Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of electroacupuncture (EA) at Neiguan (PC 6) on myocardial fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs), and to explore the contribution of interleukin-1 β (IL-1 β), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and transforming growth factor β 1 (TGF- β 1) to the effects.
Methods
Nine 12-weeks-old Wistar Kyoto (WKY) male rats were employed as the normal group. Twenty-seven SHRs were equally randomized into SHR, SHR+EA, and SHR + sham groups. EA was applied at bilateral PC 6 once a day 30 min per day in 8 consecutive weeks. After 8-weeks EA treatment at PC 6, histopathologic changes of collagen type I (Col I), collagen type 1 (Col 1) and the levels of IGF-1, 1L-1 β, TGF- β 1, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 were examined in myocardial tissure respectively.
Results
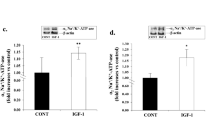
After 8-weeks EA treatment at PC 6, the enhanced myocardial fibrosis in SHRs were characterized by the increased mean fluorescence intensity of Col I and Col 1 in myocardium tissue (P<0.01). All these abnormal alterations above in SHR + EA group was significantly lower compared with the SHR group (P<0.01). Meanwhile, the increased levels of IL-1 β, IGF-1, TGF-β 1 in serum or myocardial tissue of SHRs, diminished MMP 9 mRNA expression in SHRs were also markedly inhibited after 8 weeks of EA treatment (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Furthermore, the contents of IL-1 β, IGF-1, TGF-β 1 in myocardial tissue were positively correlated with the systolic blood pressure and hydroxyproline respectively (P<0.01).
Conclusion
EA at bilateral PC 6 could ameliorate cardiac fibrosis in SHRs, which might be mediated by regulation of 1L-1 β/IGF-1-TGF- β 1-MMP9 pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frangogiannis NG. Cardiac fibrosis: Cell biological mechanisms, molecular pathways and therapeutic opportunities. Mol Aspects Med 2019;65:70–99.
Frangogiannis NG. Cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res 2021;117:1450–1488.
Díez J. Arterial hypertension in patients with heart failure. Heart Fail Clin 2014;10:233–242.
Kong P, Christia P, Frangogiannis NG. The pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2014;71:549–574.
Xu GR, Zhang C, Yang HX, Sun JH, Zhang Y, Yao TT, et al. Modified citrus pectin ameliorates myocardial fibrosis and inflammation via suppressing galectin-3 and TLR4/MyD88/NF- κ B signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 2020;126:110071.
Gao L, Wang LY, Liu ZQ, Jiang D, Wu SY, Guo YQ, et al. TNAP inhibition attenuates cardiac fibrosis induced by myocardial infarction through deactivating TGF- β 1/Smads and activating P53 signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis 2020;11:44.
Ock S, Ham W, Kang CW, Kang H, Lee WS, Kim J. IGF-1 protects against angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting α SMA. Cell Death Dis 2021;12:688.
Shi L, Fang J, Zhao J, Liu G, Zhao Q, Zhang J, et al. Comparison of the therapeutic effects of acupuncture at PC 6 and ST 36 for chronic myocardial ischemia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017;2017:7358059.
Murakami H, Li S, Foreman R, Yin J, Hirai T, Chen J. Ameliorating effects of electroacupuncture on dysmotility, inflammation, and pain mediated via the autonomic mechanism in a rat model of postoperative ileus. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 2019;25:286–299.
Lin R, Yu K, Li X, Tao J, Lin Y, Zhao C, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates post-stroke learning and memory through minimizing ultrastructural brain damage and inhibiting the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med Rep 2016;14:225–233.
Li P, Shibata R, Maruyama S, Kondo M, Ohashi K, Ouchi N, et al. Fenofibrate promotes ischemia-induced revascularization through the adiponectin-dependent pathway. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2010;299:E560–E566.
Jia H, Chen XL, Chen C, Hu YY, Yun XJ. Baicalin prevents the up-regulation of connective tissue growth factor in fibrotic lungs of rats. Acta Physiol Sin (Chin) 2010;62:535–540.
