Abstract
Objective
To determine the effect of combined treatment with Chinese medicine (CM) and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) on patients with severe aplastic anemia (SAA).
Methods
Eleven patients were treated with CM plus allo-HSCT. Nine patients received a conditioning regimen consisting of fludarabine (Flu), anti-thymocyte globulin (pig ALG), or anti-lymphocyte globulin (Rabbit ATG) and cyclophosphamide (CY), and two patients received pig ALG and CY. All patients were treated with Kidney (Shen)-reinforcing, blood-activating, and stasis-removing (KBS) herbal preparation beginning at 1 week before transplantation and ending at 8 weeks after transplantation. Chimerism status was assessed by analyzing short tandem repeat (STR) polymorphisms.
Results
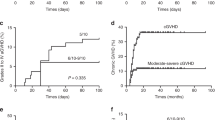
All patients recovered hematopoietic function and none had graft failure. The median number of days required for the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) increased to >0.5×109/L was 15 days (12–22 days) and for spontaneous platelet recovery to >20×109/L without post-transplantation transfusion was 17 days (15–27 days). Nine patients were long-term survivors and achieved full donor chimerism. The overall cumulative incidence of acute graft versus host disease (GVHD) grades I–II and III–IV was 18.2% (2/11) and 9.1% (1/11), respectively. The overall accumulated incidence of chronic GVHD was 27.3% and all patients had limited chronic GVHD. At a median follow-up time of 32 months (range: 12–97 months), 9 patients were still alive. The estimated 5-year overall survival (OS) rate was 81.8%. The incidence of treatment-related mortality, 2-year post-transplantation, was 18.2%. Two patients died from GVHD after transplantation.
Conclusion
Treatment with the KBS formulation may reduce the rate of graft failure and treatment-related mortality and improve the rate of OS in SAA patients with allo-HSCT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young NS, Bacigalupo A, Marsh JC. Aplastic anemia: pathophysiology and treatment. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010;16:S119–S125.
British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 2009;147:43–70.
Locasciulli A, Oneto R, Bacigalupo A, Socié G, Korthof E, Bekassy A, et al. Outcome of patients with acquired aplastic anemia given first line bone marrow transplantation or immunosuppressive treatment in the last decade: a report from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2007;92:11–18.
Passweg JR, Pérez WS, Eapen M, Camitta BM, Gluckman E, Hinterberger W, et al. Bone marrow transplants from mismatched related and unrelated donors for severe aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2006;37:641–649.
Bacigalupo A, Socie’ G, Lanino E, Prete A, Locatelli F, Locasciulli A, et al. Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, antithymocyte globulin, with or without low dose total body irradiation, for alternative donor transplants, in acquired severe aplastic anemia: a retrospective study from the EBMT-SAA working party. Haematologica 2010;95:976–982.
Viollier R, Socié G, Tichelli A, Bacigalupo A, Korthof ET, Marsh J, et al. Recent improvement in outcome of unrelated donor transplantation for aplastic anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant 2008;41:45–50.
Deeg HJ, O’Donnell M, Tolar J, Agarwal R, Harris RE, Feig SA, et al. Optimization of conditioning for marrow transplantation from unrelated donors for patients with aplastic anemia after failure of immunosuppressive therapy. Blood 2006;108:1485–1491.
Aki SZ, Sucak GT, Ozkurt ZN, Yeğin ZA, Yağci M, Haznedar R. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: graft rejection remains a problem. Transfus Apher Sci 2009;40:5–11.
Jeong DC, Chung NG, Kang HJ, Koo HH, Kook H, Kim SK, et al. Epidemiology and clinical long-term outcome of childhood aplastic anemia in Korea for 15 years: retrospective study of the Korean Society of Pediatric Hematology Oncology (KSPHO). J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2011;33:172–178.
Yu RX, Zhou YH, Lin SY. Effects of combined therapy of human leucocyte antigen haploidentical related bone marrow transplantation and Chinese medicine in treating leukaemia. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2006;26:600–603.
Shen JP, Ye BD, Zhou YH. Treatment of refractory severe autoimmune disease by combined therapy with Chinese drug and autohemopoietic stem cell transplantation. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2008;28:212–215.
Camitta BM, Thomas ED, Nathan DG, Gale RP, Kopecky KJ, Rappeport JM, et al. A prospective study of androgens and bone marrow transplantation for treatment of severe aplastic anemia. Blood 1979;53:504–514.
Zhang ZN, Shen D, eds. Diagnosis and treatment standards for blood diseases. 3rd ed. Beijing: Science Press; 2007:19–23.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA, et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974;18:295–304.
Martin PJ, Schoch G, Gooley T, Anasetti C, Deeg HJ, Nash R, et al. Methods for assessment of graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1998;92:3479–3481.
Sullivan KM. Graft-versus-host disease. In: Thomas ED, Blume KG, Forman SJ, eds. Hematopoietic cell transplantation. Malden, MA: Blackwell Sciences, Inc.; 1999:515–536.
Eapen M, Ramsay NK, Mertens AC, Robison LL, DeFor T, Davies SM. Late outcomes after bone marrow transplant for aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 2000;111:754–760.
Kang HJ, Shin HY, Park JE, Chung NG, Cho B, Kim HK, et al. Successful engraftment with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and thymoglobulin conditioning regimen in unrelated transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: a phase II prospective multicenter study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2010;16:1582–1588.
Wu DJ, Hu ZP, Shen YP, Zhou YH, Shen JP, Wu LQ, et al. Approach of staging evidences of acute aplastic anemia. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm (Chin) 2010;25:1099–1101.
Fang B, Li N, Song Y, Li J, Zhao RC, Ma Y. Cotransplantation of haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells to enhance engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells and to reduce the risk of graft failure in two children with severe aplastic anemia. Pediatr Transplant 2009;13:499–502.
Perez-Albuerne ED, Eapen M, Klein J, Gross TJ, Lipton JM, Baker KS, Woolfrey A, et al. Outcome of unrelated donor stem cell transplantation for children with severe aplastic anemia. Br J Haematol 2008;141:216–223.
Lee JW, Kang HJ, Kim EK, Kim H, Shin HY, Ahn HS. Effect of iron overload and iron-chelating therapy on allogeneic hematopoietic SCT in children. Bone Marrow Transplant 2009;44:793–797.
Armand P, Kim HT, Cutler CS, Ho VT, Koreth J, Alyea EP, et al. Prognostic impact of elevated pretransplantation serum ferritin in patients undergoing myeloablative stem cell transplantation. Blood 2007;109:4586–4588.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. JDZX2012178), 2011 Special Research Funds for the Traditional Chinese Medicine Industry (No. 201107001) and Zhejiang Provincial Traditional Chinese Medicine Administration Bureau Program (No. 2007CA025)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, Bd., Zhang, X., Shao, Kd. et al. Combined use of Chinese medicine with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for severe aplastic anemia patients. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 20, 903–909 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-2026-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-014-2026-9