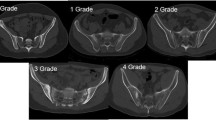
Abstract
Purpose
Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the axial skeleton and typically has an early onset. Although earlier onset is associated with worse prognosis, there have been few studies of bone mineral density (BMD) in adolescent patients with axSpA.
Methods
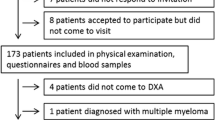
We analysed the clinical characteristics of 43 adolescent patients with axSpA at a baseline assessment and at a follow-up 2 years later. The baseline assessment included age, disease duration, treatment agents, and clinical, radiologic, and laboratory data. BMD of the lumbar spine, femoral neck, and total hip were measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry during both the baseline assessment and the 2-year follow-up. We performed multivariate linear regression analyses to identify factors independently associated with BMD. We analysed the associations between changes in BMD and reductions in inflammatory markers.
Results
The average age of participants was 17.9 years and the mean disease duration was 2.2 years. Of the 43 patients, 10 (23%) had low BMD at any site (lumbar spine, femoral neck, and/or total hip). At baseline, multivariate analysis showed that body mass index (BMI), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and spinal structural damage were associated with lumbar spine Z-scores. Increases in BMD in the lumbar spine were correlated with reductions in ESR (r = 0.40, P = 0.02) and C-reactive protein (CRP) (r = 0.40, P = 0.02). Increases in BMD in the total hip were correlated with reductions in CRP (r = 0.38, P = 0.03).
Conclusion
In adolescent axSpA patients, bone health was associated with systemic inflammation and the severity of structural damage. Reduced systemic inflammation was associated with improvements in bone health.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiss PF, Colbert RA (2018) Juvenile spondyloarthritis: a distinct form of juvenile arthritis. Pediatr Clin N Am 65:675–690
Gmuca S, Weiss PF (2015) Juvenile spondyloarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 27:364–372
Bao J, Chen Y, Bao Y-X (2014) Prevalence and risk factors of low bone mineral density in juvenile onset ankylosing spondylitis. Calcif Tissue Int 95:108–111
Maillefert JF, Aho LS, El Maghraoui A, Dougados M, Roux C (2001) Changes in bone density in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a two-year follow-up study. Osteoporos Int 12:605–609
Mitra D, Elvins DM, Collins AJ (1999) Biochemical markers of bone metabolism in mild ankylosing spondylitis and their relationship with bone mineral density and vertebral fractures. J Rheumatol 26:2201–2204
Magrey M, Khan MA (2010) Osteoporosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 12:332–336
Kang KY, Kim IJ, Park S-H, Hong YS (2018) Associations between trabecular bone score and vertebral fractures in patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 57:1033–1040
Thornton J, Pye SR, O’Neill TW, Rawlings D, Francis RM, Symmons DPM et al (2011) Bone health in adult men and women with a history of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 38:1689–1693
Kang KY, Chung MK, Kim HN, Hong YS, Ju JH, Park S-H (2018) Severity of sacroiliitis and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are associated with a low trabecular bone score in young male patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 45:349–356
Rudwaleit M, Landewé R, van der Heijde D, Listing J, Brandt J, Braun J et al (2009) The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann Rheum Dis 68:770–776
Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A (1994) A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol 21:2286–2291
Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy LG, O’Hea J, Mallorie P et al (1994) A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol 21:2281–2285
van der Heijde D, Lie E, Kvien TK, Sieper J, Van den Bosch F, Listing J et al (2009) ASDAS, a highly discriminatory ASAS-endorsed disease activity score in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1811–1818
Baim S, Leonard MB, Bianchi M-L, Hans DB, Kalkwarf HJ, Langman CB, Rauch F (2008) Official positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry and executive summary of the 2007 ISCD Pediatric Position Development Conference. J Clin Densitom 11:6–21
