplying these alloys. In addition, the authors want to acknowledge support of the NSF I/UCRC Center for Advanced Non-Ferrous Structural Alloys and the member companies as well as the use of the instruments in the Electron Microscopy Laboratory at the Colorado School of Mines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 9, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Field, R., Konitzer, D. et al. Development of Grain Boundary Precipitate-Free Zones in a Ni-Mo-Cr-W Alloy. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 2425–2434 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4019-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4019-8