Abstract
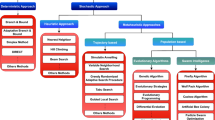
Swarm intelligence has become a hot research field of artificial intelligence. Considering the importance of swarm intelligence for the future development of artificial intelligence, we discuss and analyze swarm intelligence from a broader and deeper perspective. In a broader sense, we are talking about not only bio-inspired swarm intelligence, but also human-machine hybrid swarm intelligence. In a deeper sense, we discuss the research using a three-layer hierarchy: in the first layer, we divide the research of swarm intelligence into bio-inspired swarm intelligence and human-machine hybrid swarm intelligence; in the second layer, the bio-inspired swarm intelligence is divided into single-population swarm intelligence and multi-population swarm intelligence; and in the third layer, we review single-population, multi-population and human-machine hybrid models from different perspectives. Single-population swarm intelligence is inspired by biological intelligence. To further solve complex optimization problems, researchers have made preliminary explorations in multi-population swarm intelligence. However, it is difficult for bio-inspired swarm intelligence to realize dynamic cognitive intelligent behavior that meets the needs of human cognition. Researchers have introduced human intelligence into computing systems and proposed human-machine hybrid swarm intelligence. In addition to single-population swarm intelligence, we thoroughly review multi-population and human-machine hybrid swarm intelligence in this paper. We also discuss the applications of swarm intelligence in optimization, big data analysis, unmanned systems and other fields. Finally, we discuss future research directions and key issues to be studied in swarm intelligence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Zhang, H. Mei. A constructive model for collective intelligence. National Science Review, vol. 7, no. 8, pp. 1273–1277, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwaa092.
Y. Jiang, W. Zhang, P. Wang, X. Y. Zhang, H. Mei. Knowledge graph construction method via internet-based collective intelligence. Journal of Software, vol. 33, no. 7, pp. 2646–2666, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006313. (in Chinese)
B. Shen, W. Zhang, H. Y. Zhao, Z. Jin, Y. H. Wu. Solving pictorial jigsaw puzzles via Internet-based collective intelligence. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 206–230, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/SSI-2019-0150. (in Chinese)
W. Zhang, H. Mei. Software development based on collective intelligence on the Internet: Feasibility, state-of-the-practice, and challenges. SCIENTIA SINICA Informations, vol. 47, no. 12, pp. 1601–1622, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/N112017-00117. (in Chinese)
J. H. Holland. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: An Introductory Analysis with Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence, Ann Arbor, USA: University of Michigan Press, 1975.
R. Storn, K. Price. Differential evolution — A simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. Journal of Global Optimization, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 341–359, 1997. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008202821328.
J. Y. Li, Z. H. Zhan, J. Zhang. Evolutionary computation for expensive optimization: A survey. Machine Intelligence Research, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 3–23, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-022-1317-4.
Q. F. Ding, X. Y. Yin. Research survey of differential evolution algorithms. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 431–442, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11992/tis.201605015.
G. Beni, J. Wang. Swarm intelligence in cellular robotic systems. In Proceedings of NATO Advanced Workshop on Robots and Biological Systems: Towards a new Bionics, Springer, Toscana, Italy, pp. 703–712, 1993. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-58069-7_38.
A. Colorni, M. Dorigo, V. Maniezzo. Distributed optimization by ant colonies. In Proceedings of the 1st European Conference on Artificial Life, Paris, France, pp. 134–142, 1991.
J. Kennedy, R. Eberhart. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of EEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, pp. 1942–1948, 1995. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968.
E. Bonabeau, M. Dorigo, G. Theraulaz. Swarm Intelligence: From Natural to Artificial Systems, New York, USA: Oxford University Press, 1999.
J. Kennedy, R. C. Eberhart, Y. H. Shi. Swarm Intelligence, San Francisco, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, pp. 5–12, 2001.
H. P. Ma, S. G. Shen, M. Yu, Z. L. Yang, M. R. Fei, H. Y. Zhou. Multi-population techniques in nature inspired optimization algorithms: A comprehensive survey. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, vol. 44, pp. 365–387, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.04.011.
S. Mirjalili, S. M. Mirjalili, A. Lewis. Grey wolf optimizer. Advances in Engineering Software, vol. 69, pp. 46–61, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007.
F. Fausto, E. Cuevas, A. Valdivia, A. González. A global optimization algorithm inspired in the behavior of selfish herds. BioSystems, vol. 160, pp. 39–55, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2017.07.010.
J. C. Sun, J. L. Wang, J. Chen, G. R. Guo. Cooperative communication based on swarm intelligence: Vision, model, and key technology. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 307–317, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/SSI-2019-0186.
X. Yao, G. L. Chen, H. M, X U, Y. Liu. A survey of evolutionary algorithms. Chinese Journal of Computers, vol. 18, no. 9, pp. 694–706, 1995. (in Chinese)
S. Mirjalili, J. S. Dong, A. S. Sadiq, H. Faris. Genetic algorithm: Theory, literature review, and application in image reconstruction. Nature-inspired Optimizers, S. Mirjalili, J. S. Dong, A. Lewis, Eds., Cham, Germany: Springer, pp. 69–85, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12127-3_5.
H. Ishibuchi, T. Yamamoto. Fuzzy rule selection by multi-objective genetic local search algorithms and rule evaluation measures in data mining. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, vol. 141, no. 1, pp. 59–88, 2004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(03)00114-3.
G. Syswerda. Uniform crossover in genetic algorithms. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Genetic Algorithms, ACM, San Francisco, USA, pp. 2–9, 1989. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5555/645512.657265.
R. Kumar, Jyotishree. Blending roulette wheel selection & rank selection in genetic algorithms. International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 365–370, 2012.
J. Grefenstette, R. Gopal, B. J. Rosmaita, D. V. Gucht. Genetic algorithms for the traveling salesman problem. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Genetic Algorithms, Carnegie-Mellon University, Pittsburgh, USA, pp. 160–168, 1985.
X. B. Hu, E. Di Paolo. An efficient genetic algorithm with uniform crossover for the multi-objective airport gate assignment problem. Multi-objective Memetic Algorithms, C. K. Goh, Y. S. Ong, K. C. Tan, Eds., Berlin, Germany: Springer, pp. 71–89, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88051-6_4.