Averns HL, Oxtoby J, Taylor HG, Jones PW, Dziedzic K, Dawes PT (1996) Radiological outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: use of the Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (SASSS). Br J Rheumatol 35:373–376
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J, Glass DN, Goldenberg J, He X, Maldonado-Cocco J, Orozco-Alcala J, Prieur AM, Suarez-Almazor ME, Woo P, International League of Associations for Rheumatology (2004) International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 31:390–392
Gensler L, Davis JC (2006) Recognition and treatment of juvenile-onset spondyloarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:507–511
Full Text PDF [Internet]. [cited 2020 Aug 31]. Available from: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com.ssl.proxy.cuk.ac.kr:8080/doi/pdfdirect/10.1002/acr.22411
Robinson Y, Sandén B, Olerud C (2013) Increased occurrence of spinal fractures related to ankylosing spondylitis: a prospective 22-year cohort study in 17,764 patients from a national registry in Sweden. Patient Saf Surg 7:2
Kang KY, Kim IJ, Jung SM, Kwok S-K, Ju JH, Park K-S et al (2014) Incidence and predictors of morphometric vertebral fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res Ther 16:R124
van der Weijden MAC, van Denderen JC, Lems WF, Heymans MW, Dijkmans BAC, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE (2011) Low bone mineral density is related to male gender and decreased functional capacity in early spondylarthropathies. Clin Rheumatol 30:497–503
Kang KY, Kwok S-K, Ju JH, Hong YS, Park S-H (2016) Assessment of fracture risk in patients with axial spondyloarthritis: a case–control study using the fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V). Scand J Rheumatol. Taylor & Francis 45:23–31
Aydin T, Karacan I, Demir SE, Sahin Z (2005) Bone loss in males with ankylosing spondylitis: its relation to sex hormone levels. Clin Endocrinol 63:467–469
Raisz LG (1988) Local and systemic factors in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. N Engl J Med 318:818–828
Lange U, Teichmann J, Strunk J, Müller-Ladner U, Schmidt KL (2005) Association of 1.25 vitamin D3 deficiency, disease activity and low bone mass in ankylosing spondylitis. Osteoporos Int 16:1999–2004
Gratacós J, Collado A, Pons F, Osaba M, Sanmartí R, Roqué M et al (1999) Significant loss of bone mass in patients with early, active ankylosing spondylitis: a followup study. Arthritis Rheum 42:2319–2324
Kang KY, Lee KY, Kwok S-K, Ju JH, Park K-S, Hong YS, Kim HY, Park SH (2011) The change of bone mineral density according to treatment agents in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Joint Bone Spine 78:188–193
Tang T, Tang X, Xu L, Huang Y, Zeng J, Li Q (2015) Evaluation of bone mass in children and young adults with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 33:758–764
Cimaz R (2002) Osteoporosis in childhood rheumatic diseases: prevention and therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 16:397–409
Cetin A, Celiker R, Dinçer F, Ariyürek M (1998) Bone mineral density in children with juvenile chronic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 17:551–553
Kang KY, Ju JH, Park S-H, Kim H-Y (2013) The paradoxical effects of TNF inhibitors on bone mineral density and radiographic progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology. 52:718–726
Poddubnyy D, Hermann K-GA, Callhoff J, Listing J, Sieper J (2014) Ustekinumab for the treatment of patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: results of a 28-week, prospective, open-label, proof-of-concept study (TOPAS). Ann Rheum Dis 73:817–823
Baeten D, Baraliakos X, Braun J, Sieper J, Emery P, van der Heijde D, McInnes I, van Laar JM, Landewé R, Wordsworth P, Wollenhaupt J, Kellner H, Paramarta J, Wei J, Brachat A, Bek S, Laurent D, Li Y, Wang YA, Bertolino AP, Gsteiger S, Wright AM, Hueber W (2013) Anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody secukinumab in treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 382:1705–1713
Pathan E, Abraham S, Van Rossen E, Withrington R, Keat A, Charles PJ et al (2013) Efficacy and safety of apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 72:1475–1480
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, SH., Kim, K., Kim, MY. et al. A 2-year longitudinal study of bone health in adolescent patients with axial spondyloarthritis. Arch Osteoporos 16, 12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-020-00860-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-020-00860-y