Abstract
Purpose
Recently, trabecular bone score (TBS) has emerged as an important supplementary assessment tool in osteoporosis diagnosis and management. The high incidence of fragility fracture within the non-osteoporotic range of bone mineral density (BMD), among systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, highlights the crucial role of bone microarchitecture in osteoporosis. This study aimed to evaluate whether TBS identified existing vertebral fractures (VF) more accurately than BMD in SLE patients.
Methods
This study enrolled 147 SLE patients from the Asia Pacific Lupus Collaboration (APLC) cohort, who had BMD and TBS assessed from January 2018 until December 2018. Twenty-eight patients sustaining VF and risk factors associated with increased fracture occurrence were evaluated. Independent risk factors and diagnostic accuracy of VF were analyzed by logistic regression and ROC curve, respectively.
Result
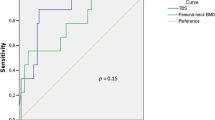
The prevalence of vertebral fracture among SLE patients was 19%. BMD, T-score, TBS, and TBS T-score were significantly lower in the vertebral fracture group. TBS exhibited higher positive predictive value and negative predictive value than L spine and left femur BMD for vertebral fractures. Moreover, TBS had a higher diagnostic accuracy than densitometric measurements (area under curve, 0.811 vs. 0.737 and 0.605).
Conclusion
Degraded microarchitecture by TBS was associated with prevalent vertebral fractures in SLE patients. Our result suggests that TBS can be a complementary tool for assessing vertebral fracture prevalence in this population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uramoto KM, Michet CJ Jr, Thumboo J, Sunku J, O’Fallon WM, Gabriel SE (1999) Trends in the incidence and mortality of systemic lupus erythematosus, 1950-1992. Arthritis Rheum 42:46–50
Gonzalez LA, Alarcon GS (2017) The evolving concept of SLE comorbidities. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 13:753–768
Xia J, Luo R, Guo S, Yang Y, Ge S, Xu G, Zeng R (2019) Prevalence and risk factors of reduced bone mineral density in systemic lupus erythematosus patients: a meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2019:3731648
Leib ES, Winzenrieth R (2016) Bone status in glucocorticoid-treated men and women. Osteoporos Int 27:39–48
Whittier X, Saag KG (2016) Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 42:177–189, x
World Health Organization (2007) Assessment osteoporosis at the primary health care level. WHO, Geneva (www.who.int/chp/topics/rheumatic/en/index.html). Accessed 12 June 2019
Bultink IE, Lems WF (2016) Lupus and fractures. Curr Opin Rheumatol 28(4):426–432
Shevroja E, Lamy O, Kohlmeier L, Koromani F, Rivadeneira F, Hans D (2017) Use of trabecular bone score (TBS) as a complementary approach to dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) for fracture risk assessment in clinical practice. J Clin Densitom 20:334–345
Harvey NC, Gluer CC, Binkley N, McCloskey EV, Brandi ML, Cooper C, Kendler D, Lamy O, Laslop A, Camargos BM, Reginster JY, Rizzoli R, Kanis JA (2015) Trabecular bone score (TBS) as a new complementary approach for osteoporosis evaluation in clinical practice. Bone 78:216–224
Schacter GI, Leslie WD, Majumdar SR, Morin SN, Lix LM, Hans D (2017) Clinical performance of an updated trabecular bone score (TBS) algorithm in men and women: the Manitoba BMD cohort. Osteoporos Int 28:3199–3203
Hans D, Stenova E, Lamy O (2017) The trabecular bone score (TBS) complements DXA and the FRAX as a fracture risk assessment tool in routine clinical practice. Curr Osteoporos Rep 15:521–531
Koumakis E, Avouac J, Winzenrieth R, Toth E, Payet J, Kahan A, Allanore Y, Cormier C (2015) Trabecular bone score in female patients with systemic sclerosis: comparison with rheumatoid arthritis and influence of glucocorticoid exposure. J Rheumatol 42:228–235
Choi YJ, Chung YS, Suh CH, Jung JY, Kim HA (2017) Trabecular bone score as a supplementary tool for the discrimination of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e8661
Chuang MH, Chuang TL, Koo M, Wang YF (2017) Trabecular bone score as a supplementary tool for the discrimination of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int 2017:4210217
Kim D, Cho SK, Kim JY, Choi YY, Sung YK (2016) Association between trabecular bone score and risk factors for fractures in Korean female patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 26:540–545
Boussoualim K, Amouzougan A, Pallot-Prades B, Denarie D, Collet P, Marotte H, Thomas T (2018) Evaluation of bone quality with trabecular bone score in active spondyloarthritis. Joint Bone Spine 85:727–731
