Abstract
Objective
To investigate the possible mechanism of San-Cao Granule (SCG, 三草颗粒) mediating antiliver fibrosis.
Methods
A total of 60 male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into the normal control group, porcine serum-treated group, ursodesoxycholic acid (UDCA, 60 mg/kg), SCG (3.6 g/kg) group, SCG (1.8 g/kg) group and SCG (0.9 g/kg) group, with 10 rats in each group. Liver fibrosis was induced with porcine serum by intraperitoneal injection for 8 weeks, except for the normal control group. Then, the rats in the three SCG-treated groups and UDCA group were administered SCG and UDCA respectively for 4 weeks. The serum levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), albumin (ALB), total bilirubin (TBIL), hyaluronic acid (HA), laminin (LN), and type IV collagen (IVC) were examined using commercial kits and hepatic histopathology was examined with hematoxylin and eosin and Masson staining. Moreover, the protein expression levels of high mobility group box-1 protein (HMGB1), transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1), phosphorylated mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (p-Smad3), Smad7, toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) were determined by western blot, immunohistochemistry and real time quantitative-reverse transcription polymerase.
Results
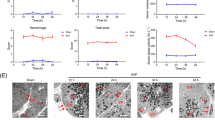
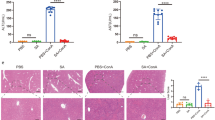
Both SCG (3.6 and 1.8 g/kg) and UDCA significantly ameliorated the liver fibrosis induced by porcine serum as indicated by retarding the serum levels increasing of ALT, AST, TBIL, HA, LN and IVC and preventing the serum level reducing of ALB compared with the model group (all P<0.01). Meanwhile, the collagen deposition was attenuated by SCG and UDCA treatment. Furthermore, SCG markedly reduced the expressions of HMGB1, TGF-β1, p-Smad3, TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB and α-SMA, and enhanced the expression of the Smad7 compared with the model group (all P<0.01).
Conclusion
SCG ameliorates hepatic fibrosis possibly through inhibiting HMGB1, TLR4/NF-κB and TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao YL, Ma X, Wang JB, Zhu Y, Li RS, Wang J, et al. Paeoniflorin alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting HIF-1a through mTOR-dependent pathway. Fitoterapia 2014;99:318–327.
Jiang W, Yang CQ, Liu WB, Wang YQ, He BM, Wang JY. Blockage of transforming growth factor ß receptors prevents progression of pig serum-induced rat liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2004;10:1634–1638.
Shen X, Cheng SS, Peng Y, Song HL, Li HM. Attenuation of early liver fibrosis by herbal compound “Diwu Yanggan” through modulating the balance between epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014;14:418.
Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol 2011;6:425–456.
Shen M, Chen K, Lu J, Cheng P, Xu L, Dai WQ, et al. Protective effect of astaxanthin on liver fibrosis through modulation of TGF-ß1 expression and autophagy. Mediators Inflamm 2014;2014:954502.
Yan HX, Wu HP, Zhang HL, Ashton C, Tong C, Wu H, et al. p53 promotes inflammation-associated hepatocarcinogenesis by inducing HMGB1 release. J Hepatol 2013;59:762–768.
Park JS, Svetkauskaite D, He Q, Kim JY, Strassheim D, Ishizaka A, et al. Involvement of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in cellular activation by high mobility group box 1 protein. J Biol Chem 2004;279:7370–7377.
Qian H, Shi J, Fan TT, Lv J, Chen SW, Song CY, et al. Sophocarpine attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:1822–1832.
Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA, et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med 2007;13:1324–1332.
Aoyama T, Paik YH, Seki E. Toll-like receptor signaling and liver fibrosis. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2010;2010.
Huang WJ, Li L, Tina XP, Yan JJ, Yang XZ, Wang XL, et al. Astragalus and Paeoniae radix rubra extract inhibits liver fibrosis by modulating the transforming growth factor-ß/Smad pathway in rats. Mol Med Rep 2015;11:805–814.
