Abstract
Objective
To investigate the potential role of Tongxinluo (TXL) in attenuating myocardial fibrosis after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (MIRI) in mice.
Methods
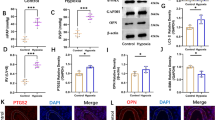
A MIRI mouse model was established by left anterior descending coronary artery ligation for 45 min. According to a random number table, 66 mice were randomly divided into 6 groups (n=11 per group): the sham group, the model group, the LY-294002 group, the TXL group, the TXL+LY-294002 group and the benazepril (BNPL) group. The day after modeling, TXL and BNPL were administered by gavage. Intraperitoneal injection of LY-294002 was performed twice a week for 4 consecutive weeks. Echocardiography was used to measure cardiac function in mice. Masson staining was used to evaluate the degree of myocardial fibrosis in mice. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of endothelial mesenchymal transition (EndMT) after MIRI was performed by immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence staining and flow cytometry, respectively. The protein expressions of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31), α-smoth muscle actin (α-SMA), phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) and phospho protein kinase B (p-AKT) were assessed using Western blot.
Results
TXL improved cardiac function in MIRI mice, reduced the degree of myocardial fibrosis, increased the expression of CD31 and inhibited the expression of α-SMA, thus inhibited the occurrence of EndMT (P<0.05 or P<0.01). TXL significantly increased the protein expressions of PI3K and p-AKT (P<0.05 or P<0.01). There was no significant difference between TXL and BNPL group (P>0.05). In addition, the use of the PI3K/AKT pathway-specific inhibitor LY-294002 to block this pathway and combination with TXL intervention, eliminated the protective effect of TXL, further supporting the protective effect of TXL.
Conclusion
TXL activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to inhibit EndMT and attenuated myocardial fibrosis after MIRI in mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fernandez Rico C, Konate K, Josse E, Nargeot J, Barrère-Lemaire S, Boisguérin P. Therapeutic peptides to treat myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Cardiovasc Med 2022;9:792885.
Lefer DJ, Marbán E. Is cardioprotection dead? Circulation 2017;136:98–109.
Curran J, Burkhoff D, Kloner RA. Beyond reperfusion: acute ventricular unloading and cardioprotection during myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 2019;12:95–106.
Liu S, Ke W, Liu Y, Zhao Z, An L, You X, et al. Function analysis of differentially expressed microRNAs in TGF-β 1-induced cardiac fibroblasts differentiation. Biosci Rep 2019;39:2018–2048.
Liu Y, Zou J, Li B, Wang Y, Wang D, Hao Y, et al. RUNX3 modulates hypoxia-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med 2017;40:65–74.
Zhang L, He J, Wang J, Liu J, Chen Z, Deng B, et al. Knockout RAGE alleviates cardiac fibrosis through repressing endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) mediated by autophagy. Cell Death Dis 2021;12:470.
Chen X, Chen C, Gao Z, Chen X, Hu J, Zhou H. Curcumin inhibits endothelial interstitial fibrosis and improves cardiac fibrosis by activating NRF2-DDAH-ADMA-NO pathway. China Chin Mate Med (Chin) 2022;47:745–752.
Anbara T, Sharifi M, Aboutaleb N. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition in the cardiogenesis and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Cardiol Rev 2020;16:306–314.
Fan Z, Guan J. Antifibrotic therapies to control cardiac fibrosis. Biomater Res 2016;20:13.
Wan CX, Xu M, Huang SH, Wu QQ, Yuan Y, Deng W, et al. Baicalein protects against endothelial cell injury by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 2018;17:3085–3091.
Wang M, Li Y, Li S, Lv J. Endothelial dysfunction and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022;13:851941.
Wei R, Xiao Y, Song Y, Yuan H, Luo J, Xu W. FAT4 regulates the EMT and autophagy in colorectal cancer cells in part via the PI3K-AKT signaling axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2019;38:112.
Zhang H, Huang X, Liu K, Tang J, He L, Pu W, et al. Fibroblasts in an endocardial fibroelastosis disease model mainly originate from mesenchymal derivatives of epicardium. Cell Res 2017;27:1157–1177.
Hu JX, Zheng ZQ, Kang T, Qian W, Huang SH, Li BG. LncRNA LINC00961 regulates endothelial-mesenchymal transition via the PTEN-PI3K-AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep 2022;26:246.