E. Semenkin, M. Semenkina. Self-configuring genetic algorithm with modified uniform crossover operator. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advances in Swarm Intelligence, Springer, Shenzhen, China, pp. 414–421, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-30976-2_50.
M. L. Mauldin. Maintaining diversity in genetic search. In Proceedings of the 4th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, USA, pp.247–250, 1984. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5555/2886937.2886983.
K. Deb, A. Pratap, S. Agarwal, T. Meyarivan. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 182–197, 2002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/4235.996017.
K. Deb, H. Jain. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point-based nondominated sorting approach, part I: Solving problems with box constraints. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 577–601, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4109/TEVC.2013.2281535.
N. Pham, A. Malinowski, T. Bartczak. Comparative study of derivative free optimization algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 592–600, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2011.2166799.
Y. P. Zhou, X. S. Gu. Development of differential evolution algorithm. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 1–6, 2007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3932.2007.03.001. (in Chinese)
K. H. Han, J. H. Kim. Quantum-inspired evolutionary algorithm for a class of combinatorial optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 580–593, 2002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2002.804320.
G. W. Zhang, R. He, Y. Liu, D. Y. Li. G. S. Chen. An evolutionary algorithm based on cloud model. Chinese Journal of Computers, vol. 31, no. 7, pp. 1082–1091, 2008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0254-4164.2008.07.003. (in Chinese)
J. Y. Li, Z. H. Zhan, K. C. Tan, J. Zhang. A meta-knowledge tranfeer-based differential evolution for multitask optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 719–734, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2021.3131236.
K. R. Opara, J. Arabas. Differential evolution: A survey of theoretical analyses. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, vol. 44, pp. 546–558, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.06.010.
J. Brest, S. Greiner, B. Boskovic, M. Mernik, V. Zumer. Self-adapting control parameters in differential evolution: A comparative study on numerical benchmark problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 646–657, 2006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2006.872133.
Q. Q. Fan, W. L. Wang, X. F. Yan. Differential evolution algorithm with strategy adaptation and knowledge-based control parameters. Artificial Intelligence Review, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 219–253, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-017-9562-6.
F. Q. Zhao, L. X. Zhao, L. Wang, H. B. Song. An ensemble discrete differential evolution for the distributed blocking flowshop scheduling with minimizing makespan criterion. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 160, Article number 113678, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113678.
Z. Y. Meng, J. S. Pan, K. K. Tseng. PaDE: An enhanced Differential Evolution algorithm with novel control parameter adaptation schemes for numerical optimization. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 168, pp. 80–99, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.01.006.
S. M. Guo, C. C. Yang. Enhancing differential evolution utilizing eigenvector-based crossover operator. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 31–49, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2013.2297160.
Y. Wang, Z. X. Cai, Q. F. Zhang. Enhancing the search ability of differential evolution through orthogonal crossover. Information Sciences, vol. 185, no. 1, pp. 153–177, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2011.09.001.
W. Y. Gong, Z. H. Cai. Differential evolution with ranking-based mutation operators. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 2066–2081, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2013.2239988.
S. Das, A. Abraham, U. K. Chakraborty, A. Konar. Differential evolution using a neighborhood-based mutation operator. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 526–553, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2008.2009457.
R. A. Sarker, S. M. Elsayed, T. Ray. Diffferential evolution with dynamic parameters selection for optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 689–707, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2013.2281528.
X. F. Liu, Z. H. Zhan, Y. Lin, W. N. Chen, Y. J. Gong, T. L. Gu, H. Q. Yuan, J. Zhang. Historical and heuristic-based adaptive differential evolution. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, vol. 49, no. 12, pp. 2623–2635, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2018.2855155.
Z. H. Zhan, Z. J. Wang, H. Jin, J. Zhang. Adaptive distributed differential evolution. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 50, no. 11, pp. 4633–4647, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2944873.
Z. G. Chen, Z. H. Zhan, H. Wang, J. Zhang. Distributed individuals for multiple peaks: A novel differential evolution for multimodal optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 708–719, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2019.2944180.
X. S. Yang. A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. Nature Inspired Cooperative Strategies for Optimization, J. R. González, D. A. Pelta, C. Cruz, G. Terrazas, N. Krasnogor, Eds., Berlin, Germany: Springer, pp. 65–74, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12538-6_6.
W. T. Pan. A new fruit fly optimization algorithm: Taking the financial distress model as an example. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 26, pp. 69–74, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2011.07.001.
H. B. Duan, P. X. Qiao. Pigeon-inspired optimization: A new swarm intelligence optimizer for air robot path planning. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Cybernetics, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 24–37, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJICC-02-2014-0005.
A. Prakasam, N. Savarimuthu. Metaheuristic algorithms and probabilistic behaviour: A comprehensive analysis of ant colony optimization and its variants. Artificial Intelligence Review, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 97–130, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-015-9441-y.
X. L. Zhang, X. F. Chen, Z. J. He. An ACO-based algorithm for parameter optimization of support vector machines. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 37, no. 9, pp. 6618–6628, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.03.067.
L. C. Lu, T. W. Yue. Mission-oriented ant-team ACO for min-max MTSP. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 76, pp. 436–444, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.11.048.
L. Shi, Z. H. Zhan, D. Liang, J. Zhang. Memory-based ant colony system approach for multi-source data associated dynamic electric vehicle dispatch optimization. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, to be published. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3150471.
A. Ratnaweera, S. K. Halgamuge, H. C. Watson. Self-organizing hierarchical particle swarm optimizer with time-varying acceleration coefficients. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 240–255, 2004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2004.826071.
S. Javed, K. Ishaque, S. A. Siddique, Z. Salam. A simple yet fully adaptive PSO algorithm for global peak tracking of photovoltaic array under partial shading conditions. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 69, no. 6, pp. 5922–5930, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2021.3091921.
W. Deng, J. J. Xu, H. M. Zhao, Y. J. Song. A novel gate resource allocation method using improved PSO-based QEA. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 1737–1745, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.3025796.
