Abstract
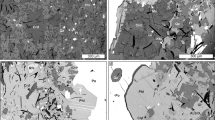
Hydrothermal alteration with bleaching of host rocks is the most important prospecting indicator for gold deposits in the Jiangnan Orogen Belt. The alteration has been identified as pre-ore carbonate (siderite)-sericitization and the Fe of siderite in the alteration zone is derived from the host rocks rather than fluids. In addition, such alteration decreases in intensity and width with depth and gold mineralization also occur in the non-bleached rocks, casting doubt on the reliability of the prospecting indicator. Detailed petrographic work and SEM analysis on the Wangu deposit indicate that there are two types of siderites, i.e., Sd1 and Sd2. Among them, Sd1 grains are relatively small and distributed along the planes of unaltered host rocks, while Sd2 grains, only occurring in the altered slates, are commonly larger. Both types of siderites were altered by auriferous fluids, producing porous cores and minerals such as pyrite, quartz, and ankerite. Compared with unaltered parts, the altered parts have lower Fe, but higher U, Pb, and REE. In addition, Sd1 and Sd2 are similar in Mn, Na, V, and Sr concentrations but different in Fe and Mg. The occurrence and geochemical compositions of both siderites indicate that Sd1 could be transformed into Sd2 by pre-mineralization alteration through dissolution-reprecipitation. Chlorite is another important Fe-bearing mineral in the host rocks, and EPMA analysis suggests that it is ripidolite with relatively high Fe contents. Consequently, chlorite can also provide Fe to form the pre-ore carbonate(siderite)-sericitization. Geochemical modeling demonstrates that both ripidolite and siderite can result in sulfidation and therefore gold precipitation. As a result, this study demonstrates that pre-ore alteration with characterized bleaching is not a prerequisite for gold mineralization despite of its prominent features. Due to the presence of Fe-bearing Sd1 and chlorite, gold mineralization could still occur through sulfidation in the unaltered rocks.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bierlein FP, Fuller T, Stüwe K (1998) Wallrock alteration associated with turbidite-hosted gold deposits. Examples from the Palaeozoic Lachlan fold belt in central Victoria, Australia. Ore Geol Rev 13(1–5):345–380
Blenkinsop TG, Oliver NHS, Dirks P (2020) Structural geology applied to the evaluation of hydrothermal gold deposits. Rev Econ Geol 21:1–23
Charvet J, Shu L, Shi Y (1996) The building of south China: collision of Yangzi and Cathaysia blocks, problems and tentative answers. J SE Asian Earth Sci 13:223–235
Cox SF, Sun SS, Etheridge MA (1995) Structural and geochemical controls on the development of turbidite-hosted gold quartz vein deposits Wattle Gully Mine, Central Victoria, Australia. Econ Geol 90:1722–1746
Deng J, Wang Q (2016) Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, 549 deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Res 36:219–274
Deng T, Xu D, Chi G (2017) Geology, geochronology, geochemistry and ore genesis of the Wangu gold deposit in northeastern Hunan Province, Jiangnan Orogen, South China. Ore Geol Rev 88:619–637
Deng T, Xu D, Chi G (2019) Revisiting the ca. 845–820-Ma S-type granitic magmatism in the Jiangnan Orogen: new insights on the Neoproterozoic tectono-magmatic evolution of South China. Int Geol Rev 61(4):383–403
Deng T, Xu D, Chi G (2020) Caledonian (Early Paleozoic) veins overprinted by Yanshanian (Late Mesozoic) gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogen: a case study on gold deposits in northeastern Hunan South China. Ore Geol Rev 124:103586
Dong SW, Zhang YQ, Long CX, Yang ZY, Ji Q, Wang T, Hu JM, Chen XH (2007) Jurassic tectonic revolution in China and new interpretation of the Yanshanian movement. Acta Geol Sinica 81(11): 1449–1461 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Foster MD (1962) Interpretation of the composition and a classification of the chlorites. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 414-A: A1–A33
Fu G (2009) Ductile shear deformation in northeastern Hunan Province and their constraint on gold mineralization (PhD Degree Thesis). Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 123 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gan C, Wang Y, Barry TL (2020) Late Jurassic High-Mg andesites in the Youjiang Basin and their significance for the southward continuation of the Jiangnan Orogen, South China. Gondwana Res 77:260–273
Gao L, Chen J, Ding X (2011) Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the tuff bed of Lengjiaxi and Banxi groups, northeastern Hunan: Constraints on the Wuling Movement. Geol Bull China 30:1001–1008 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gao L, Liu YX, Ding X (2012) SHRIMP dating of Cangshuipu Group in the middle part of the Jiangnan Orogen and its implications for tectonic evolutions. Geol China 39:12–20 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guan Y, Yuan C, Sun M (2014) I-type granitoids in the eastern Yangtze Block: implications for the Early Paleozoic intracontinental orogeny in South China. Lithos 206–207:34–51
Gu XX, Schulz O, Vavtar F, Liu JM, Zheng MH, Fu SH (2007) Rare earth element geochemistry of the Woxi W-Sb-Au deposit, Hunan Province, South China. Ore Geol Rev 31(1): 319–336