Zhai Y, Gao X, Wu Q, Peng L, Lin J, Zuo Z. Fluvastatin decreases cardiac fibrosis possibly through regulation of TGF-beta(1)/Smad 7 expression in the spontaneously hypertensive rats. Eur J Pharmacol 2008;587:196–203.
Chiang JT, Badrealam KF, Shibu MA, Cheng SF, Shen CY, Chang CF, et al. Anti-apoptosis and anti-fibrosis effects of Eriobotrya Japonica in spontaneously hypertensive rat hearts. Int J Mol Sci 2018;19:1638–1651.
Xin JJ, Gao JH, Wang YY, Lu FY, Zhao YX, Jing XH, et al. Antihypertensive and antihypertrophic effects of acupuncture at PC 6 acupoints in spontaneously hypertensive rats and the underlying mechanisms. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017;2017:9708094.
Worke LJ, Barthold JE, Seelbinder B, Novak T, Main RP, Harbin SL, et al. Densification of type I collagen matrices as a model for cardiac fibrosis. Adv Healthc Mater 2017;22[Epub 2017 Sep 7]. PMID: 28881428 PMCID: PMC5844700 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201700114
Uchinaka A, Hamada Y, Mori S, Miyagawa S, Saito A, Sawa Y, et al. SVVYGLR motif of the thrombin-cleaved N-terminal osteopontin fragment enhances the synthesis of collagen type M in myocardial fibrosis. Mol Cell Biochem 2015;408:191–203.
Wang H, Zhang X, Yu P, Zhou Q, Zhang J, Zhang H, et al. Traditional Chinese medication Qiliqiangxin protects against cardiac remodeling and dysfunction in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int J Med Sci 2017;14:506–514.
Saxena A, Chen W, Su Y, Rai V, Uche OU, Li N, et al. IL-1 induces proinflammatory leukocyte infiltration and regulates fibroblast phenotype in the infarcted myocardium. J Immunol 2013;191:4838–4848.
Troncoso R, Ibarra C, Vicencio JM, Jaimovich E, Lavandero S. New insights into IGF-1 signaling in the heart. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2014;25:128–137.
Györfi AH, Matei AE, Distler J. Targeting TGF- β signaling for the treatment of fibrosis. Matrix Biol 2018;68–69:8–27.
Dai Y, Khaidakov M, Wang X, Ding Z, Su W, Price E, et al. MicroRNAs involved in the regulation of postischemic cardiac fibrosis. Hypertension 2013;61:751–756.
Tank J, Lindner D, Wang X, Stroux A, Gilke L, Gast M, et al. Single-target RNA interference for the blockade of multiple interacting proinflammatory and profibrotic pathways in cardiac fibroblasts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2014;66:141–156.
Huang Y, Lu SF, Hu CJ, Fu SP, Shen WX, Liu WX, et al. Electro-acupuncture at Neiguan pretreatment alters genome-wide gene expressions and protects rat myocardium against ischemia-reperfusion. Molecules 2014;19:16158–16178.
Xin JJ, Dai QF, Lu FY, Zhao YX, Liu Q, Cui JJ, et al. Antihypertensive and antifibrosis effects of acupuncture at PC 6 acupoints in spontaneously hypertensive rats and the underlying mechanisms. Front Physiol 2020;11:734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The experiments were done by Xin JJ, Liu Q, Zhao YX and Zhou C. Gao JH provided advice on the statistical analyses and data interpretation. Xin JJ drafted and finalized the paper. Yu XC was responsible for the conception, design, and supervision of the implementation of the study.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81804211, No. 81774439) and China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences Foundation (No. ZZ13-YQ-065)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Jj., Gao, Jh., Liu, Q. et al. Involvement of Interleukin-1 β/Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 in Ameliorating Effects of Electroacupuncture on Myocardial Fibrosis Induced by Essential Hypertension. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29, 162–169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-2897-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-022-2897-0