M. R. Tanweer, S. Suresh, N. Sundararajan. Self regulating particle swarm optimization algorithm. Information Sciences, vol. 294, pp. 182–202, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.09.053.
R. Cheng, Y. C. Jin. A social learning particle swarm optimization algorithm for scalable optimization. Information Sciences, vol. 291, pp. 43–60, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2014.08.039.
X. W. Xia, L. Gui, F. Yu, H. R. Wu, B. Wei, Y. L. Zhang, Z. H. Zhan. Triple archives particle swarm optimization. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 50, no. 12, pp. 4862–4875, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2943928.
J. Y. Li, Z. H. Zhan, R. D. Liu, C. Wang, S. Kwong, J. Zhang. Generation-level parallelism for evolutionary computation: A pipeline-based parallel particle swarm optimization. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 51, no. 10, pp. 4848–4859, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3028070.
T. Blackwell, J. Kennedy. Impact of communication topology in particle swarm optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 689–702, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2018.2880894.
A. P. Lin, W. Sun, H. S. Yu, G. H. Wu, H. W. Tang. Global genetic learning particle swarm optimization with diversity enhancement by ring topology. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, vol. 44, pp. 571–583, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2018.07.002.
J. R. Jian, Z. G. Chen, Z. H. Zhan, J. Zhang. Region encoding helps evolutionary computation evolve faster: A new solution encoding scheme in particle swarm for large-scale optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 25, no. 4, pp. 779–793, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2021.3065659.
C. Gan, W. H. Cao, M. Wu, X. Chen. A new bat algorithm based on iterative local search and stochastic inertia weight. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 104, pp. 202–212, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.015.
M. R. Chen, Y. Y. Huang, G. Q. Zeng, K. D. Lu, L. Q. Yang. An improved bat algorithm hybridized with extremal optimization and Boltzmann selection. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 175, Article number 114812, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114812.
Q. Liu, L. Wu, W. S. Xiao, F. D. Wang, L. C. Zhang. A novel hybrid bat algorithm for solving continuous optimization problems. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 73, pp. 67–82, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.08.012.
Z. H. Cui, F. X. Li, W. S. Zhang. Bat algorithm with principal component analysis. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 603–622, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0888-4.
G. Hu, Z. Q. Xu, G. R. Wang, B. Zeng, Y. B. Liu, Y. Lei. Forecasting energy consumption of long-distance oil products pipeline based on improved fruit fly optimization algorithm and support vector regression. Energy, vol. 224, Article number 120153, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120153.
L. Wu, Q. Liu, X. Tian, J. X. Zhang, W. S. Xiao. A new improved fruit fly optimization algorithm IAFOA and its application to solve engineering optimization problems. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 144, pp. 153–173, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.12.031.
X. F. Yuan, X. S. Dai, J. Y. Zhao, Q. He. On a novel multi-swarm fruit fly optimization algorithm and its application. Applied Mathematics and Computation, vol. 233, pp. 260–271, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amc.2014.02.005.
H. B. Duan, H. X. Qiu. Advancements in pigeon-inspired optimization and its variants. Science China Information Sciences, vol. 62, no. 7, Article number 70201, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-018-9752-9.
R. Dou, H. B. Duan. Lévy flight based pigeon-inspired optimization for control parameters optimization in automatic carrier landing system. Aerospace Science and Technology, vol. 61, pp. 11–20, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2016.11.012.
Z. Y. Yang, H. B. Duan, Y. M. Fan, Y. M. Deng. Automatic carrier landing system multilayer parameter design based on Cauchy mutation pigeon-inspired optimization Aerospace Science and Technology, vol. 79, pp. 518–530, 2018 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2018.06.013.
H. B. Duan, X. H. Wang. Echo state networks with orthogonal pigeon-inspired optimization for image restoration. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 27, no. 11, pp. 2413–2425, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2479117.
X. B. Xu, Y. M. Deng. UAV power component-DC brushless motor design with merging adjacent-disturbances and integrated-dispatching pigeon-inspired optimization IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 54, no. 8, Article number 7402307, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2018.2839663.
D. F. Zhang, H. B. Duan. Social-class pigeon-inspired optimization and time stamp segmentation for multi-UAV cooperative path planning. Neurocomputing, vol. 313, pp. 229–246, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.06.032.
Y. Ning, Z. S. Peng, Y. X. Dai, D. Q. Bi, J. Wang. Enhanced particle swarm optimization with multi-swarm and multi-velocity for optimizing high-dimensional problems. Applied Intelligence, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 335–351, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-018-1258-3.
B. Farnad, A. Jafarian, D. Baleanu. A new hybrid algorithm for continuous optimization problem. Applied Mathematical Modelling, vol. 55, pp. 652–673, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apm.2017.10.001.
L. P. Wang, M. L. Feng, Q. C. Qiu, M. L. Zhang, F. Y. QiuSurvey on preference-based multi-objective evolutionary algorithms. Chinese Journal of Computers, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 1289–1315, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.01289.
Z. H. Zhan, L. Shi, K. C. Tan, J. Zhang. A survey on evolutionary computation for complex continuous optimization. Artificial Intelligence Review, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 59–110, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-021-10042-y.
X. Q. Shi, W. Long, Y. Y. Li, D. S. Deng, Y. L. Wei. Research on the performance of multi-population genetic algorithms with different complex network structures. Soft Computing, vol. 24, no. 17, pp. 13441–13459, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04759-1.
W. Wei, Q. Wang, H. Wang, H. G. Zhang. The feature extraction of nonparametric curves based on niche genetic algorithms and multi-population competition. Pattern Recognition Letters, vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 1483–1497, 2005. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2004.10.027.
Y. X. Shen, G. Y. Wang, C. H. Zeng. Study on the relationship between population diversity and learning parameters in particle swarm optimization. Acta Electronica Sinica, vol. 39, no. 6, pp. 1238–1244, 2011.
F. Kılıç, Y. Kaya, S. Yildirim. A novel multi population based particle swarm optimization for feature selection. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 219, Article number 106894, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106894.
S. K. Fan, J. M. Chang. Dynamic multi-swarm particle swarm optimizer using parallel PC cluster systems for global optimization of large-scale multimodal functions. Engineering Optimization, vol. 42, no. 5, pp. 431–451, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150903247736.