Zhao XK, Cheng ML, Wu RM, Yao YM, Mu M, Zhu JJ, et al. Effect of Danshao Huaxian Capsule on gremlin and bone morphogenetic protein-7 expression in hepatic fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:14875–14883.
Tao WT, Xu X, Wang X, Li BH, Wang YH, Li Y, et al. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumaeformula for application to cardiovascular disease. J Ethnopharmacol 2013;145:1–10.
He JY, Ge WH, Chen Y. Iron deposition and fat accumulation in dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis in rat. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:2061–2065.
Yao QY, Xu BL, Wang JQ, Liu HC, Zhang SC, Tu CT. Inhibition by curcumin of multiple sites of the transforming growth factor-beta 1 signaling pathway ameliorates the progression of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 2013;12:156.
Lv J, Nie ZK, Zhang JL, Liu FY, Wang ZZ, Ma ZL, et al. Corn peptides protect against thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis in Rats. J Med Food 2013;16:912–919.
Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008;134:1655–1669.
Czaja AJ. Hepatic inflammation and progressive liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:2515–32.
Dang SS, Wang BF, Cheng YA, Song P, Liu ZG, Li ZF. Inhibitory effects of saikosaponin-d on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrogenesis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:557–563.
Wang ME, Chen YC, Chen IS, Hsieh SC, Chen SS, Chiu CH. Curcumin protects against thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis by attenuating the inflammatory response and inducing apoptosis of damaged hepatocytes. J Nutr Biochem 2012;23:1352–1366.
Zhang Y, Zhang S, Li H, Huang M, Xu W, Chu K, et al. Ameliorative effects of Gualou Guizhi Decoction on inflammation in focal cerebral ischemic-reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 2015;12:988–994.
Wang FP, Li L, Li J, Wang JY, Wang LY, Jiang W. High mobility group box-1 promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatic stellate cells via TLR4-dependent signal pathways of PI3K/Akt and JNK. PLoS One 2013;8:e64373.
Lu N, Liu Y, Tang A, Chen L, Miao D, Yuan X. Hepatocytespecific ablation of PP2A catalytic subunit a attenuates liver fibrosis progression via TGF-ß1/Smad signaling. Biomed Res Int 2015; 2015:794862.
Jagavelu K, Routray C, Shergill U, O’Hara SP, Faubion W, Shah VH. Endothelial cell toll-like receptor 4 regulates fibrosis-associated angiogenesis in the liver. Hepatology 2010;52:590–601.
O’Neill LA. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: 10 years of progress. Immunol Rev 2008;226:10–18.
Liang B, Guo XL, Jin J, Ma YC, Feng ZQ. Glycyrrhizic acid inhibits apoptosis and fibrosis in carbon-tetrachloride-induced rat liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2015;21:5271–5280.
Chen S, Zou L, Li L, Wu T. The protective effect of glycyrrhetinic acid on carbon tetrachloride-induced chronic liver fibrosis in mice via upregulation of Nrf2. PLoS One 2013;8:e53662.
Li S, Wang L, Yan X, Wang Q, Tao Y, Li J, et al. Salvianolic acid B attenuates rat hepatic fibrosis via downregulating angiotensin signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012;2012:160726.
Meng Z, Meng L, Wang K, Li J, Cao X, Wu J, et al. Enhanced hepatic targeting, biodistribution and antifibrotic efficacy of tanshinone A loaded globin nanoparticles. Eur J Pharm Sci 2015;73:35–43.
Qu W, Huang H, Li K, Qin C. Danshensu-mediated protective effect against hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Pathol Biol (Paris) 2014;62:348–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Major Projects of the National Science and Technology (No. 2012ZX10005010-002-002) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81303120 and No. 81173571)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Sz., Luo, Sq., Wang, J. et al. San-Cao Granule (三草颗粒) Ameliorates Hepatic Fibrosis through High Mobility Group Box-1 Protein/Smad Signaling Pathway. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 24, 502–511 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2127-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-015-2127-0