Abstract
Summary
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) had higher incidences of sarcopenia, falls, osteoporosis, and vertebral osteoporotic fractures (VOPF). Sarcopenia was associated with longer disease duration, higher disease activity, and more severe RA. The interactive effect of sarcopenia and falls was associated with a higher risk of VOPF in patients with RA.
Purpose
Whether sarcopenia and falls are a risk factor for vertebral fracture in RA patients has not been demonstrated. This study aimed to explore the incidence of vertebral osteoporotic fracture (VOPF) and its relationship with sarcopenia and falls in RA patients.
Methods
A total of 474 RA patients and 156 controls were enrolled in this study. Anteroposterior and lateral X-ray examinations of the vertebral column (T4-L4) were used for the semiquantitative assessment of VOPF. Bone mineral density was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Skeletal muscle mass was measured by direct segmental multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis (DSM-BIA method).
Results
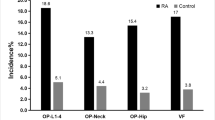
RA patients had an increased risk of sarcopenia (62.4% vs 9.0%, x2 = 47.478, P < 0.001), falls (30.2% vs 3.2%), osteoporosis (OP) (33.5% vs 12.8%, x2 = 134.276, P < 0.001), and VOPF (20.3% vs 3.8%, x2 = 47.478, P < 0.001) than controls. Patients with sarcopenia were more likely to have VOPF than RA without sarcopenia (24.0% vs 14.0%, x2 = 6.802, P = 0.009). RA with sarcopenia and prior falls had the highest incidences of VOPF (36.7%). Older age (OR = 1.056, P < 0.001, 95% CI 1.030–1.083), falls (OR = 2.043, P = 0.003, 95% CI 1.238–3.371), OP (OR = 1.819, P = 0.034, 95% CI 1.046–3.163), and usage of glucocorticoids (GCs) (OR = 1.862, P = 0.022, 95% CI 1.093–3.172) were risk factors for VOPF in RA patients, while a higher skeletal muscle index (SMI) was a protective factor (OR = 0.754, P = 0.038, 95% CI 0.578–0.984) for VOPF in RA patients.
Conclusions
The interactive effect of sarcopenia and falls is associated with a higher risk of VOPF in patients with RA.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Redlich K, Smolen JS (2012) Inflammatory bone loss: pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11:234–250. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3669
Tong JJ, Xu SQ, Zong HX, Pan MJ, Teng YZ, Xu JH (2020) Prevalence and risk factors associated with vertebral osteoporotic fractures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 39:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04787-9
Rosenberg IH (1997) Sarcopenia: origins and clinical relevance. J Nutr 127:990S-991S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/127.5.990S
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinkova E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M, European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older P (2010) Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 39:412–423. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afq034
Torii M, Hashimoto M, Hanai A, Fujii T, Furu M, Ito H, Uozumi R, Hamaguchi M, Terao C, Yamamoto W, Uda M, Nin K, Morita S, Arai H, Mimori T (2019) Prevalence and factors associated with sarcopenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 29:589–595. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2018.1510565
Di Monaco M, Vallero F, Di Monaco R, Tappero R (2011) Prevalence of sarcopenia and its association with osteoporosis in 313 older women following a hip fracture. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 52:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2010.02.002
Hong W, Cheng Q, Zhu X, Zhu H, Li H, Zhang X, Zheng S, Du Y, Tang W, Xue S, Ye Z (2015) Prevalence of sarcopenia and its relationship with sites of fragility fractures in elderly Chinese men and women. PLoS ONE 10:e0138102. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138102
Soen S, Fukunaga M, Sugimoto T, Sone T, Fujiwara S, Endo N, Gorai I, Shiraki M, Hagino H, Hosoi T, Ohta H, Yoneda T, Tomomitsu T (2013) Diagnostic criteria for primary osteoporosis: year 2012 revision. J Bone Miner Metab 31:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-013-0447-8
Minne HW, Leidig G, Wuster C, Siromachkostov L, Baldauf G, Bickel R, Sauer P, Lojen M, Ziegler R (1988) A newly developed spine deformity index (SDI) to quantitate vertebral crush fractures in patients with osteoporosis. Bone Miner 3:335–349