Gu X, Zhang Y, Schulz O, Vavtar F, Liu J, Zheng M, Zheng L, (2012) The Woxi W-Sb-Au deposit in Hunan, South China: an example of Late Proterozoic sedimentary exhalative (SEDEX) mineralization. J Asian Earth Sci. 57: 54–75
Heinrich CA, Walshe JL, Harrold BP (1996) Chemical mass transfer modelling of ore-forming hydrothermal systems: current practise and problems. Ore Geol Rev 10(3–6):319–338
Henley RW, McNabb A (1978) Magmatic vapor plumes and ground-water interaction in porphyry copper emplacement. Econ Geol 73(1):1–20
HNBGMR (Bureau of geology and mineral Resource of Hunan province) (1988) Regional geology of Hunan province. Geological Publishing House, Beijing: 1722 in Chinese
Hu SY, Evans K, Craw D (2017) Resolving the role of carbonaceous material in gold precipitation in metasediment-hosted orogenic gold deposits. Geology 45(2):167–170
Hurtig NC, Williams-Jones AE (2014) An experimental study of the transport of gold through hydration of AuCl in aqueous vapour and vapour-like fluids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 127:305–325
Inoue A, Kurokawa K, Hatta T (2010) Application of chlorite geothermometry to hydrothermal alteration in Toyoha geothermal system, Southwestern Hokkaido, Japan. Resour Geol 60(1):52–70
Jia D, Hu R, Zhao J (2003) Lithogeochemical characteristics of the Mesozoic granitic intrusion from the Wangxiang area in northeastern Hunan Province and its tectonic setting. Acta Geologica Sinica-Chinese Edition 77:97–103
Johnson CA, Day WC, Rye RO (2016) Oxygen, Hydrogen, Sulfur, and Carbon Isotopes in the Pea Ridge Magnetite-Apatite Deposit, Southeast Missouri, and Sulfur Isotope Comparisons to Other Iron Deposits in the Region. Econ Geol 111(8):2017–2032
Li ZX, Li XH (2007) Formation of the 1300-km-wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenic magmatic province in Mesozoic South China: A flat-slab subduction model. Geol 35(2):179
Li PC, Xu DR, Chen GH (2005) Constraints of petrography, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes on the Jinjing granitoids from northeastern Hunan province, China: implications for petrogenesis and geodynamic setting. Acta Petrologica Sinica 21:921–934
Liao Y (2019). Study on Metallogenic Theory and Prospecting Indicators of Danan Gold Deposit in Wangu Mining Area. World Nonferrous Metals, 13 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S (2008) In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internalstandard. Chem Geol 257:34–43
Liu X, Fan HR, Hu FF (2016) Nature and evolution of the ore-forming fluids in the giant Dexing porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit, Southeastern China. J Geochem Explor 171:83–95
Liu Q, Shao Y, Chen M (2019) Insights into the genesis of orogenic gold deposits from the Zhengchong gold field, northeastern Hunan Province. China Ore Geol Rev 105:337–355
Ma W, Deng T, Xu D (2021) Geological and geochemical characteristics of hydrothermal alteration in the Wangu deposit in the central Jiangnan Orogenic Belt and implications for gold mineralization. Ore Geol Rev 139:104479
Mao JW, Li YH, (1997) Research on genesis of the gold deposits in the Jiangnan terrain. Geochemica 26(5): 71–81 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mao J, Pirajno F, Cook N (2011) Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings—an introduction to the special issue. Ore Geol Rev 43(1):1–7
Mao J, Li H, Xu J (1997) Geology and genesis of the Wangu gold deposit in Hunan Province, China. Atomic Energy Press, Beijing, pp. 1–133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Myers AT, Havens RG, Niles WW (1970) Glass reference standards for trace element analysis of geologic materials. Springer, New York
Myint AZ, Wagner T, Fusswinkel T (2022) Calcite trace element geochemistry of Au deposits in the Singu-Tabeikkyin Gold District, Myanmar: Implications for the sources of ore-forming fluids. Ore Geol Rev 145:104892
Ni P, Wang GG, Chen H (2015) An Early Paleozoic orogenic gold belt along the Jiang Shao Fault, South China: Evidence from fluid inclusions and Rb–Sr dating of quartz in the Huangshan and Pingshui deposits. J Asian Earth Sci 103:87–102
Paton C, Hellstrom J, Paul B, Woodhead J, Hergt J (2011) Iolite: freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J Anal at Spectrom. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ja10172b
Petrella L, Thébaud N, Evans K (2021) The role of competitive fluid-rock interaction processes in the formation of high-grade gold deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 313:38–54
Phillips GN, Groves DI, Martyn JE (1984) An epigenetic origin for Archean banded iron-formation-hosted gold deposits. Econ Geol 79(1):162–171
Pirajno F, Yu HC (2021) Cycles of hydrothermal activity, precipitation of chemical sediments, with special reference to Algoma-type BIF. Gondwana Res 100:251–260
Reed WP (1992a) Certificate of analysis: standard reference materials 610 and 611. National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Reed WP (1992b) Certificate of analysis: standard reference materials 610 and 611. National Institute of Standards and Technology
Roberts C (1995) The fosterville project—perseverance exploration Pty., Gold in central Victoria. 125th Anniversary Symposium, Ballarat: 49–51.
