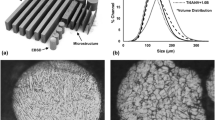
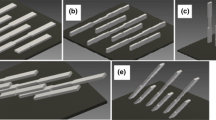
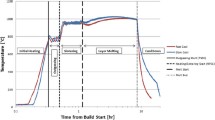
Abstract
Electron beam melting (EBM) is a powder bed fusion-based additive manufacturing process in which selective areas of a layer of powder are melted with an electron beam and a part is built layer by layer. EBM scanning strategies within the Arcam AB® A2X EBM system rely upon governing relationships between the scan length of the beam path, the beam current, and speed. As a result, a large parameter process window exists for Ti-6Al-4V. Many studies have reviewed various properties of EBM materials without accounting for this effect. The work performed in this study demonstrates the relationship between scan length and the resulting density, microstructure, and mechanical properties of EBM-produced Ti-6Al-4V using the scanning strategies set by the EBM control software. This emphasizes the criticality of process knowledge and careful experimental design, and provides an alternate explanation for reported orientation-influenced strength differences.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
ISO/ASTM Standard 52921, 2013, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2013.
M. Svensson: Arcam AB, Molndal Sweden, unpublished research, 2011.
M. Svensson: Arcam AB, Molndal Sweden, unpublished research, 2012.
B.S. Bass: North Carolina State University, Raleigh, North Carolina, unpublished research 2008.
H.K. Rafi, N.V. Karthik, T.L. Starr, and B.E. Stucker: Solid Freeform Fabr. Symp. Proc., 2012, vol. 22, pp. 526–35.
U. Ackelid and M. Svensson: Mater. Sci. Technol. Conf. Exhib., 2009, vol. 4, pp. 2711–19.
A.A. Antonysamy: University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom, unpublished research, 2012.
H. Suo, Z. Chen, J. Liu, S. Gong, and J. Xiao: Rare Metal Mater. Eng., 2014, vol. 43–4, pp. 780–85.
S.S. Al-Bermani, M.L. Blackmore, W. Zhang, and I. Todd: Metall. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41–13, pp. 3422–34.
X. Tan, Y. Kok, Y.J. Tan, M. Descoins, D. Mangelinck, S.B. Tor, and C.K. Chua: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 97, pp. 1–16.
L. Murr, S. Gaytan, F. Medina, E. Martinez, D. Hernandez, L. Martinez, M. Lopez, R. Wicker, S. Collins, and Arcam A.B.: Solid Freeform Fabr. Symp. Proc., 2009, vol. 20, pp. 3–5.
N. Hrabe and T. Quinn: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 573, pp. 264–70.
N. Hrabe and T. Quinn: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, vol. 573, pp. 271–77.
L. Ladani: Metall. Trans. A, 2015, vol. 46–9, 3835–41.
W. Everhart, E. Sawyer, T. Neidt, J. Dinardo, and B. Brown: J. Mater. Sci., 2016, vol. 51, pp. 1–10.
ASTM Standard E8, 2015, “Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials,” ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, doi: 10.1520/E0008-15A, www.astm.org.
ASTM Standard E4, 2014, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, doi: 10.1520/E0004-14, www.astm.org.
ASTM Standard E83, 2010, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, doi: 10.1520/E0083-10A, www.astm.org.
ASTM Standard B962, 2015, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2015, doi: 10.1520/B0962-15, www.astm.org.
J.R. Davis, P. Allen, S. Lampman, T.B. Zorc, S.D. Henry, J.L. Daquila, and A.W. Ronke (Eds.): Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials, 10th ed., ASM International, Conshohocken, PA, 1990, vol. 2, pp. 592–633.
Acknowledgments
The Authors would like to acknowledge the assistance provided for this research by AM equipment technician Justin Tannehill, microscopists Wayne McLarren and Diana Goedecke, and tensile testing personnel Ed Wenski, Bill Lepley, and Jason Rogers. All data prepared, analyzed, and presented have been developed in a specific context of work and were prepared for internal evaluation and use pursuant to that work authorized under the referenced contract. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the United States Government, any agency thereof or Honeywell Federal Manufacturing & Technologies, LLC. This presentation has been authored by Honeywell Federal Manufacturing & Technologies under Contract No. DE-NA0002839 with the U.S. Department of Energy. The United States Government retains, and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the United States Government retains a nonexclusive, paid up, irrevocable, world-wide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this manuscript, or allow others to do so, for the United States Government purposes.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted May 10, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Everhart, W., Dinardo, J. & Barr, C. The Effect of Scan Length on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Electron Beam-Melted Ti-6Al-4V. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 697–705 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3866-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3866-z