Abstract
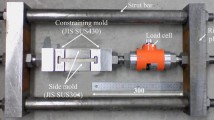
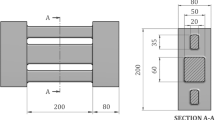
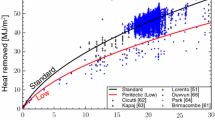
Modeling the thermo-mechanical behavior of steel during casting is of great importance for the prediction of distortions and cracks. In this study, an elasto–visco–plastic constitutive law is calibrated with mechanical measurements from casting experiments. A steel bar is solidified in a sand mold and strained by applying a force to bolts that are embedded in the two ends of the bar. The temporal evolutions of the restraint force and the bar’s length change are measured in situ. The experiments are simulated by inputting calculated transient temperature fields into a finite element stress analysis that employs the measured forces as boundary conditions. The thermal strain predictions are validated using data from experiments without a restraint. Initial estimates of the constitutive model parameters are obtained from available mechanical test data involving reheated steel specimens. The temperature dependence of the strain rate sensitivity exponent is then adjusted until the measured and predicted length changes of the strained bars agree. The resulting calibrated mechanical property dataset is valid for the high-temperature austenite phase of steel. The data reveal a significantly different mechanical behavior during casting compared to what the stress–strain data from reheated specimens show.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Feltham: Phys. Soc. Proc., 1953, vol. 66(406B), pp. 865–83.
P.J. Wray and M.F. Holmes: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1975, vol. 6A, no. 6, pp. 1189–96.
P.J. Wray: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, no. 1, pp. 125-34.
T. Suzuki, K.H. Tacke, K. Wunnenberg, and K. Schwerdtfeger: Ironmaking Steelmaking, 1988, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 90-100.
L. Anand: J. Eng. Mater. Tech., 1982, vol. 104, no. 1, pp. 12-17.
P.F. Kozlowski, B.G. Thomas, J.A. Azzi, and H. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 903-18.
C. Li and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp 1151-72.
S. Koric and B.G. Thomas: Int. J. Num. Met. Eng., 2006, vol. 66, pp. 1955-89.
S. Koric and B.G. Thomas: 2007 Abaqus Users Conference, Paris, 2007.
S. Koric and B.G. Thomas: J. Mater. Processing Tech., 2008, vol. 197, pp. 408-18.
S. Koric and B.G. Thomas: Int. J. Num. Met. Eng., 2009, vol. 78, pp. 1-31.
J. Sengupta, C. Ojeda, and B.G. Thomas: Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 2009, vol. 22(1–4), pp. 8–14.
A.E. Huespe, A. Cardona, N. Nigro and V. Fachinotti: J. Mater. Processing Tech., 2000, vol. 102, pp. 143-52.
A.E. Huespe, A. Cardona and V. Fachinotti: Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. Eng., 2000, vol. 182, pp. 439-55.
C. Zhang, M. Bellet, M. Bobadilla, H. Shen, and B. Liu, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 41A, pp. 2304-17.
R.N. Parkins and A. Cowan: Proceedings of the Institute of British Foundation, Paper No. 1062, 1953, p. A101-9.
C. Monroe and C. Beckermann: 61st Steel Founders Society of America Technical and Operating Conference, Paper No. 5.7, Steel Founders’ Society of America, Chicago, IL, 2006.
P. Ackermann, J.D. Wagniere, and W. Kurz: Mat. Sci. Eng., 1985, vol. 75, pp. 79-86.
M. Rowan, B.G. Thomas, R. Pierer, and C. Bernhard: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 837-51.
MAGMASOFT® v4.6, Magma GmbH, Aachen.
J. Miettinen: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 281-97.
D. Galles and C. Beckermann: 66th Steel Founders Society of America Technical and Operating Conference, Paper No. 5.2, Steel Founders’ Society of America, Chicago, IL, 2012.
K.D. Carlson and C. Beckermann: Int. J. Cast Metals Res., vol. 25, 2012, pp. 75-92.
C. Monroe: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, 2009.
M. Pokorny, C. Monroe, and C. Beckermann: Int. J. Metalcast., 2008, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 41-53.
J. Bluhm and R. DeBoer: ZAMM – J. Appl. Math. Mech., 1997, vol. 77, no. 8, pp. 563–77.
A.P. Roberts and E.J. Garboczi: J. American Ceramic Soc., vol. 83, no. 12, 2000, pp. 3041-48.
R.A. Hardin and C. Beckermann: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 2992-3006.
ABAQUS®, Abaqus, Inc., Providence, RI.
J.C. Simo and T.J.R. Hughes: Computational Inelasticity, Springer-Verlag New York Inc., New York, NY, 1998.
C. Martin, M. Braccini, and M. Suery: Int. J. Plast., 2002, vol. 15, pp. 981-1008.
A.C.F. Cocks: J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1989, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 693-715.
V. Tvergaard and A. Needleman: Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 157-69.
E.B. Marin and D.L. McDowell: Comput. Struct., 1997, vol. 63, no. 3, pp. 579-600.
B.G. Thomas: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 737-743.
C.A. Monroe, C. Beckermann, and J. Klinkhammer: Modelling of Casting, Welding, and Advanced Solidification Processes XII, S.L. Cockcroft and D.M. Maijer, Wiley, Warrendale, PA, 2009, pp. 643–49.
A. Stangeland, A. Mo, O. Nielsen, D. Eskin and M. M’Hamdi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 2903-15
Acknowledgments
This research was sponsored through the Defense Logistics Agency through the American Metal Consortium and the Steel Founders’ Society of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted February 10, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galles, D., Beckermann, C. In Situ Measurement and Prediction of Stresses and Strains During Casting of Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 47, 811–829 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3184-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-3184-x