Seward TM, Williams-Jones AE, Migdisov AA (2014) The chemistry of metal transport and deposition by ore forming hydrothermal fluids. Treatise Geochem, pp 29–57
Shu LS, Wang B, Cawood PA (2015) Early Paleozoic and Early Mesozoic intraplate tectonic and magmatic events in the Cathaysia Block, South China. Tectonics 34:1600–1621
Sibson R (1985) A note on fault reactivation. J Struct Geology 7:3–6
Sibson RH, Robert F, Poulsen KH (1988) High-angle reverse faults, fluid-pressure cycling, and mesothermal gold-quartz deposits. Geology 16(6):551–555
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry. Wiley, New York
Su W, Heinrich CA, Pettke T (2009) Sediment-hosted gold deposits in Guizhou, China: products of wall-rock sulfidation by deep crustal fluids. Econ Geol 104:73–93
Sun S, Zhang L, Wu S (2018) Metallogenic mechanism of the Huangjindong gold deposit, Jiangnan Orogenic Belt: Constraints from mineral formation environment and physicochemical conditions of metallogenesis. Acta Geol Sinica 34:1469–1483 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sun SC, Yang LQ, Zhang L (2020) In-situ trace elements on pyrite and arsenopyrite of the Zhengchong gold deposit, Jiangnan Orogen: insights for the mineralization mechanism. Ore Geol Rev 122:103486
Wang LX, Ma CQ, Zhang C (2014) Genesis of leucogranite by prolonged fractional crystallization: a case study of the Mufushan complex, South China. Lithos 206–207:147–163
Wang JQ, Shu LS, Santosh M (2016) Petrogenesis and tectonic evolution of Lianyunshan complex, South China: insights on Neoproterozoic and late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the central Jiangnan Orogen. Gondwana Res 39:114–130
Wang R, Cudahy T, Laukamp C (2017) White mica as a hyperspectral tool in exploration for the Sunrise Dam and Kanowna Belle gold deposits Western Australia. Econ Geol 112(5):1153–1176
Wang C, Shao Y, Zhang X (2020) Metallogenesis of the Hengjiangchong gold deposit in Jiangnan Orogen. South China Ore Geology Reviews 118:103350
Wen Z, Deng T, Dong G (2016) Study on the characters and rules of the ore-controlling structures of the Wangu gold deposit in northeastern Hunan Province. Geotecton Metallog 40:281–294 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wiewióra A, Weiss Z (1990) Crystallochemical classifications of phyllosilicates based on the unified system of projection of chemical composition: II The Chlorite Group. Clay Miner 25(1):83–92
Williams-Jones AE, Bowell RJ, Migdisov AA (2009) Gold in solution. Elements 5(5):281–287
Wilson SA, Ridley WI, Koenig AE (2002) Development of sulfide calibration standards for the laser ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique. J Anal Atom Spectrosc 17(4):406–409
Wu RX, Zheng YF, Wu YB (2006) Reworking of juvenile crust: element and isotope evidence from neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China. Precambr Res 146(3–4):179–212
Xu D, Chen G, Xia B (2006) The Caledonian adakite-like granodiorites in Banshanpu Area eastern Hunan Province, South China petrogenesis and geological significance. Geol J China Univ 12:507–521 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu D, Gu X, Li P (2007) Mesoproterozoic-Neoproterozoic transition: Geochemistry, provenance and tectonic setting of clastic sedimentary rocks on the SE margin of the Yangtze Block, South China. J Asian Earth Sci 29:637–650
Xu D, Wang L, Li P (2009) Petrogenesis of the Lianyunshan granites in northeastern Hunan Province, South China, and its geodynamic implication. Acta Petrologica Sinica 25:1056–1078 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu D, Deng T, Chi G (2017b) Gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt of South China: geological, geochemical and geochronological characteristics, ore deposit-type and geodynamic setting. Ore Geol Rev 88(565):618
Xu K, Xu D, Deng T (2022) Genesis of altered slate type ores in the Huangjindong gold deposit, Jiangnan Orogenic Belt, South China. J Geochem Explor 241:107047
Xu D, Chi G, Zhang Y (2017a) Yanshanian (Late Mesozoic) ore deposits in China—an introduction to the Special Issue. Ore Geol Rev 88: 481-490.