H. Basak, R. Kundu, S. Chakraborty, N. Das. Cervical cytology classification using PCA and GWO enhanced deep features selection. SN Computer Science, vol. 2, no. 5, Article number 369, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00741-2.
A. Gupta, Y. S. Ong, L. Feng. Multifactorial evolution: Toward evolutionary multitasking. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 343–357, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2015.2458037.
A. Gupta, Y. S. Ong, L. Feng, K. C. Tan. Multiobjective multifactorial optimization in evolutionary multitasking. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 1652–1665, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2016.2554622.
A. Gupta, J. Mańdziuk, Y. S. Ong. Evolutionary multitasking in bi-level optimization. Complex & Intelligent Systems, vol. 1, no. 1–4, pp. 83–95, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-016-0011-y.
G. H. Li, Q. Z. Lin, W. F. Gao. Multifactorial optimization via explicit multipopulation evolutionary framework. Information Sciences, vol. 512, pp. 1555–1570, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.10.066.
K. Chen, B. Xue, M. J. Zhang, F. Y. Zhou. Evolutionary multitasking for feature selection in high-dimensional classification via particle swarm optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 446–460, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2021.3100056.
Z. G. Chen, Z. H. Zhan, Y. Lin, Y. J. Gong, T. L. Gu, F. Zhao, H. Q. Yuan, X. F. Chen, Q. Li, J. Zhang. Multiobjective cloud workflow scheduling: A multiple populations ant colony system approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 49, no. 8, pp. 2912–2926, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2832640.
Z. J. Wang, Z. H. Zhan, W. J. Yu, Y. Lin, J. Zhang, T. L. Gu, J. Zhang. Dynamic group learning distributed particle swarm optimization for large-scale optimization and its application in cloud workflow scheduling. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 50, no. 6, pp. 2715–2729, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2933499.
X. F. Liu, Z. H. Zhan, Y. Gao, J. Zhang, S. Kwong, J. Zhang. Coevolutionary particle swarm optimization with bottleneck objective learning strategy for many-objective optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 587–602, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2018.2875430.
Z. J. Wang, Z. H. Zhan, S. Kwong, H. Jin, J. Zhang. Adaptive granularity learning distributed particle swarm optimization for large-scale optimization. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 1175–1188, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977956.
M. A. Potter, K. A. De Jong. A cooperative coevolutionary approach to function optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, Springer, Jerusalem, Israel, pp. 249–257, 1994. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-58484-6_269.
W. Du, L. Tong, T. Yang. Effective resource allocation in cooperative co-evolutionary algorithm for large-scale fully-separable problems. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Toronto, Canada, pp. 4198–4203, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC42975.2020.9283410.
X. L. Ma, X. D. Li, Q. F. Zhang, K. Tang, Z. P. Liang, W. X. Xie, Z. X. Zhu. A survey on cooperative co-evolutionary algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 23, no. 3, pp. 421–441, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2018.2868770.
Z. H. Zhan, X. F. Liu, H. X. Zhang, Z. T. Yu, J. Weng, Y. Li, T. L. Gu, J. Zhang. Cloudde: A heterogeneous differential evolution algorithm and its distributed cloud version. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 704–716, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TP-DS.2016.2597826.
J. Y. Li, K. J. Du, Z. H. Zhan, H. Wang, J. Zhang. Distributed differential evolution with adaptive resource allocation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, to be published. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2022.3153964.
M. Mavrovouniotis, S. X. Yang, X. Yao. Multi-colony ant algorithms for the dynamic travelling salesman problem. In Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Dynamic and Uncertain Environments, Orlando, USA, pp. 9–16, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CIDUE.2014.7007861.
I. Bailey, J. P. Myatt, A. M. Wilson. Group hunting within the carnivora: Physiological, cognitive and environmental influences on strategy and cooperation. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, vol. 67, no. 1, pp. 1–17, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-012-1423-3.
B. Li, H. S. Deng, J. Wang. Optimal scheduling of microgrid considering the interruptible load shifting based on improved biogeography-based optimization algorithm. Symmetry, vol. 13, no. 9, Article number 1707, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/sym13091707.
J. M. Lien, S. Rodriguez, J. P. Malric, N. M. Amato. Shepherding behaviors with multiple shepherds. In Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, pp. 3402–3407, 2005. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2005.1570636.
P. G. Keil. Human-sheepdog distributed cognitive systems: An analysis of interspecies cognitive scaffolding in a sheepdog trial. Journal of Cognition and Culture, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 508–529, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/15685373-12342163.
H. T. Nguyen, T. D. Nguyen, M. Garratt, K. Kasmarik, S. Anavatti, M. Barlow, H. A. Abbass. A deep hierarchical reinforcement learner for aerial shepherding of ground swarms. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Springer, Sydney, Australia, pp.688–699, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-36708-4_54.
N. K. Long, K. Sammut, D. Sgarioto, M. Garratt, H. A. Abbass. A comprehensive review of shepherding as a bio-inspired swarm-robotics guidance approach. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 523–537, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TETCI.2020.2992778.
D. F. Zhang, J. L. Zhang. Multi-species evolutionary algorithm for wireless visual sensor networks coverage optimization with changeable field of views. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 96, Article number 106680, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106680.
S. Mirjalili, A. Lewis. The Whale Optimization Algorithm. Advances in Engineering Software, vol. 95, pp. 51–67, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008.
Y. J. Sun, Y. Chen. Multi-population improved whale optimization algorithm for high dimensional optimization. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 112, Article number 107854, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107854.
Q. Fan, Z. J. Chen, Z. Li, Z. H. Xia, J. Y. Yu, D. Z. Wang. A new improved whale optimization algorithm with joint search mechanisms for high-dimensional global optimization problems. Engineering with Computers, vol. 37, no. 3, pp. 1851–1878, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00917-8.
S. Chakraborty, A. K. Saha, R. Chakraborty, M. Saha. An enhanced whale optimization algorithm for large scale optimization problems. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 233, Article number 107543, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.107543.
S. Shadravan, H. R. Naji, V. K. Bardsiri. The sailfish optimizer: A novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving constrained engineering optimization problems. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 80, pp. 20–34, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2019.01.001.