Chen LK, Liu LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW, Bahyah KS, Chou MY, Chen LY, Hsu PS, Krairit O, Lee JS, Lee WJ, Lee Y, Liang CK, Limpawattana P, Lin CS, Peng LN, Satake S, Suzuki T, Won CW, Wu CH, Wu SN, Zhang T, Zeng P, Akishita M, Arai H (2014) Sarcopenia in Asia: consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J Am Med Dir Assoc 15:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2013.11.025
Smulders E, Schreven C, Weerdesteyn V, van den Hoogen FH, Laan R, Van Lankveld W (2009) Fall incidence and fall risk factors in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1795–1796. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.109009
Lodder MC, de Jong Z, Kostense PJ, Molenaar ET, Staal K, Voskuyl AE, Hazes JM, Dijkmans BA, Lems WF (2004) Bone mineral density in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: relation between disease severity and low bone mineral density. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1576–1580. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2003.016253
Ghazi M, Kolta S, Briot K, Fechtenbaum J, Paternotte S, Roux C (2012) Prevalence of vertebral fractures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: revisiting the role of glucocorticoids. Osteoporos Int 23:581–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1584-3
Munro R, Capell H (1997) Prevalence of low body mass in rheumatoid arthritis: association with the acute phase response. Ann Rheum Dis 56:326–329. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.56.5.326
Mochizuki T, Yano K, Ikari K, Okazaki K (2019) Sarcopenia-associated factors in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study. Geriatr Gerontol Int 19:907–912. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.13747
Mochizuki T, Yano K, Ikari K, Okazaki K (2020) Sarcopenia in Japanese younger patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional study. Mod Rheumatol: 1-2. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2020.1740411
Tada M, Yamada Y, Mandai K, Hidaka N (2018) Matrix metalloprotease 3 is associated with sarcopenia in rheumatoid arthritis - results from the CHIKARA study. Int J Rheum Dis 21:1962–1969. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13335
Barone M, Viggiani MT, Anelli MG, Fanizzi R, Lorusso O, Lopalco G, Cantarini L, Di Leo A, Lapadula G, Iannone F (2018) Sarcopenia in patients with rheumatic diseases: prevalence and associated risk factors. J Clin Med 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120504
Bravo-Jose P, Moreno E, Espert M, Romeu M, Martinez P, Navarro C (2018) Prevalence of sarcopenia and associated factors in institutionalised older adult patients. Clin Nutr ESPEN 27:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2018.05.008
Volpato S, Bianchi L, Cherubini A, Landi F, Maggio M, Savino E, Bandinelli S, Ceda GP, Guralnik JM, Zuliani G, Ferrucci L (2014) Prevalence and clinical correlates of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older people: application of the EWGSOP definition and diagnostic algorithm. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 69:438–446. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glt149
Han P, Kang L, Guo Q, Wang J, Zhang W, Shen S, Wang X, Dong R, Ma Y, Shi Y, Shi Z, Li H, Li C, Ma Y, Wang L, Niu K (2016) Prevalence and factors associated with sarcopenia in suburb-dwelling older Chinese using the Asian Working Group for sarcopenia definition. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 71:529–535. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glv108
Morley JE, Abbatecola AM, Argiles JM, Baracos V, Bauer J, Bhasin S, Cederholm T, Coats AJ, Cummings SR, Evans WJ, Fearon K, Ferrucci L, Fielding RA, Guralnik JM, Harris TB, Inui A, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kirwan BA, Mantovani G, Muscaritoli M, Newman AB, Rossi-Fanelli F, Rosano GM, Roubenoff R, Schambelan M, Sokol GH, Storer TW, Vellas B, von Haehling S, Yeh SS, Anker SD, Society on Sarcopenia C, Wasting Disorders Trialist W (2011) Sarcopenia with limited mobility: an international consensus. J Am Med Dir Assoc 12:403–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2011.04.014
Schaap LA, Pluijm SM, Deeg DJ, Harris TB, Kritchevsky SB, Newman AB, Colbert LH, Pahor M, Rubin SM, Tylavsky FA, Visser M, Health ABCS (2009) Higher inflammatory marker levels in older persons: associations with 5-year change in muscle mass and muscle strength. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64:1183–1189. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glp097