Zhang L, Yang LQ, Groves DI (2018) Geological and isotopic constraints on ore genesis, Huangjindong gold deposit, Jiangnan Orogen, southern China. Ore Geol Rev 99:264–281
Zhang L, Groves DI, Yang LQ (2020) Utilization of pre-existing competent and barren quartz veins as hosts to later orogenic gold ores at Huangjindong gold deposit, Jiangnan Orogen, southern China. Miner Deposita 55:363–380
Zhao G (2015) Jiangnan Orogen in South China: developing from divergent double subduction. Gondwana Res 27(3):1173–1180
Zhao G, Cawood PA (2012) Precambrian geology of China. Precambr Res 222–223:13–54
Zhong J, Pirajno F, Chen YJ (2017) Epithermal deposits in South China: Geology, geochemistry, geochronology and tectonic setting. Gondwana Res 42:193–219
Zhou X, Sun T, Shen W (2006) Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: a response to tectonic evolution. Episodes 29(1):26
Zhou Y, Xu D, Dong G (2021) The role of structural reactivation for gold mineralization in northeastern Hunan Province South China. J Struct Geol 145:104306
Zhou D, Ye D, Yu D (1989) A preliminary discussion on the genesis of the Mobin quartz vein-type gold deposit in Hunan Province. Mineral Deposits 1.
Zhou Y, Dong G, Xu D (2020) The scheelite Sm-Nd age of the Huangjindong Au deposit in Hunan and its geological significance. Geochimica H202002004 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhu YN, Peng JT (2015) Infrared microthermometric and noble gas isotope study of fluid inclusions in ore minerals at the Woxi orogenic Au–Sb–W deposit, western Hunan South China. Ore Geol Rev 65:55–69
Zimmer K, Zhang Y, Lu P (2016) SUPCRTBL: a revised and extended thermodynamic dataset and software package of SUPCRT92. Comput Geosci 90:97–111
Zou S, Zou F, Ning J (2018) A stand-alone Co mineral deposit in northeastern Hunan Province, South China: Its timing, origin of ore fluids and metal Co, and geodynamic setting. Ore Geol Rev 92:42–60
Acknowledgements
This work was co-founded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42002090, 41930428), Jiangxi Double Thousand Plan (SQJH2019XDR), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC0604200), Open Research Fund Program of State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resources and Environment, East China University of Technology (No. NRE1915), Open Research Fund Program of Jiangxi Engineering Laboratory on Radioactive Geoscience and Big Data Technology (JELRGBDT202006), International Geoscience Programme (IGCP-675) and Jiangxi province graduate student innovation special fund project (YC2019-S271, DHYC-202001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Teng Deng (First Author): Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing - Original Draft; Longyue Zhou: Data Curation, Writing - Original Draft; Visualization, Investigation; Zenghua Li: Software, Validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The manuscript has not been submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration. The manuscript has not been published previously (partly or in full), unless the new work concerns an expansion of previous work. A single study is not split up into several parts to increase the quantity of submissions and submitted to various journals or to one journal over time. No data have been fabricated or manipulated (including images) to support our conclusions. No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were the authors own. Proper acknowledgements to other works must be given, quotation marks are used for verbatim copying of material, and permissions are secured for material that is copyrighted.
Consent publication
The journal may use software to screen for plagiarism. Consent to submit has been received from all co-authors and responsible authorities at the institute/organization where the work has been carried out before the work is submitted.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, T., Zhou, L. & Li, Z. Fe-bearing minerals and implications for gold mineralization for the Wangu deposit in Central Jiangnan Orogen. Acta Geochim 42, 552–571 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-023-00599-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-023-00599-6