Caparbo VF, Furlam P, Saad CGS, Alvarenga JC, Aubry-Rozier B, Hans D, de Brum-Fernandes AJ, Pereira RMR (2019) Assessing bone impairment in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) using the trabecular bone score (TBS) and high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT). Bone 122:8–13
Kandane-Rathnayake R, Golder V, Louthrenoo W, Luo SF, Jan Wu YJ, Li Z, An Y, Lateef A, Sockalingam S, Navarra SV, Zamora L, Hamijoyo L, Katsumata Y, Harigai M, Chan M, O’Neill S, Goldblatt F, Hao Y, Zhang Z, Al-Saleh J, Khamashta M, Takeuchi T, Tanaka Y, Bae SC, Lau CS, Hoi A, Nikpour M, Morand EF (2019) Development of the Asia Pacific Lupus Collaboration cohort. Int J Rheum Dis 22:425–433
Petri M, Orbai AM, Alarcon GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR, Bruce IN, Isenberg D, Wallace DJ, Nived O, Sturfelt G, Ramsey-Goldman R, Bae SC, Hanly JG, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Clarke A, Aranow C, Manzi S, Urowitz M, Gladman D, Kalunian K, Costner M, Werth VP, Zoma A, Bernatsky S, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA, Jacobsen S, Buyon JP, Maddison P, Dooley MA, van Vollenhoven RF, Ginzler E, Stoll T, Peschken C, Jorizzo JL, Callen JP, Lim SS, Fessler BJ, Inanc M, Kamen DL, Rahman A, Steinsson K, Franks AG Jr, Sigler L, Hameed S, Fang H, Pham N, Brey R, Weisman MH, McGwin G Jr, Magder LS (2012) Derivation and validation of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64:2677–2686
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8(9):1137–1148
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL (1988) Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics 44(3):837–845
Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB Sr, D’Agostino RB Jr, Vasan RS (2008) Evaluating the added predictive ability of a new marker: from area under the ROC curve to reclassification and beyond. Stat Med 27(2):157–212
Coury F, Peyruchaud O, Machuca-Gayet I (2019) Osteoimmunology of bone loss in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Front Immunol 10:679
Bultink IE, Vis M, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Lems WF (2012) Inflammatory rheumatic disorders and bone. Curr Rheumatol Rep 14:224–230
Frostegard J, Svenungsson E, Wu R, Gunnarsson I, Lundberg IE, Klareskog L, Horkko S, Witztum JL (2005) Lipid peroxidation is enhanced in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and is associated with arterial and renal disease manifestations. Arthritis Rheum 52:192–200
Svenungsson E, Fei GZ, Jensen-Urstad K, de Faire U, Hamsten A, Frostegard J (2003) TNF-alpha: a link between hypertriglyceridaemia and inflammation in SLE patients with cardiovascular disease. Lupus 12:454–461
Teichmann J, Lange U, Stracke H, Federlin K, Bretzel RG (1999) Bone metabolism and bone mineral density of systemic lupus erythematosus at the time of diagnosis. Rheumatol Int 18:137–140
Muñoz-Torres M, Manzanares Córdova R, García-Martín A, Avilés-Pérez MD, Nieto Serrano R, Andújar-Vera F, García-Fontana B (2019) Usefulness of trabecular bone score (TBS) to identify bone fragility in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism. J Clin Densitom 22(2):162–170
Florez H, Hernández-Rodríguez J, Muxi A, Carrasco JL, Prieto-González S, Cid MC, Espinosa G, Gómez-Puerta JA, Monegal A, Guañabens N, Peris P (2019) Trabecular bone score improves fracture risk assessment in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez464
Pencina MJ, D’Agostino RB, Pencina KM, Janssens AC, Greenland P (2012) Interpreting incremental value of markers added to risk prediction models. Am J Epidemiol 176(6):473–481
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Biostatistics Task Force of Taichung Veterans General Hospital for their assistance in performing the statistical analysis. The authors thank Brian Brown, NIH Library Writing Center, for manuscript editing assistance.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan (TCVGH-1087312C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Clinical Research, Taichung Veterans General Hospital (CE17111A). As the patients’ data were anonymized before analysis, the requirement for written consent from patients was waived for this study.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, EL., Huang, WN., Chen, HH. et al. Degraded microarchitecture by low trabecular bone score is associated with prevalent vertebral fractures in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Osteoporos 15, 54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-020-00726-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-020-00726-3