Abstract
Objective
To investigate the hepatoprotective effect of Xijiao Dihuang Decoction (犀角地黄汤, XJDHD) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α)-induced acute liver failure (ALF) as well as the underlying mechanism of action, and to clarify the key herbs and components of XJDHD.
Methods
LPS/D-galactosamine (D-GalN) or TNF-α/D-GalN were intraperitoneally injected into C57BL/6J mice to induce ALF. Simultaneously, XJDHD or its individual herbs and components were orally administered. Survival rates, transaminase levels in serum, and hepatic histology were examined to evaluate the effects of XJDHD. The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay and real-time polymerase chain reaction were additionally performed to expound the mechanism underlying the anti-apoptotic activity of XJDHD.
Results
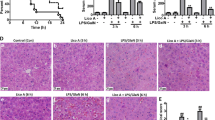
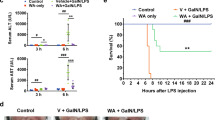
Oral administration of XJDHD protected mice from lethal liver failure induced by LPS and TNF-α, with notable amelioration of liver injury in histology and a significant decrease in transaminase levels in serum. XJDHD significantly inhibited apoptosis of hepatocytes and enhanced expression of the antiapoptosis genes, c-Flip, Iap1, Gadd45b and A20. In addition, Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. was identified as the key herb of XJDHD and galactose as the effective component of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. that protects against ALF.
Conclusions
XJDHD inhibits TNF-α-induced apoptosis of hepatocytes by promoting the expression of nuclear factor κ B-regulated anti-apoptotic genes. Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. is the effective herb of XJDHD and galactose is an active component in this protection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee WM. Acute liver failure. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2012;33:36–45.
Tiegs G, Wolter M, Wendel A. Tumor necrosis factor is a terminal mediator in galactosamine/endotoxin-induced hepatitis in mice. Biochem Pharmacol 1989;38:627–631.
Galanos C, Freudenberg MA, Reutter W. Galactosamineinduced sensitization to the lethal effects of endotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1979;76:5939–5943.
Chen WP, Bi L, Zhang X, Zeng L. A preliminary study of Liangxue Huayu Recipe (LHR) on the effects of hepatocyte apoptosis in rats with liver failure and related mechanism of particular gene expression. Chin J Tradit Med Sci Technol (Chin) 2006;13:143–145.
Jiang ZQ, Yan XJ, Bi L, Chen JP, Zhou Q, Chen WP. Mechanism for hepato-protective action of Liangxue Huayu Recipe (LHR): blockade of mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase activation. J Ethnopharmacol 2013;148:851–860.
Abdel-Salam BK, Sayed AA. Beneficial effect of garlic on D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced acutehepatic failure in male albino rats. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 2012;40:238–243.
Hou CC, Huang CC, Shyur LF. Echinacea alkamides prevent lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced acute hepatic injury through JNK pathway-mediated HO-1 expression. J Agric Food Chem 2011;59:11966–11974.
Lian LH, Jin X, Wu YL, Cai XF, Lee JJ, Nan JX. Hepatoprotective effects of Sedum sarmentosum on D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced murine fulminant hepatic failure. J Pharmacol Sci 2010;114:147–157.
Zhang JL, Zeng H, Wang XB. Discussion of Chinese syndrome typing in acute hepatic failure model. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2011;31:659–662.
Liu R, Wang M, Duan JA. Antipyretic and antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract of Cornu bubali (water buffalo horn). Am J Chin Med 2010;38:293–306.
Noda J, Imai T, Kida K, Otagiri M. The physicochemical and biopharmaceutical properties of fragmented keratin as a new drug carrier. Biol Pharm Bull 1996;19:466–473.
Lau TW, Lam FF, Lau KM, Chan YW, Lee KM, Sahota DS, et al. Pharmacological investigation on the wound healing effects of Radix rehmanniae in an animal model of diabetic foot ulcer. J Ethnopharmacol 2009;123:155–162.