K. Asghari, M. Masdari, F. S. Gharehchopogh, R. Saneifard. A chaotic and hybrid gray wolf-whale algorithm for solving continuous optimization problems. Progress in Artificial Intelligence, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 349–374, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13748-021-00244-4.
M. Karakoyun, A. Ö zkis, H. Kodaz. A new algorithm based on gray wolf optimizer and shuffled frog leaping algorithm to solve the multi-objective optimization problems. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 96, Article number 106560, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106560.
P. Dhal, C. Azad. A multi-objective feature selection method using Newton’s law based PSO with GWO. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 107, Article number 107394, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107394.
X. M. Zhang, X. Wang, H. Y. Chen, D. D. Wang, Z. H. Fu. Improved GWO for large-scale function optimization and MLP optimization in cancer identification. Neural Computing and Applications, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 1305–1325, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04483-4.
S. K. Nseef, S. Abdullah, A. Turky, G. Kendall. An adaptive multi-population artificial bee colony algorithm for dynamic optimisation problems. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 104, pp. 14–23, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.04.005.
G. H. Wu, R. Mallipeddi, P. N. Suganthan, R. Wang, H. K. Chen. Differential evolution with multi-population based ensemble of mutation strategies. Information Sciences, vol. 329, pp. 329–345, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2015.09.009.
Q. Wang, L. Tan. Optimization algorithm for accurately theme-aware task assignment in crowd computing on big data. Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 2777–2783, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2016.10.2777. (in Chinese)
W. Li, J. Chen. Review and prospect of cooperative combat of manned/unmanned aerial vehicle hybrid formation. Aerospace Control, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 90–96 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.16804/j.cnki.issn1006-3242.2017.03.017. (in Chinese)
A. B. Kao, A. M. Berdahl, A. T. Hartnett, M. J. Lutz, J. B. Bak-Coleman, C. C. Ioannou, X. Giam, I. D. Couzin. Counteracting estimation bias and social influence to improve the wisdom of crowds. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, vol. 15, no. 141, Article number 20180130, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2018.0130.
J. Surowiecki. The Wisdom of Crowds: Why the Many are Smarter than the Few and How Collective Wisdom Shapes Business, Economies, Societies and Nations, New York, USA: Doubleday, 2004.
J. Lorenz, H. Rauhut, F. Schweitzer, D. Helbing. How social influence can undermine the wisdom of crowd effect. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 108, no. 22, pp. 9020–9025, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008636108.
M. S. Lobo, D. Yao. Human Judgement is Heavy Tailed: Empirical Evidence and Implications for the Aggregation of Estimates and Forecasts, Technical Report ZDB-ID 2112291-X, Department of Decision Sciences, European Institute of Business Administration (INSEAD), Paris, France, 2010.
B. T. Chen, L. Q. Wang, X. M. Jiang, H. B. Yao. Survey of task assignment for crowd-based cooperative computing. Computer Engineering and Applications, vol. 57, no. 20, pp. 1–2, 2021.
I. Lykourentzou, V. J. Khan, K. Papangelis, P. Markopoulos. Macrotask crowdsourcing: An integrated definition. Macrotask Crowdsourcing, V. J. Khan, K. Papangelis, I. Lykourentzou, P. Markopoulos, Eds., Cham, Germany: Springer, pp. 1–13, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12334-5_1.
Z. Y. Zheng, G. L. Jiang, X. J. Zhang, Z. F. Wang, D. Li. Crowdsourcing quality evaluation algorithm based on sliding task window. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, vol. 38, no. 9, pp. 2125–2129, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2017.09.038. (in Chinese)
Y. Yan, R. Rosales, G. Fung, J. G. Dy. Active learning from crowds. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, ACM, Bellevue, USA, pp. 1161–1168, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5555/3104482.3104628.
J. Goncalves, M. Feldman, S. B. Q. Hu, V. Kostakos, A. Bernstein. Task routing and assignment in crowdsourcing based on cognitive abilities. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web Companion, ACM, Perth, Australia, pp. 1023–1031, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3041021.3055128.
D. Hettiachchi, N. Van Berkel, V. Kostakos, J. Goncalves. CrowdCog: A cognitive skill based system for heterogeneous task assignment and recommendation in crowdsourcing. Proceedings of ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, vol. 4, no. CSCW2, Article number 110, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3415181.
Q. C. Li, H. Cao, S. K. Wang, X. L. Zhao. A reputation-based multi-user task selection incentive mechanism for crowdsensing. IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 74887–74900, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989406.
S. Jagabathula, L. Subramanian, A. Venkataraman. Reputation-based worker filtering in crowdsourcing. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, ACM, Montreal, Canada, pp.2492–2500, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5555/2969033.2969105.
K. L. Huang, S. S. Kanhere, W. Hu. Are you contributing trustworthy data? The case for a reputation system in participatory sensing. In Proceedings of the 13th ACM International Conference on Modeling, Analysis, and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems, Bodrum, Turkey, pp. 14–22, 2010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/1868521.1868526.
J. X. Wu, Z. H. Zhang. Collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on user rating and similarity of explicit and implicit interest. Computer Science, vol. 48, no. 5, pp. 147–154, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11896/jsjkx.200300072. (in Chinese)
V. Ambati, S. Vogel, J. G. Carbonell. Towards task recommendation in micro-task markets. In Proceedings of the 11th AAAI Conference on Human Computation, Palo Alto, USA, pp. 80–83, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5555/2908698.2908712.
F. Xu, Z. C. Ji, B. Wang. Dual role model for question recommendation in community question answering. In Proceedings of the 35th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Portland, USA, pp. 771–780, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2348283.2348387.
Z. W. Guo, C. W. Tang, W. J. Niu, Y. Q. Fu, T. Wu, H. Y. Xia, H. Tang. Fine-grained recommendation mechanism to curb astroturfing in crowdsourcing systems. IEEE Access, vol. 5, pp. 15529–15541, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2731360.
