Abstract
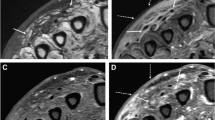
To assess whether our epidemiological data on infections in exposed fractures were in line with the literature, we evaluated the wound swabs and osteosynthesis material that reached the Laboratory of Microbiology and Virology of AOU-Careggi Hospital during the period September 2017-September 2018. We observed a different trend between wound samples from all departments and samples sent only from the orthopaedic department, which showed a higher Gram-negative isolates level in the orthopaedics population (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) compared to Gram-positive levels (Staphylococcus aureus) in other departments. If we consider wound swabs as the first analysis for early infection and the material sample as post-surgical analysis and, therefore, an index of delayed or late infection, then we can confirm that our epidemiological data are consistent with the aetiological models described in the literature, where a shift of Gram-negative to Gram-positive bacterial flora is observed. However, our data cannot represent the epidemiology of infections on exposed fractures because sample information is scarce.


Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliografia
Trampuz A, Zimmerli W (2006) Diagnosis and treatment of infections associated with fracture-fixation devices. Inj Int J Care Inj 37:S59–S66
Bhatty S, Rajesh P, Harjit K (2018) Study of microbiological flora and role of primary bacterial cultures in management of open fractures of long bones. Int J Orthop Sci 4(2):91–94
Trampuz A, Zimmerli W (2005) Prosthetic joint infections: update in diagnosis and treatment. Swiss Med Weekly 135(17–18):243–251
Del Pozo JL, Patel R (2009) Clinical practice. Infection associated with prosthetic joints. N Engl J Med 361(8):787–794
PHE 2016 Public Health England (2016) Investigation of orthopaedic implant associated infections. UK Standards for Microbiology Investigations. B 44 Emissione n°2 del 23 febbraio 2016
Jones ME, Karlowsky JA, Draghi DC et al. (2003) Epidemiology and antibiotic susceptibility of bacteria causing skin and soft tissue infections in the USA and Europe: a guide to appropriate antimicrobial therapy. J Antimicrob Agents 22:406–419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflitto di interesse
Gli autori Guendalina Vaggelli, Eleonora Riccobono, Blerina Jance e Gian Maria Rossolini dichiarano di non avere alcun conflitto di interesse.
Consenso informato e conformità agli standard etici
Tutte le procedure descritte nello studio e che hanno coinvolto esseri umani sono state attuate in conformità alle norme etiche stabilite dalla dichiarazione di Helsinki del 1975 e successive modifiche. Il consenso informato è stato ottenuto da tutti i pazienti inclusi nello studio.
Human and Animal Rights
L’articolo non contiene alcuno studio eseguito su esseri umani e su animali da parte degli autori.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaggelli, G., Riccobono, E., Jance, B. et al. Epidemiologia delle fratture esposte presso AOU Careggi, Firenze; criticità nel percorso diagnostico. LO SCALPELLO 33, 8–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11639-019-00307-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11639-019-00307-1