Sasaki H, Nishimura H, Morota T, Chin M, Mitsuhashi H, Komatsu Y, et al. Immunosuppressive principles of Rehmannia glutinosa var. hueichingensis. Planta Med 1989;55:458–462.
Wu PS, Wu SJ, Tsai YH, Lin YH, Chao JC. Hot water extracted Lycium barbarum and Rehmannia glutinosa inhibit liver inflammation and fibrosis in rats. Am J Chin Med 2011;39:1173–1191.
Li R, Guo W, Fu Z, Ding G, Zou Y, Wang Z. Hepatoprotective action of Radix Paeoniae Rubra aqueous extract against CCl4-induced hepatic damage. Molecules 2011;16:8684–8694.
Wang R, Xiong AZ, Teng ZQ, Yang QW, Shi YH, Yang L. Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba attenuate CCl4-induced acute liver injury: an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS) based metabolomic approach for the pharmacodynamic study of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs). Int J Mol Sci 2012;13:14634–14647.
Fu PK, Yang CY, Tsai TH, Hsieh CL. Moutan cortex radicis improves lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats through anti-inflammation. Phytomedicine 2012;19:1206–1215.
Liu KY, Hu S, Chan BC, Wat EC, Lau CB, Hon KL, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic activities of Pentaherb formula, Moutan Cortex (Danpi) and gallic acid. Molecules 2013;18:2483–2500.
Yun CS, Choi YG, Jeong MY, Lee JH, Lim S. Moutan Cortex Radicis inhibits inflammatory changes of gene expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated gingival fibroblasts. J Nat Med 2013;67:576–589.
Park J, Kim HY, Lee SM. Protective effects of Moutan Cortex Radicis against acute hepatotoxicity. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med 2011;8:220–225.
Shon YH, Nam KS. Protective effect of Moutan Cortex extract on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2004;90:415–419.
Tomoda M, Tanaka M, Kondo N. Water-soluble constituents of Rehmanniae Radix. II. On the constituents of roots of Rehmannia glutinosa var. purpurea. Chem Pharm Bull 1971;19:2411–2413.
Li JP, Ma H, Wang YS, Hao JD. Comparison of contents of catalpol and sugars in fresh and dried Rehmannia glutinosa. Chin Pharm J (Chin) 2001;36:300–302.
Kucharczak J, Simmons MJ, Fan Y, Gelinas C. To be, or not to be: NF-kappaB is the answer—role of Rel/NF-kappaB in the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 2003;22:8961–8982.
Zhang RX, Li MX, Jia ZP. Rehmannia glutinosa: review of botany, chemistry and pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol 2008;117:199–214.
Aggarwal BB. Tumour necrosis factors receptor associated signalling molecules and their role in activation of apoptosis, JNK and NF-kappaB. Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59 (Suppl 1):i6–i16.
Karin M, Lin A. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 2002;3:221–227.
Ma A, Malynn BA. A20: linking a complex regulator of ubiquitylation to immunity and human disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2012;12:774–785.
Arvelo MB, Cooper JT, Longo C, Daniel S, Grey ST, Mahiou J, et al. A20 protects mice from D-galactosamine/ lipopolysaccharide acute toxic lethal hepatitis. Hepatology 2002;35:535–543.
Chang WT, Choi YH, van der Heijden R, Lee MS, Lin MK, Kong H, et al. Traditional processing strongly affects metabolite composition by hydrolysis in Rehmannia glutinosa roots. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2011;59:546–552.
Kubo M, Asano T, Matsuda H, Yutani S, Honda S. Studies on Rehmanniae radix. III;. The relation between changes of constituents and improvable effects on hemorheology with the processing of roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Yakugaku Zasshi (Jpn)1996;116:158–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81072766), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7112066), and 215 Program from Beijing Public Health Bureau (No. 2013-2-11)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Ym., Zhu, LL., Li, R. et al. Xijiao Dihuang Decoction (犀角地黄汤) and Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. protect mice against lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced acute liver failure. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 25, 446–453 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2141-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2141-2