J. Yan, S. P. Ku, C. Yu. Reputation model of crowdsourcing workers based on active degree. Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 37, no. 7, pp. 2039–2043, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2017.07.2039. (in Chinese)
Z. M. Shi. Multi-objective Task Recommendation Method Based on Different Task Characteristics for Crowdsourcing, Master dissertation, School of Mathematics, China University of Mining and Technology, China, 2019. (in Chinese)
Q. Zhou, M. Fang. Research on crowdsourcing task allocation algorithm based on multi-agent. Intelligent Computer and Applications, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 104–107, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2095-2163.2019.01.024. (in Chinese)
M. M. Kamel, A. Gil-Solla, M. Ramos-Carber. Tasks recommendation in crowdsourcing based on workers’ implicit profiles and performance history. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Software and Information Engineering, ACM, Cairo, Egypt, pp. 51–55, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3436829.3436834.
D. E. Difallah, G. Demartini, P. Cudré-Mauroux. Pick-a-crowd: Tell me what you like, and i’ll tell you what to do. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on World Wide Web, ACM, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, pp. 367–374, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2488388.2488421.
G. Wu, Z. Y. Chen, J. Liu, D. H. Han, B. Y. Qiao. Task assignment for social-oriented crowdsourcing. Frontiers of Computer Science, vol. 15, no. 2, Article number 152316, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11704-019-9119-8.
H. Rahman, S. B. Roy, S. Thirumuruganathan, S. Amer-Yahia, G. Das. Optimized group formation for solving collaborative tasks. The VLDB Journal, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 1–23, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00778-018-0516-7.
K. Mao, Y. Yang, Q. Wang, Y. Jia, M. Harman. Developer recommendation for crowdsourced software development tasks. In Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Service-Oriented System Engineering, San Francisco, USA, pp. 347–356, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/SOSE.2015.46.
W. Shao, X. N. Wang, W. P. Jiao. A developer recommendation framework in software crowdsourcing development. In Proceedings of the 15th National Software Application Conference on Software Engineering and Methodology for Emerging Domains, Springer, Kunming, China, pp. 151–164, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3482-4_11.
Y. M. Li, C. Y. Hsieh, L. F. Lin, C. H. Wei. A social mechanism for task-oriented crowdsourcing recommendations. Decision Support Systems, vol. 141, Article number 113449, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2020.113449.
M. C. Yuen, I. King, K. S. Leung. Task recommendation in crowdsourcing systems. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Crowdsourcing and Data Mining, ACM, Beijing, China, pp. 22–26, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2442657.2442661.
M. C. Yuen, I. King, K. S. Leung. An online-updating algorithm on probabilistic matrix factorization with active learning for task recommendation in crowdsourcing systems. Big Data Analytics, vol. 1, no. 1, Article number 14, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41044-016-0012-2.
M. C. Yuen, I. King, K. S. Leung. TaskRec: A task recommendation framework in crowdsourcing systems. Neural Processing Letters, vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 223–238, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-014-9343-z.
M. Safran, D. R. Che. Efficient learning-based recommendation algorithms for top-N tasks and top-N workers in large-scale crowdsourcing systems. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, vol. 37, no. 1, Article number 2, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3231934.
M. C. Yuen, I. King, K. S. Leung. Temporal context-aware task recommendation in crowdsourcing systems. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 219, Article number 106770, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2021.106770.
D. W. Gong, C. Peng, X. J. Yao, T. Tian. A model of new workers’ accurate acceptance of tasks using capable sensing. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, vol. 59, Article number 100732, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2020.100732.
Z. M. Shi, D. W. Gong, X. J. Yao, M. Y. Yang. New task oriented recommendation method based on Hungarian algorithm in crowdsourcing platform. Proceedings of IEEE World Congress on Services, Beijing, China, pp. 134–144, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/SERVICES48979.2020.00040.
J. Y. Tu, P. Cheng, L. Chen. Quality-assured synchronized task assignment in crowdsourcing. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 1156–1168, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/tkde.2019.2935443.
G. Wang, F. Ali, J. Yang, S. Nazir, T. Yang, A. Khan, M. Imtiaz. Multicriteria-based crowd selection using ant colony optimization. Complexity, vol. 2021, Article number 6622231, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6622231.
Y. S. Zhu, S. C. Yue, C. Yu, Y. C. Shi. CEPT: Collaborative editing tool for non-native authors. In Proceedings of ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing, Portland, USA, pp. 273–285, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2998181.2998306.
Y. N. Chen, X. J. Su, F. Tian, J. Huang, X. L. Zhang. Pactolus: A method for mid-air gesture segmentation within EMG. In Proceedings of CHI Conference Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, ACM, San Jose, USA, pp. 1760–1765, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/2851581.2892492.
M. M. Sheng, Z. D. Wang, W. B. Liu, X. Wang, S. Y. Chen, X. H. Liu. A particle swarm optimizer with multilevel population sampling and dynamic p-learning mechanisms for large-scale optimization. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 242, Article number 108382, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108382.
W. Z. Li, W. A. Guo, Y. M. Li, L. Wang, Q. D. Wu. Multi-swarm competitive swarm optimizer for large-scale optimization by entropy-assisted diversity measurement and management. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, vol. 33, no. 9, Article number e6126, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6126.
H. W. Ge, M. D. Zhao, Y. Q. Hou, Z. Kai, L. Sun, G. Z. Tan, Q. Zhang, C. L. P. Chen. Bi-space Interactive Cooperative Coevolutionary algorithm for large scale blackbox optimization. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 97, Article number 106798, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106798.
Y. J. Ma, L. Zhu, Y. L. Bai. Improved multi-population differential evolution for large-scale global optimization. Computing and Informatics, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 481–509, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31577/cai_2020_3_481.
M. Yang, A. M. Zhou, C. H. Li, J. Guan, X. S. Yan. CCFR2: A more efficient cooperative co-evolutionary framework for large-scale global optimization. Information Sciences, vol. 512, pp. 64–79, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.09.065.
W. N. Chen, Y. H. Jia, F. Zhao, X. N. Luo, X. D. Jia, J. Zhang. A cooperative co-evolutionary approach to large-scale multisource water distribution network optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 23, no. 5, pp. 842–857, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2019.2893447.