Tsujinaka T, Fujita J, Ebisui C, Yano M, Kominami E, Suzuki K, Tanaka K, Katsume A, Ohsugi Y, Shiozaki H, Monden M (1996) Interleukin 6 receptor antibody inhibits muscle atrophy and modulates proteolytic systems in interleukin 6 transgenic mice. J Clin Invest 97:244–249. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI118398
Wang Y, Welc SS, Wehling-Henricks M, Tidball JG (2018) Myeloid cell-derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes sarcopenia and regulates muscle cell fusion with aging muscle fibers. Aging Cell 17:e12828. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12828
Ensrud KE, Ewing SK, Taylor BC, Fink HA, Stone KL, Cauley JA, Tracy JK, Hochberg MC, Rodondi N, Cawthon PM, Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research G (2007) Frailty and risk of falls, fracture, and mortality in older women: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 62:744–751. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/62.7.744
KazKaz H, Johnson D, Kerry S, Chinappen U, Tweed K, Patel S (2004) Fall-related risk factors and osteoporosis in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:1267–1271. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keh304
Tarantino U, Piccirilli E, Fantini M, Baldi J, Gasbarra E, Bei R (2015) Sarcopenia and fragility fractures: molecular and clinical evidence of the bone-muscle interaction. J Bone Joint Surg Am 97:429–437. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.N.00648
Seeman E, Delmas PD (2006) Bone quality–the material and structural basis of bone strength and fragility. N Engl J Med 354:2250–2261. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra053077
Deschenes MR (2004) Effects of aging on muscle fibre type and size. Sports Med 34:809–824. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200434120-00002
Verschueren S, Gielen E, O’Neill TW, Pye SR, Adams JE, Ward KA, Wu FC, Szulc P, Laurent M, Claessens F, Vanderschueren D, Boonen S (2013) Sarcopenia and its relationship with bone mineral density in middle-aged and elderly European men. Osteoporos Int 24:87–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-012-2057-z
Iolascon G, Giamattei MT, Moretti A, Di Pietro G, Gimigliano F, Gimigliano R (2013) Sarcopenia in women with vertebral fragility fractures. Aging Clin Exp Res 25(Suppl 1):S129-131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-013-0102-1
Hida T, Shimokata H, Sakai Y, Ito S, Matsui Y, Takemura M, Kasai T, Ishiguro N, Harada A (2016) Sarcopenia and sarcopenic leg as potential risk factors for acute osteoporotic vertebral fracture among older women. Eur Spine J 25:3424–3431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-015-3805-5
Petermann-Rocha F, Chen M, Gray SR, Ho FK, Pell JP, Celis-Morales C (2020) Factors associated with sarcopenia: a cross-sectional analysis using UK Biobank. Maturitas 133:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.01.004
Malkov S, Cawthon PM, Peters KW, Cauley JA, Murphy RA, Visser M, Wilson JP, Harris T, Satterfield S, Cummings S, Shepherd JA, Health ABCS (2015) Hip fractures risk in older men and women associated with DXA-derived measures of thigh subcutaneous fat thickness, cross-sectional muscle area, and muscle density. J Bone Miner Res 30:1414–1421. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2469
Frost HM (2004) A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod 74:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1043/0003-3219(2004)074%3c0003:AUOBPA%3e2.0.CO;2
Sun X, Lei SF, Deng FY, Wu S, Papacian C, Hamilton J, Recker RR, Deng HW (2006) Genetic and environmental correlations between bone geometric parameters and body compositions. Calcif Tissue Int 79:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-006-0041-3
Karasik D, Kiel DP (2008) Genetics of the musculoskeletal system: a pleiotropic approach. J Bone Miner Res 23:788–802. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.080218
Perrini S, Laviola L, Carreira MC, Cignarelli A, Natalicchio A, Giorgino F (2010) The GH/IGF1 axis and signaling pathways in the muscle and bone: mechanisms underlying age-related skeletal muscle wasting and osteoporosis. J Endocrinol 205:201–210. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-09-0431
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1308085MH163).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, Jj., Xu, Sq., Wang, Jx. et al. Interactive effect of sarcopenia and falls on vertebral osteoporotic fracture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Osteoporos 16, 145 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-021-01017-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-021-01017-1