Liu YS, Li BG. Research progress of endothelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation in cardiovascular diseases. J Med Res Combat Trauma 2016,29:872–876.
Damian L, Lebovici A, Pamfil C, Belizna C, Vulturar R. Rheumatoid arthritis and CLOVES syndrome: a tricky diagnosis. Diagnostics (Basel) 2020;10:467.
Souilhol C, Harmsen MC, Evans PC, Krenning G. Endothelial-mesenchymal transition in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 2018;114:565–577.
Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X, Peng J. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep 2020;47:4587–4629.
Cheng S, Zhang X, Feng Q, Chen J, Shen L, Yu P, et al. Astragaloside IV exerts angiogenesis and cardioprotection after myocardial infarction via regulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Life Sci 2019;227:82–93.
Chen X, Zhabyeyev P, Azad AK, Wang W, Minerath RA, DesAulniers J, et al. Endothelial and cardiomyocyte PI3Kβ divergently regulate cardiac remodelling in response to ischaemic injury. Cardiovasc Res 2019;115:1343–1356.
Angulo-Urarte A, Casado P, Castillo SD, Kobialka P, Kotini MP, Figueiredo AM, et al. Endothelial cell rearrangements during vascular patterning require PI3-kinase-mediated inhibition of actomyosin contractility. Nat Commun 2018;9:4826.
Li X, Sun S, Chen D, Yuan T, Chen Y, Wang D, et al. Puerarin attenuates the endothelial-mesenchymal transition induced by oxidative stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells through PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 2020;886:173472.
Zhang B, Pei WJ, Cai PP, Wang ZX, Qi FH. Recent advances in Chinese patent medicines entering the international market. Drug Discov Ther 2022;16:258–272.
Yin Y, Zhang Q, Zhao Q, Ding G, Wei C, Chang L, et al. Tongxinluo attenuates myocardiac fibrosis after acute myocardial infarction in rats via inhibition of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomed Res Int 2019;2019:6595437.
Yu ZH, Cai M, Xiang J, Zhang ZN, Zhang JS, Song XL, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway contributes to neuroprotective effect of Tongxinluo against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2016;181:8–19.
Liu MN, Luo G, Dong L, Yang TF, Liu Y, Yang SJ. Based on TGF-β effect of Zhilong Huoxue Tongyu Capsule on hypertensive myocardial fibrosis. Chin Med Mater (Chin) 2022:2726–2730.
Zhang H, Hui H, Li Z, Pan J, Jiang X, Wei T, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor attenuates myocardial fibrosis via inhibiting endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Sci Rep 2017;7:41932.
Liu Y, Li Y, Li J, Zuo X, Cao Q, Xie W, et al. Inhibiting miR-1 attenuates pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Mol Med Rep 2021;23:283.
Nie L, Liu M, Chen J, Wu Q, Li Y, Yi J, et al. Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates doxorubicin-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol Med Rep 2021;23:299.
Kazakov A, Hall R, Jagoda P, Bachelier K, Müller-Best P, Semenov A, et al. Inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase induces and enhances myocardial fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res 2013;100:211–221.
Duan S, Huang W, Liu XT, Liu XM, Chen N, Xu Q, et al. IMPDH2 promotes colorectal cancer progression through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2018;37:304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jia ZH, Hou YL, and Yin YJ conceived and designed the corresponding project. Wei YR, Li Z, Han NX, and Wang ZX performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Wei YR participated in the design and prepared the paper. Hou YL, Yin YJ, Li Z, Han NX, and Liu L revised the manuscript. Wang ZX, Liu Y, Ma K, Wang XQ, Hao YJ and Gu JJ participated in the production of the MIRI model. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest. The pharmaceutical company only provided drug support for this experiment and did not participate in the experimental process, data collection and statistics.
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81973692), Traditional Chinese Medicine Innovation Project of Hebei Province (No. 223777120D) and High-Level Talent Funding Program of Hebei (No. E2020100001)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Yr., Hou, Yl., Yin, Yj. et al. Tongxinluo Activates PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway to Inhibit Endothelial Mesenchymal Transition and Attenuate Myocardial Fibrosis after Ischemia-Reperfusion in Mice. Chin. J. Integr. Med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3652-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-024-3652-5