L. Rodriguez-Coayahuitl, A. Morales-Reyes, H. J. Escalante, C. A. C. Coello. Cooperative co-evolutionary genetic programming for high dimensional problems. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature, Springer, Leiden, Netherlands, pp. 48–62, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58115-2_4.
J. F. Chen, Y. H. Wang, X. S. Xue, S. Cheng, M. El-Abd. Cooperative co-evolutionary metaheuristics for solving large-scale TSP art project. In Proceedings of IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, Xiamen, China, pp. 2706–2713, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI44817.2019.9002754.
X. Zhang, K. J. Du, Z. H. Zhan, S. Kwong, T. L. Gu, J. Zhang. Cooperative coevolutionary bare-bones particle swarm optimization with function independent decomposition for large-scale supply chain network design with uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 50, no. 10, pp. 4454–4468, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2937565.
J. Y. Li, Z. H. Zhan, K. C. Tan, J. Zhang. Dual differential grouping: A more general decomposition method for large-scale optimization. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, to be published. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2022.3158391.
N. Y. Zeng, D. D. Song, H. Li, Y. C. You, Y. R. Liu, F. E. Alsaadi. A competitive mechanism integrated multi-objective whale optimization algorithm with differential evolution. Neurocomputing, vol. 432, pp. 170–182, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.12.065.
D. W. Gong, B. Xu, Y. Zhang, Y. N. Guo, S. X. Yang. A similarity-based cooperative co-evolutionary algorithm for dynamic interval multiobjective optimization problems. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 24, no. 1, pp. 142–156, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2019.2912204.
W. M. Huang, W. Zhang. Multi-objective optimization based on an adaptive competitive swarm optimizer. Information Sciences, vol. 583, pp. 266–287, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.11.031.
J. T. Shen, P. Wang, H. C. Dong, J. L. Li, W. X. Wang. A multistage evolutionary algorithm for many-objective optimization. Information Sciences, vol. 589, pp. 531–549, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.12.096.
S. C. Liu, Z. G. Chen, Z. H. Zhan, S. W. Jeon, S. Kwong, J. Zhang. Many-objective job-shop scheduling: A multiple populations for multiple objectives-based genetic algorithm approach. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, to be published. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3102642.
X. Zhang, Z. H. Zhan, W. Fang, P. J. Qian, J. Zhang. Multipopulation ant colony system with knowledge-based local searches for multiobjective supply chain configuration. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 512–526, 2022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEVC.2021.3097339.
S. Kashef, H. Nezamabadi-Pour. An advanced ACO algorithm for feature subset selection. Neurocomputing, vol. 147, pp. 271–279, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2014.06.067.
Y. Zelenkov, E. Fedorova, D. Chekrizov. Two-step classification method based on genetic algorithm for bankruptcy forecasting. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 88, pp. 393–401, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.07.025.
L. Nanni, A. Lumini. Particle swarm optimization for prototype reduction. Neurocomputing, vol. 72, pp. 4–6, 2009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2008.03.008.
W. W. Hu, Y. Tan. Prototype generation using multiobjective particle swarm optimization for nearest neighbor classification. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 46, no. 12, pp. 2719–2731, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2015.2487318.
I. Triguero, S. García, F. Herrera. Differential evolution for optimizing the positioning of prototypes in nearest neighbor classification. Pattern Recognition, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 901–916, 2011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2010.10.020.
J. Perez-Rodriguez, A. G. Arroyo-Peña, N. García-Pedrajas. Simultaneous instance and feature selection and weighting using evolutionary computation: Proposal and study. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 37, pp. 416–443, 2015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.07.046.
M. R. G. Raman, N. Somu, K. Kirthivasan, R. Liscano, V. S. S. Sriram. An efficient intrusion detection system based on hypergraph-genetic algorithm for parameter optimization and feature selection in support vector machine. Knowledge-based Systems, vol. 134, pp. 1–12, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.07.005.
R. Xu, J. Xu, D. C. Wunsch. A comparison study of validity indices on swarm-intelligence-based clustering. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 1243–1256, 2012. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2188509.
W. J. Luo, W. J. Zhu, L. Ni, Y. Y. Qiao, Y. G. Yuan. SCA2: Novel efficient swarm clustering algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 442–456, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TETCI.2019.2961190.
K. Georgieva, A. P. Engelbrecht. A cooperative multipopulation approach to clustering temporal data. In Proceedings of IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Cancun, Mexico, pp. 1983–1991, 2013. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CEC.2013.6557802.
Y. H. Liu. Crowd sensing computing. Communications of CCF, vol. 8, no. 10, pp. 38–41, 2012. (in Chinese)
H. L. Sun, Y. L. Fang, G. L. Li. Quality assurance method of collective intelligence system. Communications of CCF, vol. 14, no. 11, pp. 18–25, 2018. (in Chinese)
Y. H. Ma, H. Zhang, Y. Z. Zhang, R. Z. Gao, Z. Xu, J. Yang. Coordinated optimization algorithm combining GA with cluster for multi-UAVs to multi-tasks task assignment and path planning. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation, Edinburgh, UK, pp. 1026–1031, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCA.2019.8899987.
F. Wang, H. Zhang, M. C. Han, L. N. Xing. Co-evolution based mixed-variable multi-objective particle swarm optimization for UAV cooperative multi-task allocation problem. Chinese Journal of Computers, vol. 44, no. 10, pp. 1967–1983, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.01967.
Y. B. Chen, D. Yang, J. Q. Yu. Multi-UAV task assignment with parameter and time-sensitive uncertainties using modified two-part wolf pack search algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, vol. 54, no. 6, pp. 2853–2872, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TAES.2018.2831138.
W. N. Wu, X. G. Wang, N. G. Cui. Fast and coupled solution for cooperative mission planning of multiple heterogeneous unmanned aerial vehicles. Aerospace Science and Technology, vol. 79, pp. 131–144, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2018.05.039.
T. Q. Chang, D. P. Kong, N. Hao, K. H. Xu, G. Z. Yang. Solving the dynamic weapon target assignment problem by an improved artificial bee colony algorithm with heuristic factor initialization. Applied Soft Computing, vol. 70, pp. 845–863, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2018.06.014.
X. Yi, A. M. Zhu, S. X. Yang, C. M. Luo. A bio-inspired approach to task assignment of swarm robots in 3-D dynamic environments. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 47, no. 4, pp. 974–983, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2016.2535153.
Z. X. Zheng, J. Guo, E. Gill. Distributed onboard mission planning for multi-satellite systems. Aerospace Science and Technology, vol. 89, pp. 111–122, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ast.2019.03.054.
W. Q. Xu, C. Chen, S. X. Ding, P. M. Pardalos. A bi-objective dynamic collaborative task assignment under uncertainty using modified MOEA/D with heuristic initialization. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 140, Article number 112844, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112844.
C. T. Shi, Y. Y. Zeng, S. M. Hou. Summary of application of swarm intelligence algorithms in image segmentation. Computer Engineering and Applications, vol. 57, no. 8, pp. 36–47, 2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011-0416. (in Chinese)
L. X. Xu, H. Y. Wu. Collective intelligence based software engineering. Journal of Computer Research and Development, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 487–512, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20190626. (in Chinese)
Y. Y. Fanjiang, Y. Syu. Semantic-based automatic service composition with functional and non-functional requirements in design time: A genetic algorithm approach. Information and Software Technology, vol. 56, no. 3, pp. 352–373, 2014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2013.12.001.
H. Zhu, H. Z. He, Q. H. Fang, Y. Dai, D. H. Jiang. Ant colony algorithm and density peaks clustering for medical image segmentation. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 1–8, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-4616.2019.02.001. (in Chinese)
J. Zhao, X. L. Wang, M. Li. A novel neutrosophic image segmentation based on improved fuzzy C-means algorithm (NIS-IFCM). International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, no. 5, Article number 2055011, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218001420550113.
S. L. Zhang, J. L. Huang, J. Hanan, L. Qin. A hyperspectral GA-PLSR model for prediction of pine wilt disease. Multimedia Tools and Applications, vol. 79, no. 23–24, pp. 16645–16661, 2020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-019-07976-5.
M. Harman, B. F. Jones. Search-based software engineering. Information and Software Technology, vol. 43, no. 14, pp. 833–839, 2001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0950-5849(01)00189-6.
K. Mao, L. Capra, M. Harman, Y. Jia. A survey of the use of crowdsourcing in software engineering. Journal of Systems and Software, vol. 126, pp. 57–84, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2016.09.015.
Q. W. Wu, F. Ishikawa, Q. S. Zhu, Y. N. Xia, J. H. Wen. Deadline-constrained cost optimization approaches for workflow scheduling in clouds. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, vol. 28, no. 12, pp. 3401–3412, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TPDS.2017.2735400.
Q. W. Wu, F. Ishikawa, Q. S. Zhu, Y. N. Xia. Energy and migration cost-aware dynamic virtual machine consolidation in heterogeneous cloud datacenters. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 550–563, 2019. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TSC.2016.2616868.
S. Gheisari, M. R. Meybodi. BNC-PSO: Structure learning of Bayesian networks by particle swarm optimization. Information Sciences, vol. 348, pp. 272–289, 2016. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.090.
C. Su, T. Hou. Using multi-population intelligent genetic algorithm to find the Pareto-optimal parameters for a Nano-particle milling process. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 2502–2510, 2008. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.04.017.
S. Suganthi, S. P. Rajagopalan. Multi-swarm particle swarm optimization for energy-effective clustering in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, vol. 94, no. 4, pp. 2487–2497, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3564-6.
G. Y. Wang. DGCC: Data-driven granular cognitive computing. Granular Computing, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 343–355, 2017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41066-017-0048-3.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 62221005, 61936001 and 62006029), Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China (Nos. cstc2020jscxlyjsAX0008, cstc2019jcyjcxttX0002, cstc2021ycjh-bgzxm0013 and CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX0258), Chongqing Postdoctoral Innovative Talent Support Program, China (No. CQBX2021024), and the Project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission, China (No. HZ2021008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guo-Yin Wang received the B. Sc. and M. Sc. degrees in computer software from Xi’an Jiaotong University, China in 1992 and 1994, respectively, and the Ph. D. degree in computer organization and system structure from Xi’an Jiaotong University, China in 1996. He was at University of North Texas, USA, and University of Regina, Canada, as a visiting scholar during 1998–1999. Since 1996, he has been at the Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China, where he is currently a professor, the vice president of the university, and the director of the Chongqing Key Laboratory of Computational Intelligence. He was the director of the Institute of Electronic Information Technology, Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China, during 2011–2017. He is the author of 13 books and the editor of dozens of proceedings of national and international conferences and has more than 300 reviewed research publications. He was the president of the International Rough Set Society (IRSS) from 2014 to 2017, and is currently a vice president of the Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence (CAAI) and a council member of the China Computer Federation (CCF). He is a fellow of IRSS, CAAI and CCF.
His research interests include rough sets, granular computing, knowledge technology, data mining, neural networks, and cognitive computing.
Dong-Dong Cheng received the B. Sc. degree in computer science from Chongqing Normal University, China in 2013, and the Ph. D. degree in software engineering from Chongqing University, China in 2018. She is currently an associate professor of College of Big Data and Intelligent Engineering at Yangtze Normal University, and she is also a postdoctoral fellow at the Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China. She has published more than 10 academic papers in top international journals, such as IEEE TKDE, IEEE TNNLS, and IEEE TSMC-S. She was selected into the Chongqing Postdoctoral Innovative Talent Support Program in 2021.
Her research interests include clustering analysis, data mining and swarm intelligence.
De-You Xia received the M. Sc. degree in systems science from the Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China in 2018. He is currently a Ph. D. degree candidate in computer science and technology at Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China.
His research interests include machine learning, granular computing, rough sets and swarm intelligence.
Hai-Huan Jiang received the M. Sc. degree in systems science from Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China in 2020. She is currently a Ph.D. degree candidate in computer science and technology at Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China.
Her research interests include granular computing, rough sets and swarm intelligence.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, GY., Cheng, DD., Xia, DY. et al. Swarm Intelligence Research: From Bio-inspired Single-population Swarm Intelligence to Human-machine Hybrid Swarm Intelligence. Mach. Intell. Res. 20, 121–144 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-022-1367-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-022-1367-7